![]() 6 Dec 2023
6 Dec 2023
The capacity to store and transmit knowledge has significantly propelled human evolution, with education playing a central role in enhancing this capacity and fostering human growth. The labor skills of an educated individual are notably higher than those of an uneducated one, leading to increased income generation and a substantial contribution to economic growth.
Besides financial benefits, education elevates one’s social standing, enables informed life choices, and fosters innovation. Furthermore, it facilitates the adaptation of new technologies, accelerating national development.
Therefore, the expansion of educational opportunities is widely advocated for, as it not only enriches individual lives but also catalyzes economic and societal advancement.
Human capital refers to the transformation of human resources into a more skilled and knowledgeable workforce, like engineers and doctors, through education and training. This transformation is analogous to turning physical resources like land into physical capital like factories.
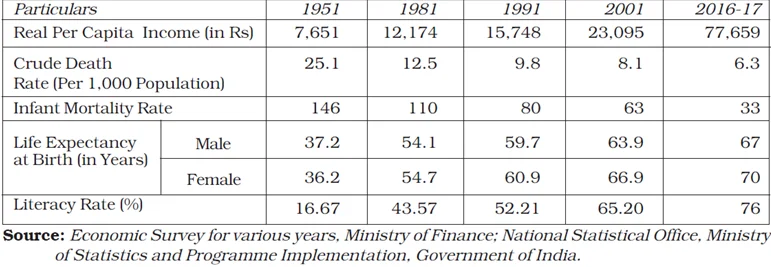
Select Indicators of Development in Education and Health Sectors
| Physical and Human Capital
Both physical and human capital formations are the results of deliberate investment decisions aimed at increasing the asset base and enhancing productivity. However, they differ fundamentally in several aspects, from the decision-making process to their impact on society and the economy.
|
There is a positive relationship between human capital and economic growth. A sufficient amount of human capital is essential for producing more skilled professionals, which, in turn, is critical for economic growth.
|
POINTS TO PONDER Human capital refers to the transformation of human resources into a more skilled and knowledgeable workforce through education and training. Can you list out the schemes by the central government in education, health and training for developing human capital? |
|---|
|
POINTS TO PONDER According to the World Economic Forum, Gender parity can boost India’s GDP by 27% by increasing women’s participation in the labour force. However, we have seen the greatest decline in women’s labour force participation in recent years. Can you think of the reasons why women’s capital development is lacking and what steps can be taken to ensure their participation? |
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>