Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and individual states or regions. This distribution of authority allows for a dual government structure, where both levels have distinct powers and responsibilities. Federalism aims to balance national unity with regional autonomy, promoting a more flexible and adaptable governance model.
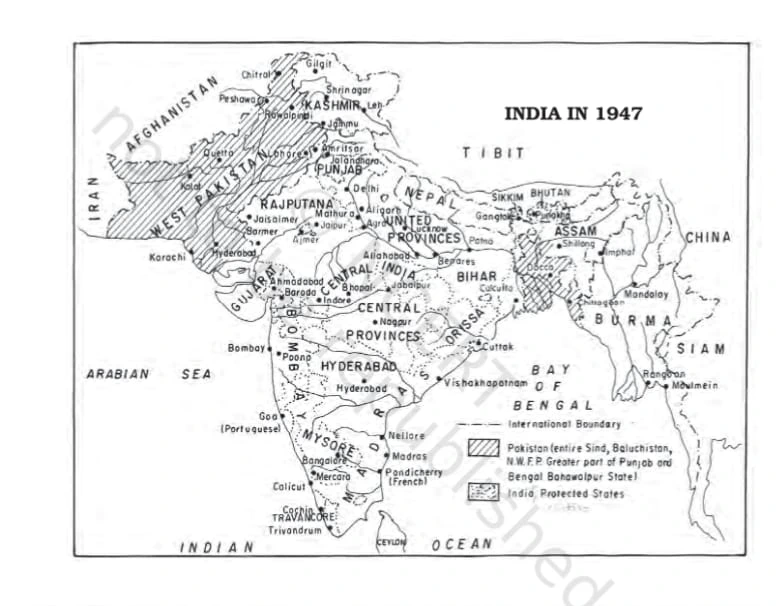
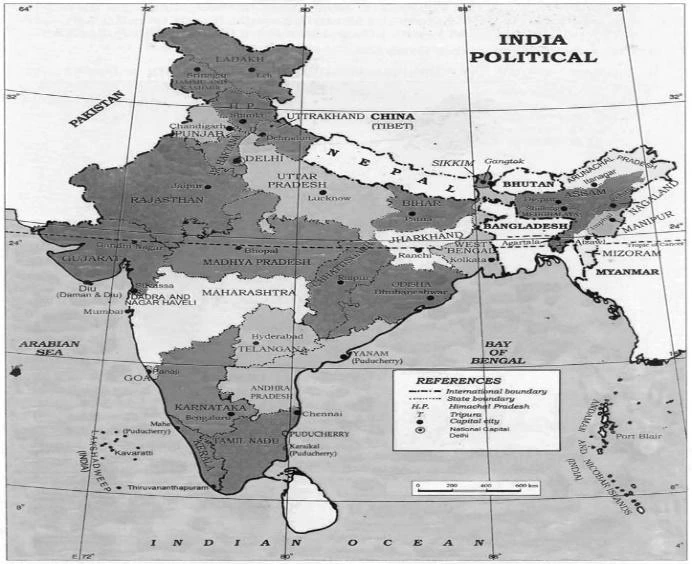
From 1947 to 2017, not only did the boundaries of states change, but in some instances, even their names were altered according to the wishes of the people residing in those states.
Other Tit-bits:
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
