![]() 4 Dec 2023
4 Dec 2023
In the 1970s, food security was primarily about the “availability at all times of adequate supply of basic foodstuffs.” However, Amartya Sen introduced a new dimension by emphasizing “access” to food through entitlements, which include what one can produce, exchange in the market, and state or socially-provided supplies.
This led to a significant shift in the understanding of food security.
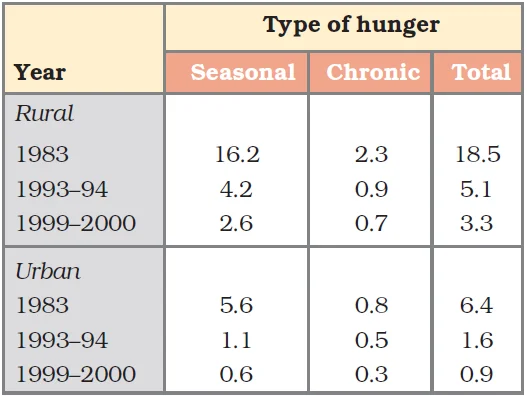
Percentage of Households with Hunger in India
Green Revolution and Self-Sufficiency
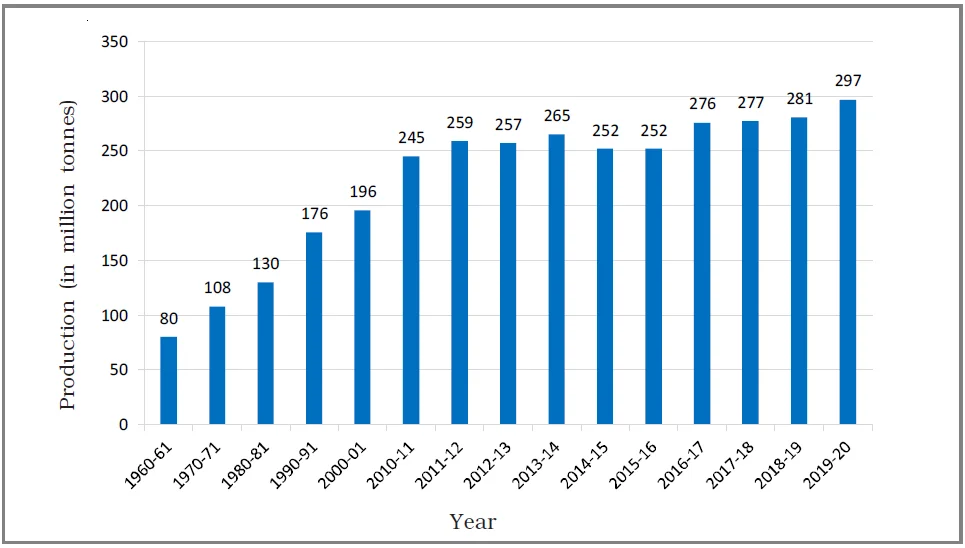
Production of Foodgrains in India (Million Tonnes)
|
Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY) AAY was launched in December 2000. Under it, 1 crore of the poorest among the BPL families, benefiting from Targeted PDS, were identified by the respective state rural development departments through a Below Poverty Line (BPL) survey. Twenty-five kilograms of foodgrains were made available to each eligible family at a highly subsidised rate of Rs 2 per kg for wheat and Rs 3 per kg for rice. This quantity has been enhanced from 25 to 35 kg with effect from April 2002. |
|---|
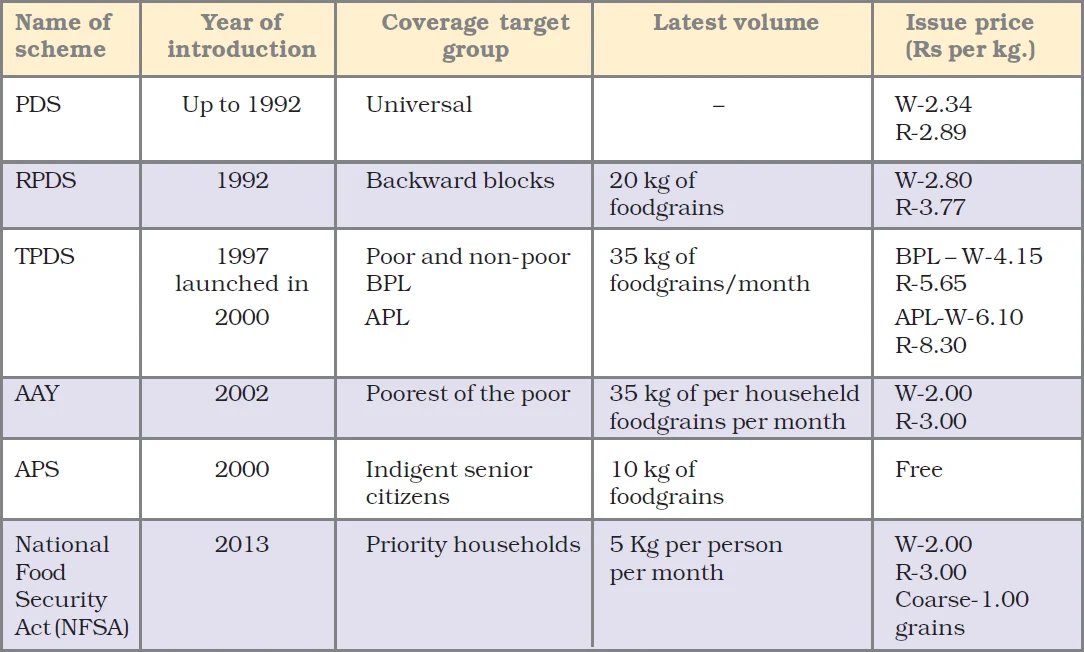
Some Important Features of PDS
Despite overflowing granaries, instances of hunger persist in India.
|
POINTS TO PONDER Food security is crucial to ensure that all individuals have access to food at all times, including during calamities and disasters. India has been self-sufficient since the Green Revolution. It has maintained buffer stocks and been able to deliver food through the PDS network even during the COVID-19. |
|---|
Conclusion
India’s strides in food security, from the Green Revolution to innovative cooperatives, underscore its commitment to overcoming challenges and ensuring sustained access to nutrition for all. Despite challenges, cooperatives and innovative solutions play a vital role in ensuring sustained access to food, reinforcing the nation’s commitment to addressing hunger and malnutrition.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>