![]() 23 Nov 2023
23 Nov 2023
The Constitution offers all citizens, individually and collectively, some basic freedoms. These are guaranteed in the Constitution in the form of six broad categories of Fundamental Rights, which are justifiable. Fundamental Rights are so fundamental in nature that without which a person can not accomplish its full potential.


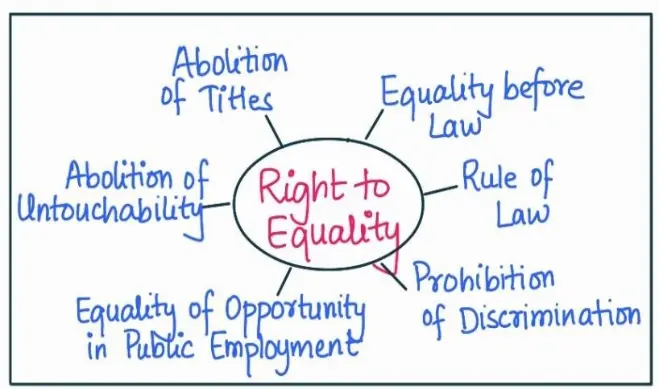
Case Study:
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>