![]() 6 Dec 2023
6 Dec 2023
Population composition can be defined as the demographic structure of the population. It gives information about age, sex, literacy, health condition, occupation, income level, etc.
A country’s population composition can be effectively understood through the study of a population pyramid. It is also known as an age-sex pyramid.
Also, In this article the composition of Indian population with respect to their rural-urban characteristics, language, religion and pattern, occupation will be discussed.
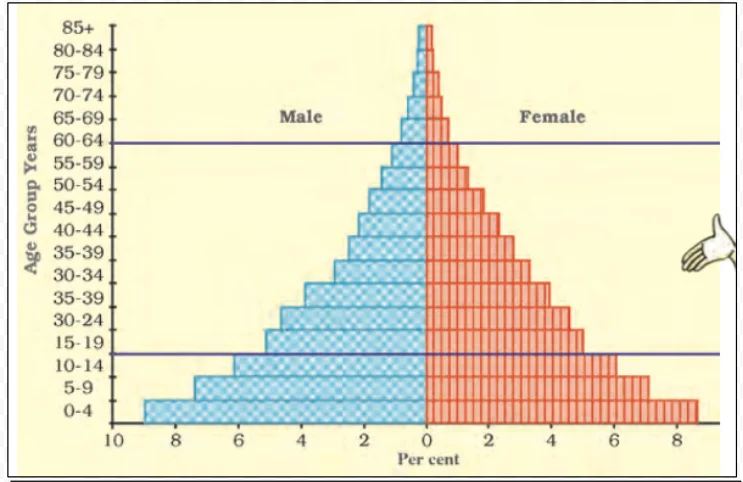
Population Pyramid
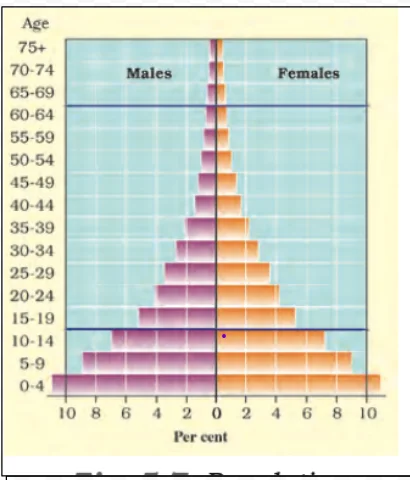 Population Pyramid of Kenya
Population Pyramid of Kenya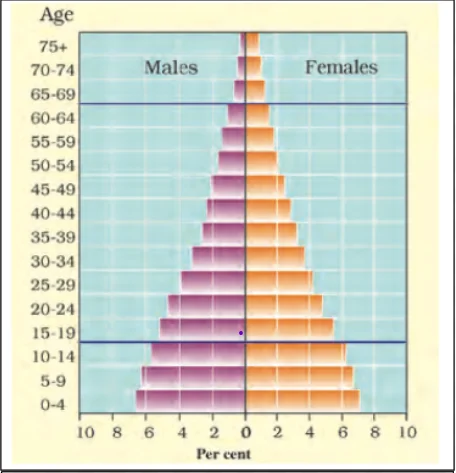
Population Pyramid of India
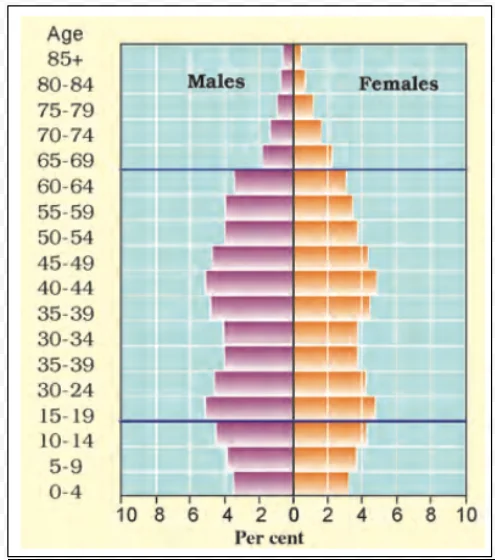
Population Pyramid of Japan
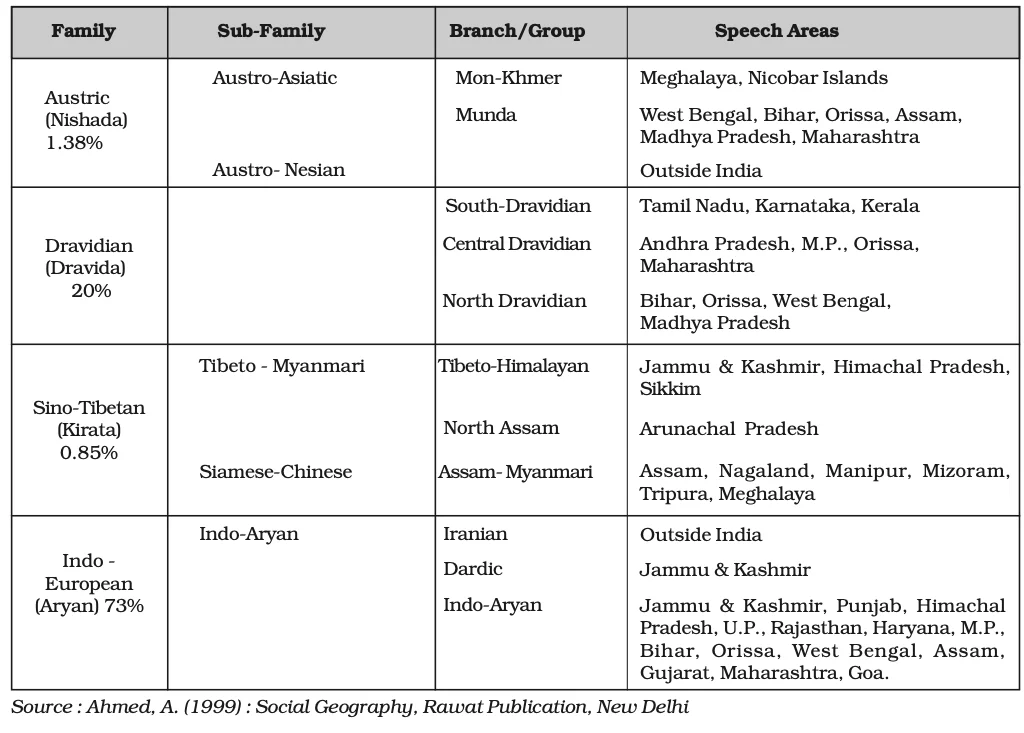
Classification of Modern Indian Languages
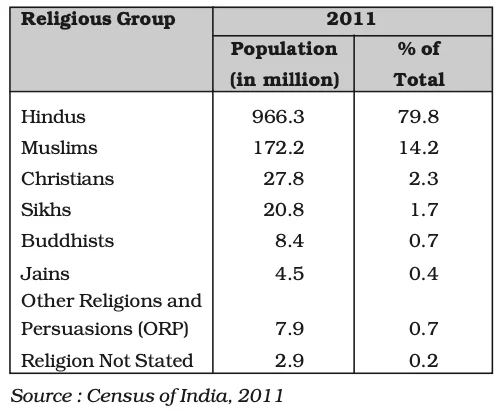
Religious Communities of India, 2011
India’s diversity in rural-urban distribution, languages, and religions, and population composition provides insights into its complex socio-cultural fabric, which has evolved over millennia and is reflective of the country’s rich history and heritage.
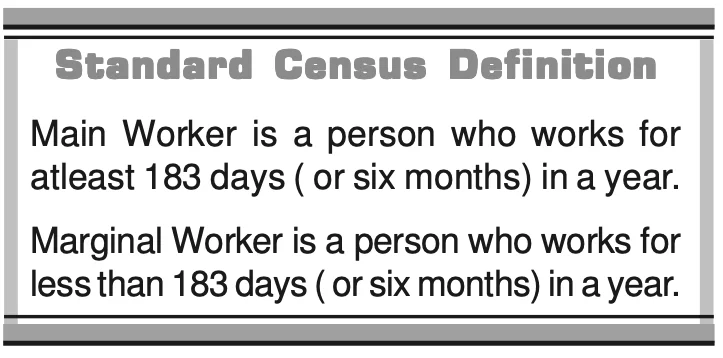
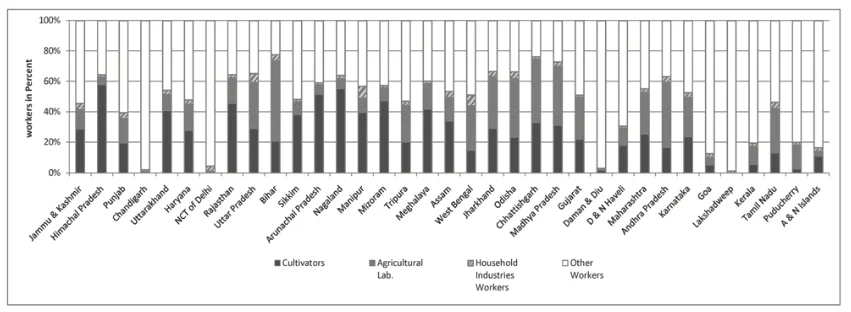
Occupational Structure, 2011
| WPR = (Total Workers (Main+Marginal) / Total Population ) ) × 100 |
|---|
Conclusion
The intricate tapestry of India’s socio-cultural landscape, shaped by its diverse rural-urban distribution, languages, religions, and population composition, reflects a rich history and heritage. The unique blend of these elements underscores the dynamic nature of the country, serving as a testament to its resilience and adaptability over the millennia.
Also Read: Exploring the Density of Population, Distribution Patterns, Growth Trends
<div class="new-fform">
</div>