![]() 23 Nov 2023
23 Nov 2023
Inequality affects different groups and communities by exclusion from the mainstream. three groups, namely the Adivasis, Muslims and Women. These three groups have been chosen because the causes that contribute to each group’s marginalization are different, and they sometimes experience marginalization in different ways.
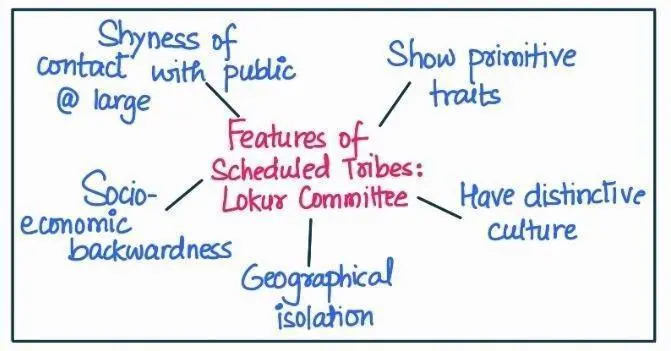
Forest and Tribal: A Historical Tapestry of Resource Extraction, Traditional Lifestyles, and Forced Migrations
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>