![]() 29 Nov 2023
29 Nov 2023
Market demand for a good at a particular price is the total Market demand of all consumers taken together. Understanding market demand is crucial for businesses and policymakers to make informed decisions about pricing, production, and resource allocation. It serves as a fundamental concept in economics and plays a vital role in shaping market dynamics.
Explanation of Market Demand for a Good: Calculating from Two Consumers to Graphical Derivation
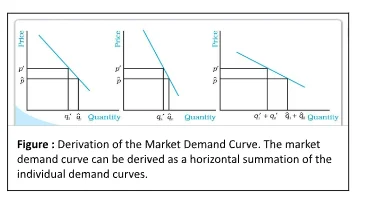
Fig: Derivation of the Market Curve
Adding up Two Linear Demand Curves: Analyzing Consumer Curves for Market Demand
The Price elasticity of demand is different at different points on the linear demand curve.
Geometric Measure of Elasticity along a Linear Demand Curve: Evaluating Elasticity
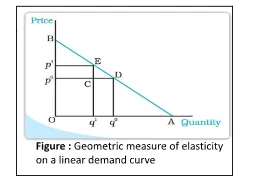
Fig: Geometric Measure of Elasticity Curve
Constant Elasticity Demand Curve: the Unitary Elastic Demand Curve
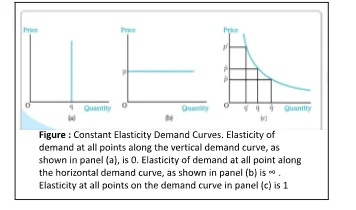
Fig: Constant Elasticity Demand Curve
Elasticity and Expenditure: Analyzing Price Changes and Goods
<div class="new-fform">
</div>