![]() 4 Dec 2023
4 Dec 2023
Measurements of Poverty is a crucial aspect of understanding and addressing socioeconomic challenges. Various methods and indicators are employed globally to assess and quantify the extent of poverty, providing valuable insights for policymaking and interventions.
The concept of the “poverty line” is central to discussions and measurements of poverty.
Poverty Line Calculations: A Method of Measurement of Poverty in India
|
Note: Measurements of Poverty: The World Bank updated in September 2022 is $2.15 Definition by World Bank: The indicator “proportion of the population below the international poverty line” is defined as the percentage of the population living on less than $2.15 a day at 2017 international prices. |
|---|
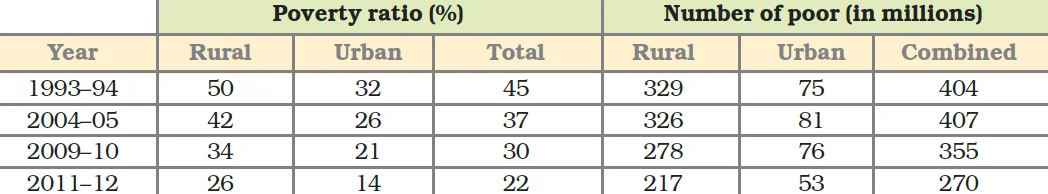
Estimates of Poverty in India
<div class="new-fform">
</div>