![]() 22 Jun 2024
22 Jun 2024
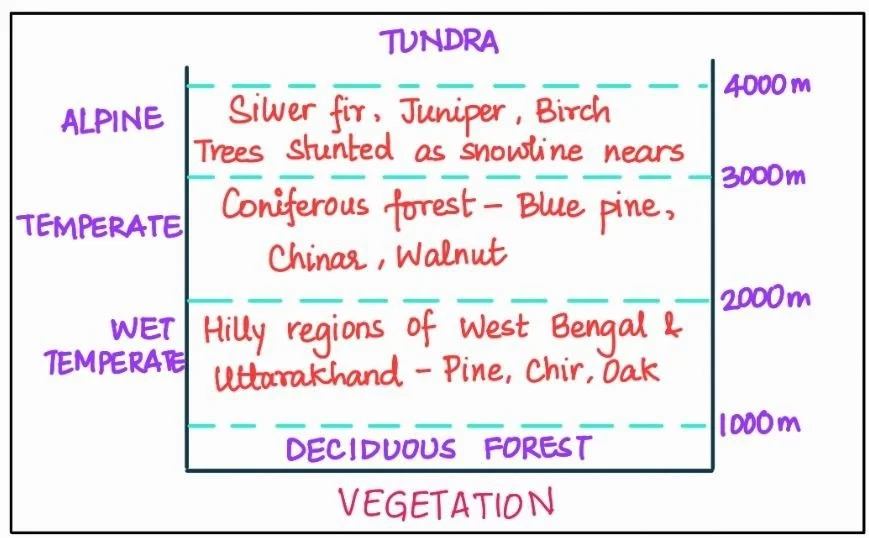
These Montane Forests are characterized by the decrease in temperature with increasing altitude that leads to a corresponding change in natural vegetation.
As such, there is a succession of natural vegetation belts in the same order as observed from the tropical to the tundra region.
Mangrove Forests

| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>