![]() 27 Nov 2023
27 Nov 2023
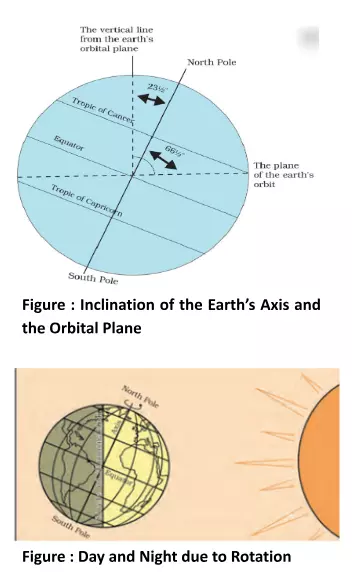
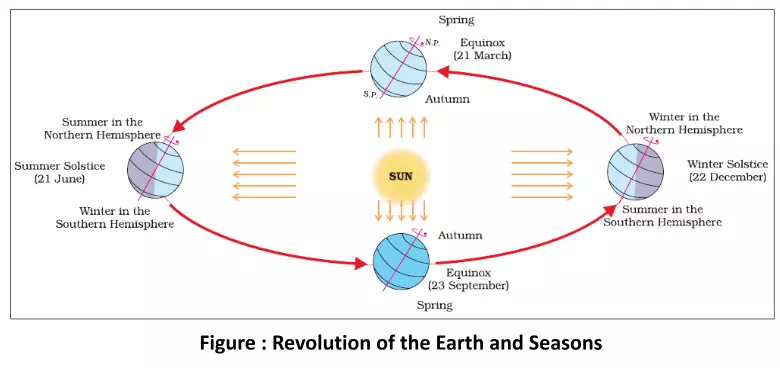
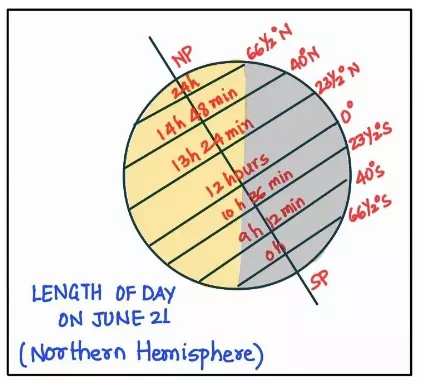
The Earth undergoes several motions that govern its position and orientation in space. These motions of the Earth include its rotation on its axis, which causes day and night, its revolution around the Sun, which gives rise to seasons, and its axial tilt, which results in variations in climate and daylight throughout the year. These Earthly motions play a crucial role in shaping the planet’s geography and climatic patterns.
Do You Know:
|
The earth has two types of motions of the Earth, namely Rotation and Revolution.
The origin and evolution of the earth is a complex and ongoing process that has occurred over billions of years. In this process of evolution life appeared on earth. Astronomers and scientists started exploring the universe and we have come very far. But we still haven’t fully figured out the truth of the Universe.
| Timeline | Event |
| 13.7 billion years ago | The event of big bang |
| 5-6 billion years ago | Formation of stars |
| 4.6 billion years ago | Planets were formed |
| 4.4 billion years ago | Moon was formed |
| 4000 million years ago | Formation of oceans |
| 3800 million years ago | Life began to evolve |
| 2500-3000 million years ago | Process of Photosynthesis got evolved |
Glossary
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>