![]() 19 Jul 2024
19 Jul 2024
When the Japanese invaded China in 1937, the Guomindang retreated. The long and exhausting war weakened China. Prices rose 30 per cent per month between 1945 and 1949, and utterly destroyed the lives of ordinary people. Rural China faced two crises: one ecological, with soil exhaustion, deforestation, and floods, and the second, a socio-economic one caused by exploitative land-tenure systems, indebtedness, primitive technology, and poor communications
 Rural China was grappling with two major crises:
Rural China was grappling with two major crises:
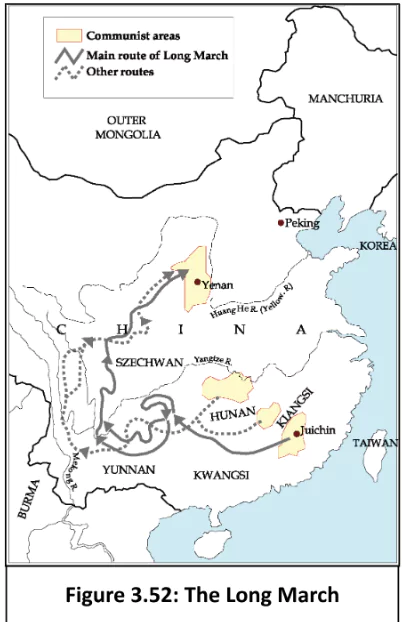 The Birth of the Chinese Communist Party: The CCP was founded in 1921, soon after the Russian Revolution.
The Birth of the Chinese Communist Party: The CCP was founded in 1921, soon after the Russian Revolution. 

Birth of the People’s Republic: The People’s Republic of China was established in 1949, and founded on the principles of “New Democracy,” which aimed to ally with all social classes, in contrast to the “dictatorship of the proletariat” adopted by the Soviet Union.
The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution: The conflict between Maoists and those who objected to this approach culminated in Mao launching the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution in 1965 to counter his critics.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
The establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949 marked a new era of social and economic transformation. Through policies like the Great Leap Forward and the Cultural Revolution, the CCP sought to reshape Chinese society, despite facing internal conflicts and disruptions. By the late 1970s, the focus shifted towards industrial growth and global positioning.
| Related Articles | |
| Measures for India’s Social Inequality: Economic, Social, and Political Strata in India | COMMUNALISM |
| Green Revolution and Beyond | ECONOMIC GROWTH |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>