An economy is best understood when we study its components or sectors. Sectoral classification can be done on the basis of several criteria. In this article, three types of classifications are discussed:
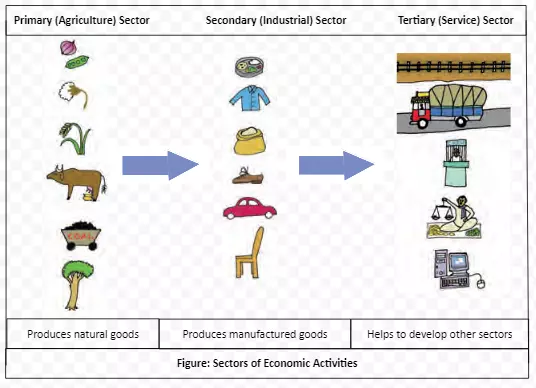
The primary sector in India employs the highest number of people yet has a very smaller share in the GDP contribution than the tertiary sector. Can you think of the reasons why this is so? Also, find out why the tertiary sector grew rapidly in India than the secondary.
The primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors collectively generate a vast array of goods and services. These sectors also employ a significant workforce to produce these goods and services. To gain a comprehensive understanding of an economy, it’s crucial to assess the quantity of goods and services produced and the number of people employed within each sector.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
