Socialization is the transformative process through which a helpless infant gradually evolves into a self-aware, knowledgeable individual, skilled in the ways of the culture into which they are born. It encompasses the development of a child’s understanding of what is considered appropriate behaviour within their society, distinguishing between right and wrong, and grasping the behaviors that receive approval or disapproval.
Without Socialization, an individual would not behave like a human being. For instance, the story of ‘Wolf-children of Midnapore‘, mentioned 2 girls, who walked and howled like wolves and lacked any form of speech.
Hence, Socialization shapes an individual’s ability to function as a human being within their culture.
 Active Engagement in Socialization: This process isn’t a passive absorption of cultural influences but rather an active engagement where individuals assert their will and express their needs.
Active Engagement in Socialization: This process isn’t a passive absorption of cultural influences but rather an active engagement where individuals assert their will and express their needs.The child is socialized by several agencies and institutions in which s/he participates, viz. family, school, peer group, neighbourhood, occupational group and by social class/caste, region, and religion.
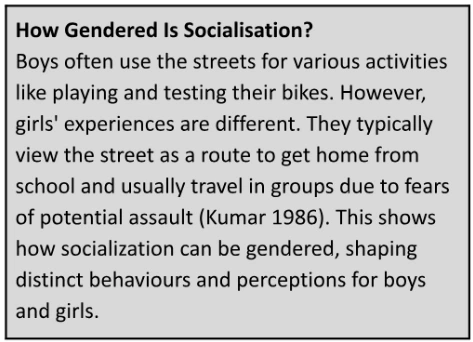
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
