![]() 25 Nov 2023
25 Nov 2023
India, the world’s largest democracy, operates under a framework meticulously laid down by its Constitution, which was adopted in 1950. The government consists of three primary organs: the Legislature, the Executive, and the Judiciary. Together, these organs maintain law and order and cater to the welfare of the people. A crucial component of this system, is responsible for implementing laws, administering the country, and maintaining public order.
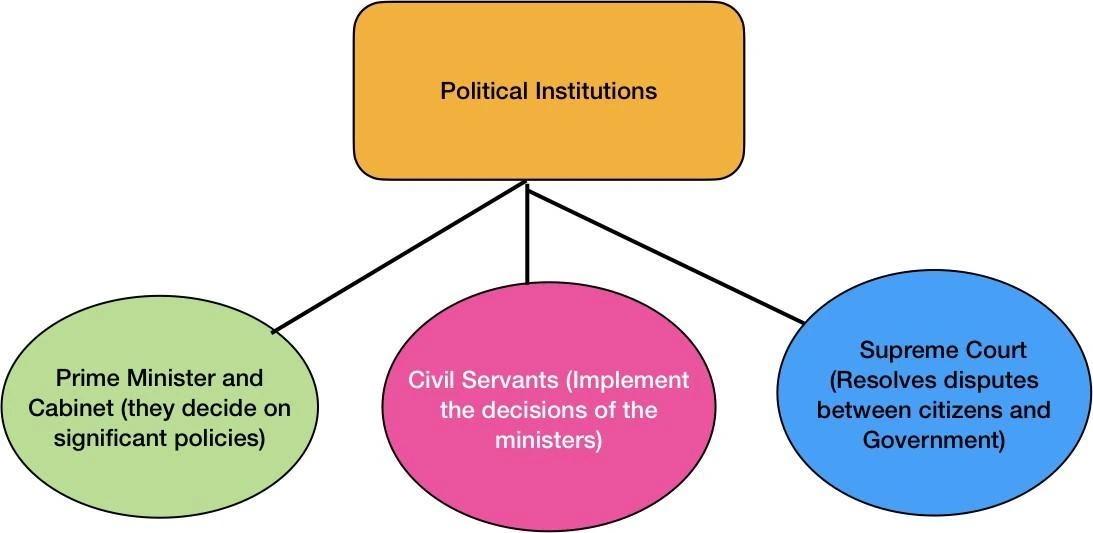
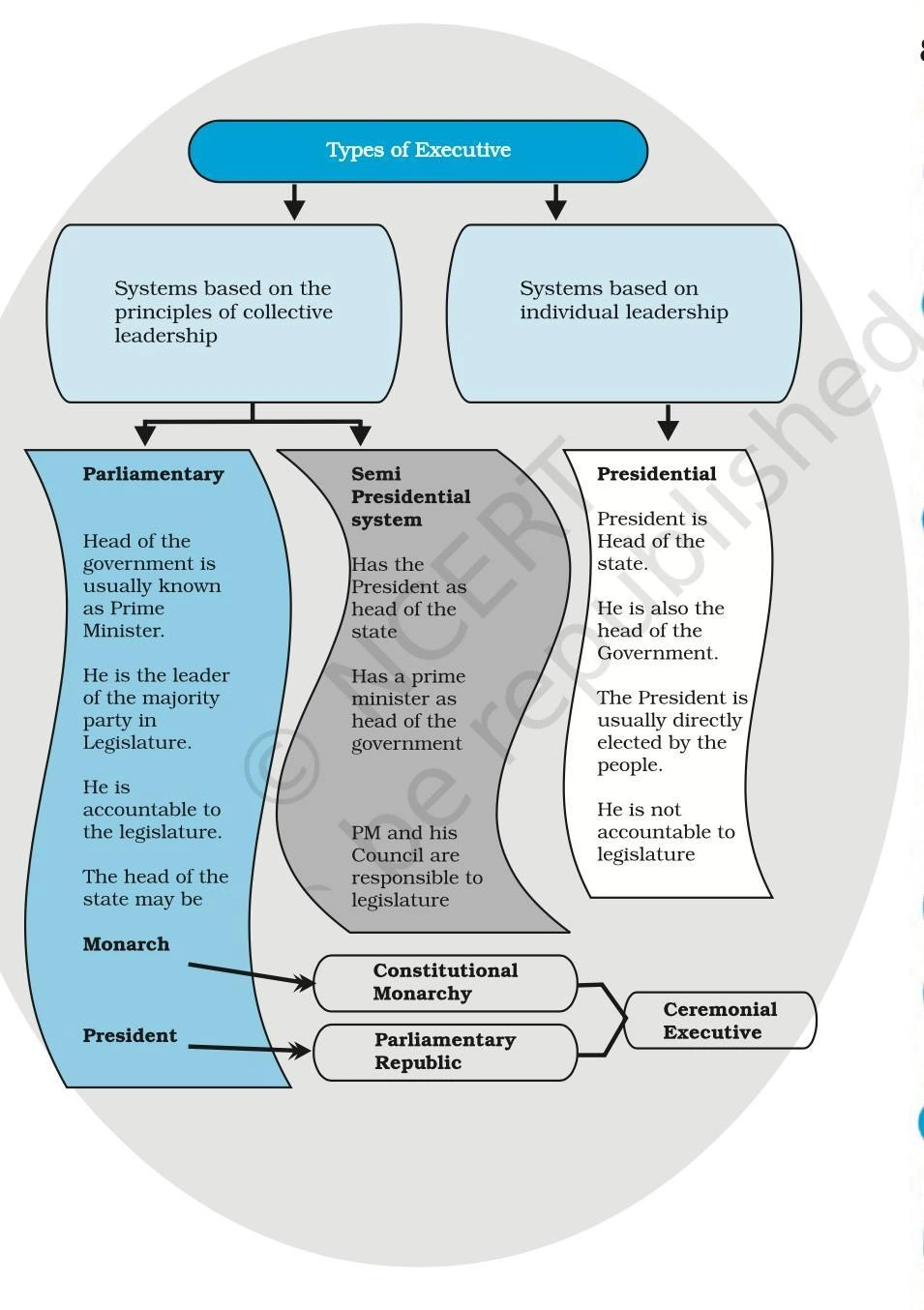
More About Executive:
|
| Type of Executive System | Description |
| Presidential System | The President plays both roles of the Head of state and the head of government, making the office highly influential. Example: USA |
| Parliamentary System | There’s a ceremonial head of state (e.g., monarch or President), but the Prime Minister is the Head of government with effective powers. Example: Canada, Japan, Germany, Italy. |
| Semi-Presidential
System |
Both a President and a Prime Minister are present. The President might also have significant day-to-day powers. Example: France, Russia, Sri Lanka. |
| Aspect | Indian System | US Presidential System |
| Head of State & Government | The President is the head of state; the Prime Minister is the head of government. | The President is both the head of state and the head of government. |
| Election of Head of State | The President is elected by MPs and MLAs, not directly by the people. | The President is directly elected by the people. |
| Appointment of Ministers | The Prime Minister appoints the ministers. | The President personally chooses and appoints all ministers. |
| Veto Power | The President can delay a bill and send it back to Parliament for reconsideration, but if the bill is passed again, then the President has to sign it. | The President can veto any law. |
| Tenure of Head of State | The President has a fixed tenure, but the
Prime Minister’s tenure depends on the majority in the Lok Sabha. |
The President has a fixed tenure, irrespective of the majority in Congress. |
| System of Government | Parliamentary system of government, where the Parliament is supreme. | Presidential form of
government. |
| Role of Head of State | The President exercises nominal powers and has a largely ceremonial role. | The President exercises wide-ranging powers and has an active role in the government. |
Conclusion
The Executive is central to a democracy’s functioning, ensuring the implementation of laws and smooth governance. Despite challenges, political institutions, including the are crucial for decision-making, accountability, and maintaining a nation’s constancy amid change.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>