The various types of loans in India can be conveniently grouped as formal sector loans and informal sector loans. As shown in the figure, you can see the various sources of credit to rural households in India.
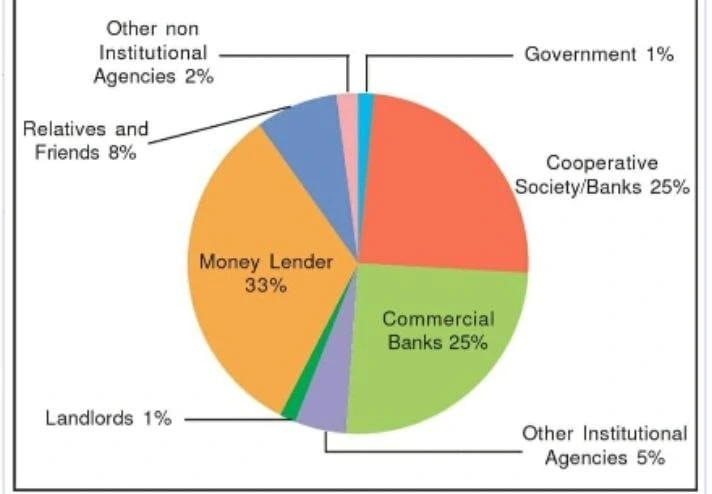
Sources of credit per Rs 1000 of Rural Households in India in 2012
Sources: Types of loans in India can be categorized in the form of moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends, etc.
Characteristics of Informal Sectors Loan:
For these reasons, banks and cooperative societies need to lend more.
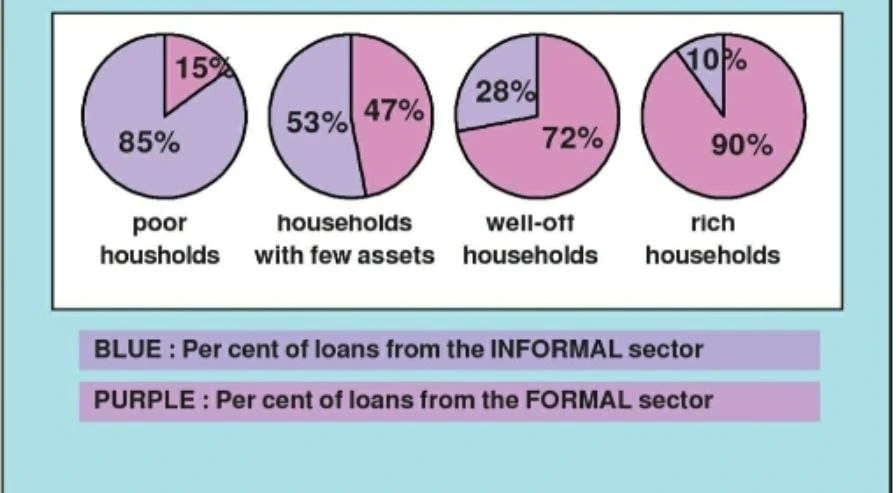
Urban Households Formal/Informal Loans
Definition: SHGs are organized groups of rural poor, particularly women, who themselves manage these groups by pooling their resources.
|
Grameen Bank of Bangladesh Bank of Bangladesh is one of the biggest success stories in reaching the poor to meet their credit needs at reasonable rates. Started in the 1970s as a small project, Grameen Bank in 2018 had over 9 million members in about 81,600 villages spread across Bangladesh. Almost all of the borrowers are women and belong to poorest sections of the society. |
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
