In an economy without a government, the ex ante aggregate demand for final goods is the sum total of the ex ante consumption expenditure and ex ante investment expenditure on such goods, viz. AD = C + I.
AD = C + I + c.Y
Y = C + I + c.Y
Y = A + c.Y
Uncovering Discrepancies Between Ex Ante Supply and Demand in Final Goods Market
In the context of economic equilibrium, the two sector model plays a pivotal role in understanding the dynamics between ex ante supply and demand.
The Nuances of Planned and Unplanned Inventory Investment in Economic Equations
Investment: It should be noted that inventories or stocks refers to that part of output produced which is not sold and therefore remains with the firm.
Inventory Investment: It is known as unanticipated accumulation or depletion of inventories.
In the two sector model, the economic landscape expands with the introduction of the government’s pivotal role.
Y = C + I + G + c (Y – T)
In microeconomic theory, Analyzing the equilibrium of supply and demand in a single market, the interaction of the demand and supply curves simultaneously determines both the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity.
However, in macroeconomic theory, we approach the analysis in two stages:
The justification for taking the price level as fixed initially can be explained for two reasons:
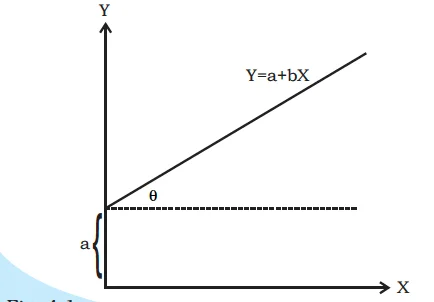
Intercept form of the linear equation
(A) Graphical Method
C= C +cY
Y = a + bX
Consumption Function – Graphical Representation
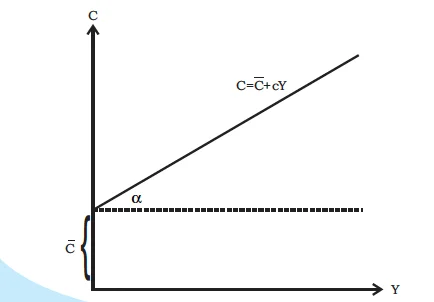
Consumption function with intercept C
Investment Function – Graphical Representation
Investment function with I as autonomous
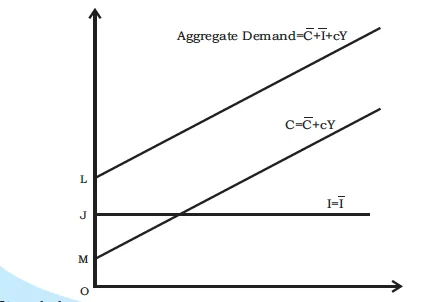
Aggregate demand is obtained by vertically adding the consumption and investment functions.
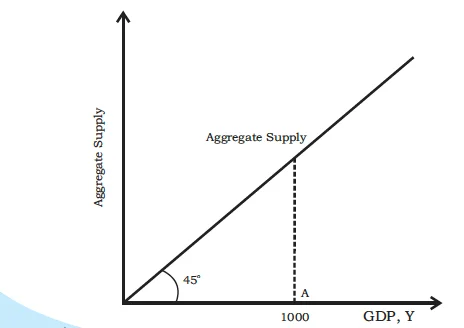
Aggregate supply curve with 45-degree line.
Equilibrium: Unifying Ex Ante Demand and Supply through Graphical and Algebraic Insights
In the two sector model, achieving equilibrium becomes a complex yet essential task.
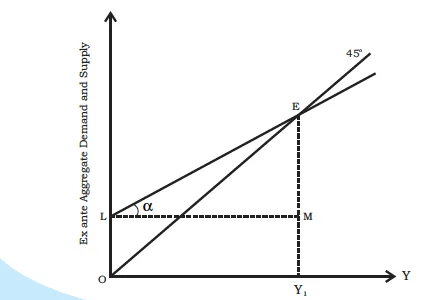
Equilibrium of ex ante aggregate demand and supply
(B) Algebraic Method
C + I + cY = Y
Y (1-c) = C + I
Y = ( C + I ) / (1-c)
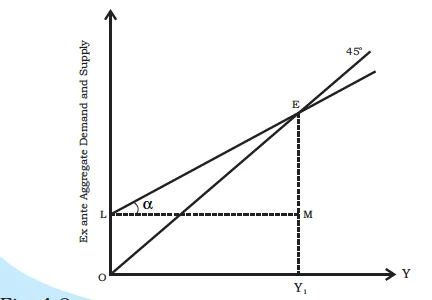
Equilibrium of ex ante aggregate demand and supply
I = E1F = E2J.
Demystifying the Investment Multiplier Mechanism and its Impact on Total Output
Investment Multiplier = Y / A
= 1 / (1-c)
= 1 / S
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
