Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Brief definition of the Oceanic salinity.
Body
- Describe the Reasons for oceanic salinity and its multi-dimensional effects and variation.
Conclusion
- Conclude your answer with significance of Oceanic salinity.
|
Introduction:
Oceanic salinity, or the concentration of salt in seawater, varies across the world’s oceans due to a range of factors. These variations can have far-reaching impacts on ocean circulation, marine ecosystems, and climate patterns. The average salinity of the water body of the oceans is 35 parts per thousand.
Body:
Reasons for oceanic salinity and its multi-dimensional effects:
- Precipitation: Regions with high precipitation rates tend to have lower salinity levels because freshwater from rain dilutes the saltwater in the ocean. On the other hand, regions with low precipitation rates have higher salinity levels.
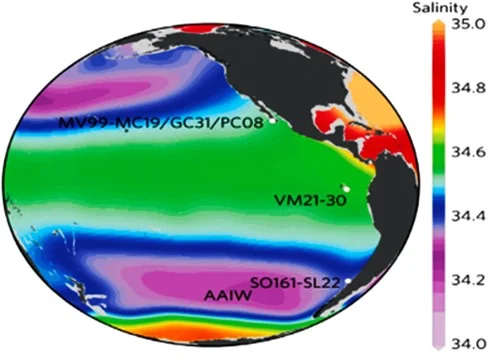
- Evaporation: When seawater evaporates, it leaves behind the dissolved salts, causing the salinity level to increase. Regions with high evaporation rates, such as the tropics, tend to have higher salinity levels.
- River runoff: Rivers carry freshwater into the ocean, which can significantly lower the salinity level in coastal regions.
The multi-dimensional effects of oceanic salinity variations include:
- Ocean currents: Differences in oceanic salinity levels drive the formation of ocean currents, which are responsible for distributing heat and nutrients around the world. Changes in ocean currents can impact climate patterns and marine ecosystems.
- Marine life: Many marine organisms are sensitive to changes in salinity levels. A significant change in salinity can affect the distribution and abundance of marine species, which can have ripple effects throughout the food chain.
- Water cycle: Oceanic salinity levels are closely tied to the global water cycle, which is responsible for moving water between the oceans, land, and atmosphere. Changes in salinity levels can affect the water cycle, leading to changes in precipitation patterns and the availability of freshwater resources.
Conclusion:
The multi-dimensional effects of oceanic salinity are vast, ranging from changes in ocean circulation and climate patterns to impacts on marine biodiversity and fisheries. Understanding the factors that contribute to variations in oceanic salinity is critical for predicting and mitigating the impacts of climate change on the world’s oceans and the communities that depend on them.
