Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Start by acknowledging the contribution of overuse and free availability of antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription.
Body
- Identify and discuss various factors that contribute to drug resistance.
- Mention the regulatory mechanisms and policies in place to control antibiotic use in India.
- Critically examine the problems hindering effective control of antibiotic misuse.
Conclusion
- Conclude, emphasizing the need for addressing the identified issues to improve the effectiveness of control mechanisms and ultimately combat the menace of antibiotic resistance.
|
Introduction:
Overuse and free availability of antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription indeed contribute significantly to the emergence of drug-resistant diseases in India. This phenomenon, known as antibiotic resistance, is a global health concern.
Body:
Contributors to Drug Resistance:
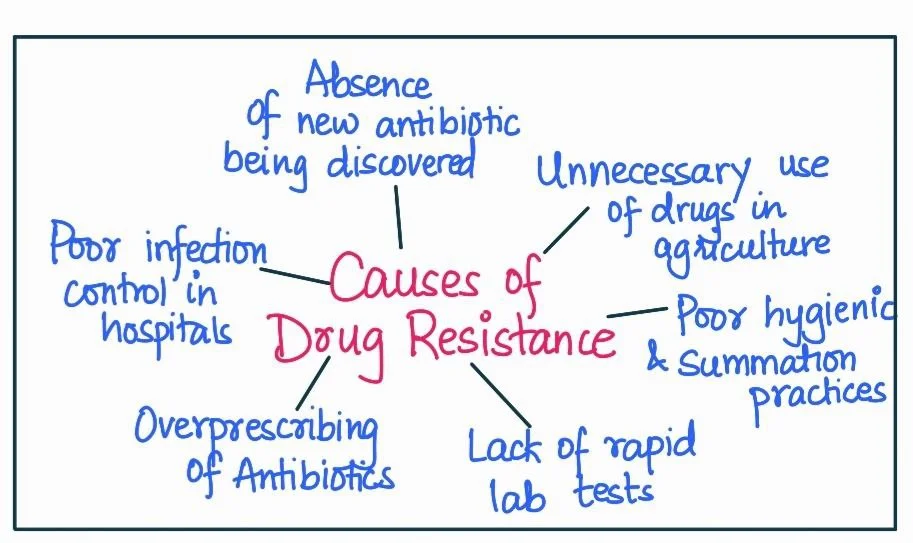
- Overuse of Antibiotics: Unnecessary or incorrect usage of antibiotics, often for viral infections where they are ineffective, can lead to antibiotic resistance.
- For instance, antibiotics are frequently misused for common colds, which are usually caused by viruses.
- Availability Without Prescription: In many parts of India, antibiotics can be easily purchased without a doctor’s prescription, leading to self-medication and misuse.
- Incomplete Courses: When patients do not complete the prescribed antibiotic course, it allows some bacteria to survive and develop resistance.
Mechanisms for Monitoring and Control:
- Schedule H1: In India, certain antibiotics are classified under Schedule H1, which requires pharmacists to maintain records of the antibiotics sold and the prescribing doctor.
- National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (NAP-AMR): The Indian government, in collaboration with WHO, has developed a plan to combat antimicrobial resistance.
However, the effectiveness of these mechanisms is limited due to inadequate enforcement and monitoring, lack of awareness, and improper medical practices.
Issues Involved:
- Lack of Awareness: Many people are unaware of the correct usage of antibiotics and the implications of their misuse.
- Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure: Due to the paucity of doctors in rural areas, people often resort to self-medication, leading to misuse of antibiotics.
- Poor Regulation: Despite regulations, many pharmacies sell antibiotics without prescriptions.
- Poultry and Aquaculture Use: Antibiotics are often used indiscriminately in poultry and aquaculture, contributing to antibiotic resistance.
Conclusion:
Overuse and free availability of antibiotics without a prescription are major contributors to the emergence of drug-resistant diseases in India. Though mechanisms for control exist, their effectiveness is compromised by various issues. Addressing these challenges is crucial to combating the growing menace of antibiotic resistance.
