Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Begin with a definition of cyber warfare and its implications for national security.
Body
- Discuss the various types of cyber threats that India is vulnerable to.
- Substantiate with appropriate facts and examples.
- Evaluate India’s preparedness to deal with these threats by looking at the policy and regulatory framework, technical and operational capabilities, international cooperation, and public-private partnerships.
Conclusion
- Conclude with an overview of the progress made in strengthening India’s cyber warfare preparedness and the need for continued improvements in technology, regulations, and human resource development.
|
Introduction:
In contemporary times, warfare is no longer confined to traditional battlefields. The digital realm has emerged as the ‘Fourth Front’ of warfare – a domain where nations engage in cyber warfare. This term refers to the strategic use of digital attacks by one nation-state against another, intending to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to critical infrastructures, computer systems, data, and networks, thereby causing substantial harm to the economy, security, and military capabilities.
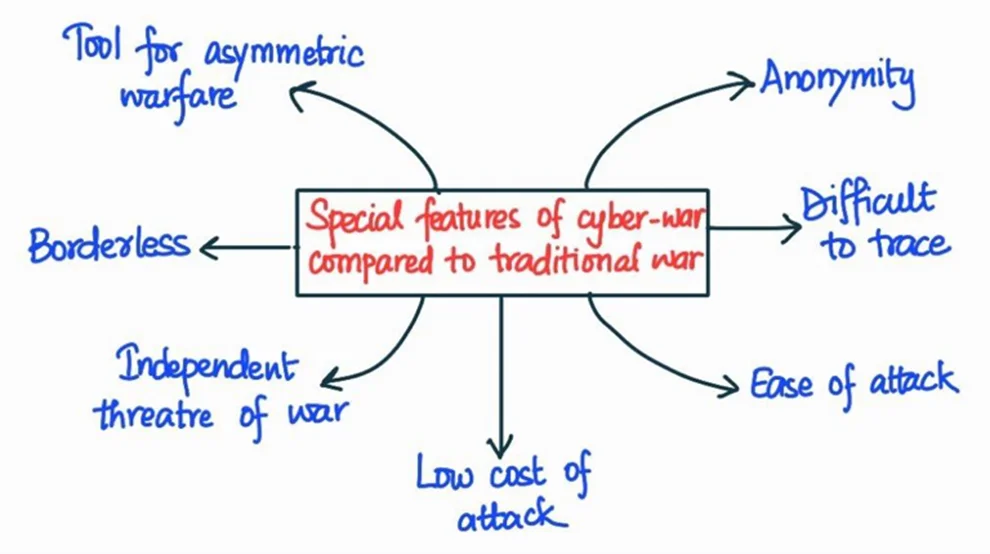
Body:
Cyber Threats Vulnerable to India
- Data Breaches:
- With the rapid digitization of services in India, threats of large-scale data breaches have increased.
- For example, the reported breach in 2020 where personal details of 2.9 crore Indians were allegedly sold on the dark web, highlighting the severity of such threats.
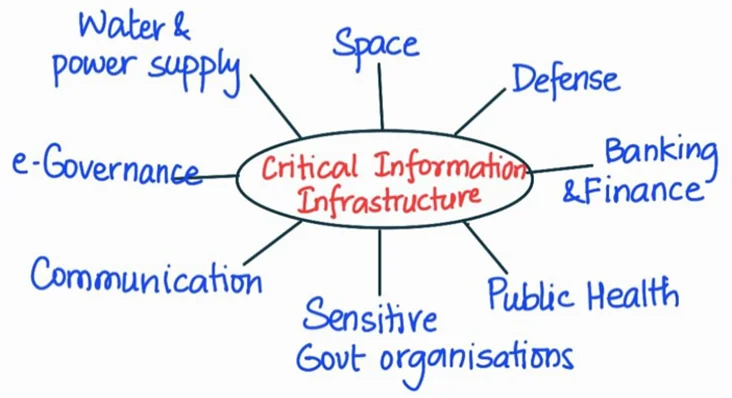
- Attacks on Critical Infrastructure:
- India’s critical infrastructures are becoming increasingly vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
- For instance, in 2020, the power system in Mumbai faced an unexpected blackout, which, as per reports, was a suspected cyber-attack.
- Cyber Espionage:
- India has been a target of numerous state-sponsored cyber-espionage attacks.
- A notable example is the ‘Operation Hangover’ attributed to Pakistan, where military, diplomatic, and corporate entities were targeted for sensitive information.
- Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks:
- These attacks are becoming more sophisticated and widespread in India.
- According to the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In), the country witnessed over 2.7 lakh cybersecurity incidents related to phishing in 2020 alone.
- Cyber Terrorism:
- The digital space has become a new medium for terror organizations to spread propaganda and orchestrate attacks.
- Groups like ISIS have been reported to use the internet to recruit members from India and spread their ideologies.
State of India’s Preparedness
- Policy and Regulatory Framework: India has established a legal and policy framework to deal with cyber threats, including the IT Act 2000 and National Cyber Security Policy 2013. However, their implementation remains a challenge.
- Technical and Operational Capabilities: Organizations like CERT-In (Indian Computer Emergency Response Team) and NCIIPC (National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre) have been established to respond to cyber threats.
- International Cooperation: India has been actively cooperating with international bodies and other nations to share intelligence and best practices in cyber security.
- Public-Private Partnership: Collaboration between government and private sector in areas like cyber threat intelligence sharing, capacity building, and research is gaining traction.
Conclusion:
While India has made strides in strengthening its cyber warfare preparedness, there’s a need for more robust technology, up-to-date regulations, and greater investment in building skilled human resources in the field of cyber security.

