Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Define Potential GDP and briefly explain about the aspects of potential GDP.
Body
- Enumerate the determinants of potential GDP and the constraints in achieving it.
Conclusion
- Conclude stating that potential GDP is a dynamic metric determined by multiple variables, but it must be looked into as a valuable tool to make informed decisions.
|
Introduction:
Potential GDP (gross domestic product) is the maximum level of output or real GDP that an economy can sustain without generating inflationary pressures. It is determined by the productive capacity of an economy, which is influenced by a range of factors such as the size and skill level of the labour force, the level of capital stock, the state of technology, and the level of natural resources.
The potential GDP is often used as a benchmark to gauge the actual level of output in an economy, and to measure the extent to which an economy is operating at or above its potential.
Body:
Determinants of Potential GDP:
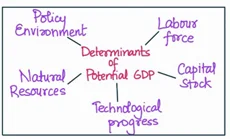
- Labour force: A growing, well-educated and skilled labour force can increase the economy’s potential for growth and productivity, while a declining labour force can limit the economy’s potential for growth.
- Capital stock: The accumulation of capital can increase the potential for productivity and output, while a lack of investment in capital can limit the economy’s potential for growth.
- Technological progress: Technological advancements can increase the potential for growth and productivity by improving the efficiency of production processes, increasing the quality of goods and services, and reducing the cost of production.
- Natural Resources: The availability of natural resources, such as land, minerals, and energy, can impact the economy’s potential for growth. If these resources are abundant and easily accessible, the economy’s potential for growth can increase, while a lack of resources can limit the potential for growth.
- Policy environment: Government policies that support investment and innovation can increase the potential for growth, while policies that stifle investment and innovation can limit the potential for growth.
There are several factors that have constrained India in achieving its potential Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth:
- Lack of Infrastructure: India faces significant infrastructure challenges, including inadequate and inefficient transportation systems, energy shortages, and limited access to modern communication and technology. These constraints limit the country’s ability to attract investment, increase productivity, and stimulate economic growth.
- Regulatory Environment: India’s complex and bureaucratic regulatory environment has been a major constraint to the country’s economic growth. Corruption remains a persistent challenge in India, affecting the delivery of public services, the business environment, and economic growth.
- Low investment: India has a low savings rate, which has contributed to low levels of investment and has hindered the growth of the capital stock.
- Agricultural productivity: Despite being one of the world’s largest agricultural producers, India’s agricultural sector is characterized by low productivity, outdated technology, and poor infrastructure.
- Education, health and skill development: Though India enjoys a favourable demographic dividend, the population lacks skill and education necessary for the dividend to become an asset rather than a liability. It has also led to a shortage of skilled workers and a mismatch between the skills of the workforce and the needs of the economy.
Conclusion:
Potential GDP is determined by various factors. Accurately estimating potential GDP is challenging, and different methods may yield different results. However, it is widely recognized as a valuable tool for understanding the underlying trends and dynamics of an economy and making informed decisions that can positively impact the overall well-being of a society.

