Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Write about photochemical smog in brief.
Body
- Discuss the formation, effects and mitigation of Photochemical Smog.
- Write about the 1999 Gothenburg Protocol in brief.
Conclusion
- Summary of the answer with urgent measures needed.
|
Introduction:
Photochemical smog refers to a type of air pollution that is formed when sunlight interacts with pollutants, primarily nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), in the presence of heat. This phenomenon is commonly observed in urban areas with high traffic and industrial activities.
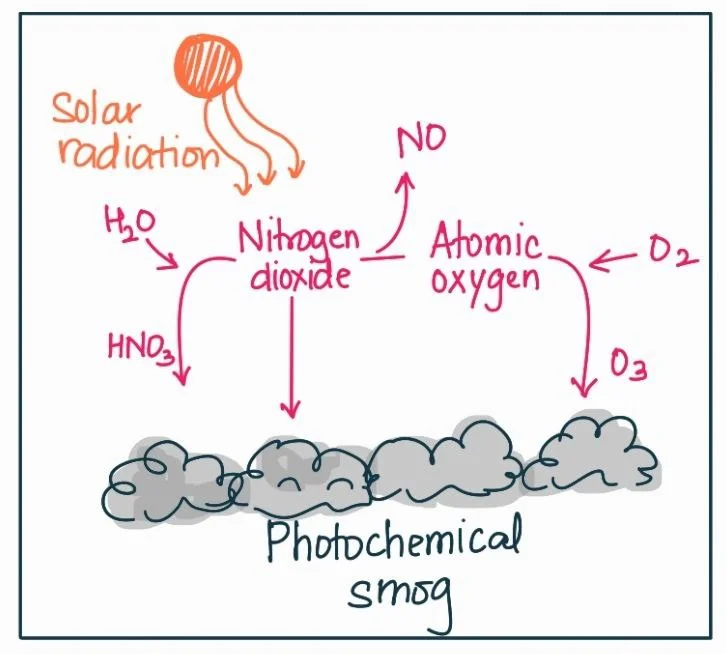
Body:
- Formation: Photochemical smog formation involves a series of complex reactions. During sunlight exposure, nitrogen oxides and VOCs are converted into secondary pollutants, such as ozone (O3) and peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN). These reactions occur due to the presence of hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides emitted by vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes.
- Effects: Photochemical smog has numerous adverse effects on human health, ecosystems, and the environment. High levels of ozone can cause respiratory problems, eye irritation, and exacerbate existing lung conditions. It also damages crops, reduces agricultural productivity, and harms aquatic life. Furthermore, photochemical smog contributes to the greenhouse effect and climate change.
- Mitigation: Efforts to mitigate photochemical smog involve a combination of regulatory measures, technological advancements, and public awareness campaigns
- Emission controls: Implementing stringent emission standards for vehicles, industries, and power plants can significantly reduce the release of nitrogen oxides and VOCs.
- Alternative fuels: Promoting the use of cleaner fuels, such as compressed natural gas (CNG) and electric vehicles, helps in reducing emissions and mitigating smog formation.
- Urban planning: Developing sustainable urban planning practices that prioritize public transportation, cycling, and pedestrian-friendly infrastructure can reduce vehicular emissions.
- Green initiatives: Increasing the number of green spaces, such as parks and gardens, helps absorb pollutants and improve air quality.
The 1999 Gothenburg Protocol:
- The Gothenburg Protocol is an international agreement aimed at reducing air pollution and acidification in Europe.
- It focuses on limiting emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), ammonia (NH3), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from various sources.
- The protocol sets national emission ceilings for member countries and encourages the use of best available techniques to control pollution. By implementing the Gothenburg Protocol, countries have achieved substantial reductions in air pollutants, leading to improved air quality and environmental protection.
Conclusion:
Photochemical smog necessitates immediate action due to its complex formation and harmful impacts on health, ecosystems, and climate. Mitigation entails strict emission controls, cleaner technologies, and the 1999 Gothenburg Protocol, which emphasizes international cooperation for cleaner and healthier environments.

