Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Begin with a brief overview of the National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC) and its transformation from a statutory body to a constitutional body through the 102nd Constitutional Amendment Act.
Body
- Discuss the various aspects of the role of the NCBC in the wake of its transformation.
Conclusion
- Write a relevant conclusion.
|
Introduction:
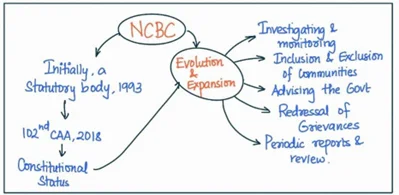
The National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC) was initially established as a statutory body under the National Commission for Backward Classes Act, 1993. In 2018, with the 102nd Constitutional Amendment Act, the NCBC was granted constitutional status, becoming an essential institution for safeguarding the interests of the socially and educationally backward classes in India.
Body:
Evolution and Expansion of NCBC: From Statutory to Constitutional Body:
- Enhanced Authority and Status: As a constitutional body, the NCBC has gained greater authority and status, making it an institution on par with the National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) and the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST).
- Investigating and Monitoring: It is tasked with ensuring that the constitutional and legal protections granted to the socially and educationally backward classes are effectively implemented and enforced.
- Inclusion and Exclusion of Communities: The NCBC has the authority to examine requests for the inclusion or exclusion of communities in the Central List of Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
- Advising the Government: The NCBC plays a crucial role in advising the central and state governments on various issues pertaining to the welfare and development of the backward classes. For example,
- The NCBC played a role in the central government’s decision to implement a 10% reservation for the Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) among the General Category in 2019.
- The NCBC contributed to the decision to establish a commission under Article 340 of the Indian Constitution to examine the sub-categorization of Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
- Redressal of Grievances: It can conduct inquiries, summon officials, and pass orders to ensure that the grievances of these communities are addressed and their rights are protected.
- Periodic Review and Reports: The NCBC is required to submit periodic reports to the President of India regarding the implementation of the constitutional safeguards and the measures taken for the welfare and development of the backward classes.
Conclusion:
With its expanded mandate and increased powers, the NCBC is better equipped to safeguard the rights and interests of these communities and ensure their effective representation and welfare in various spheres of society.

