Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Begin by defining what pressure groups are and their role as the informal face of politics. Briefly mention their function in influencing public policies and decisions without seeking formal political power.
Body
- Discuss the different types of pressure groups based on interest, issues, and identity, providing examples for each.
- Discuss the various roles of pressure groups, such as policy advocacy, public education, and representation.
Conclusion
- Conclude by summarizing the significant role of pressure groups in India’s democratic setup, highlighting their function as a bridge between the government and citizens.
|
Introduction:
Pressure groups are organized interest groups that aim to influence public policies and decisions without seeking formal political power. They are often viewed as the informal face of politics because they operate outside the formal political structure but play a significant role in shaping policy outcomes. In India, pressure groups have a diverse structure and functioning, reflecting the country’s socio-economic-political diversity.
Body:
Structure of Pressure Groups in India:
- Interest-Based: Many pressure groups are formed based on shared interests, such as business groups like FICCI, ASSOCHAM, and NASSCOM, or labor unions like the All India Trade Union Congress (AITUC) and Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh (BMS).
- Issue-Based: Some pressure groups are formed around specific issues, such as environmental groups like the Chipko Movement, or human rights groups like Amnesty International India.
- Identity-Based: Several pressure groups in India are formed based on identity lines, such as caste groups like the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK) or religious groups like the All India Muslim Personal Law Board.
Functioning of Pressure Groups in India:
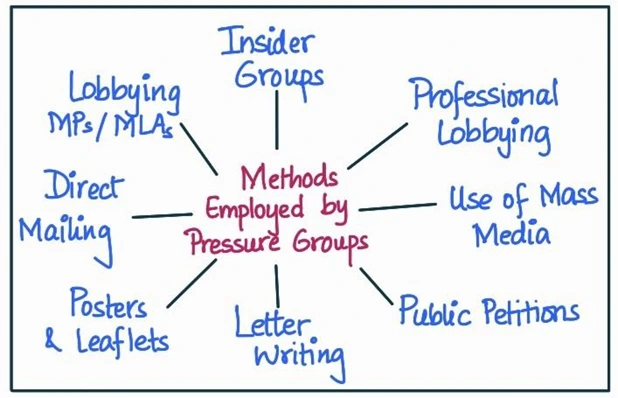
- Policy Advocacy: Pressure groups play a crucial role in policy advocacy by lobbying with government officials, mobilizing public opinion, and using various forms of protest and negotiation to influence policy outcomes.
- An example is the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), which regularly interacts with government officials to advocate for pro-business policies.
- Public Education: They often undertake public education and awareness campaigns to inform the public about specific issues and build support for their cause.
- For instance, environmental groups like Greenpeace India run campaigns to raise awareness about climate change and other environmental issues.
- Representation: Pressure groups provide a platform for marginalized and underrepresented groups to voice their concerns and interests.
Examples:
- Farmers’ Movements: The recent farmers’ protests against the new farm laws highlight the role of pressure groups in shaping policy outcomes. Various farmers’ unions came together to protest the laws, leading to a nationwide movement that significantly impacted the political discourse.
- Narmada Bachao Andolan: The movement against the construction of large dams on the Narmada river is another example of a pressure group influencing policy decisions. Led by social activist Medha Patkar, the movement highlighted the environmental and social costs of large dam projects.
Conclusion:
Pressure groups play a significant role in India’s democratic setup. They act as a bridge between the government and the citizens, influencing policy decisions, and giving voice to diverse interests. However, there is a need to ensure that they function in a transparent and accountable manner, and that they do not undermine the democratic process through undue influence or coercion.

