Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Briefly discuss the concept of decentralization and its significance in India, mentioning the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments.
Body
- Analyze the impact of decentralization on grassroots governance in India.
Conclusion
- Write a relevant conclusion focusing on the way forward.
|
Introduction:
The decentralization of power in India has significantly changed the governance landscape at the grassroots level. The 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments in 1992, which formalized the Panchayati Raj system and urban local bodies, respectively, have been instrumental in this process.
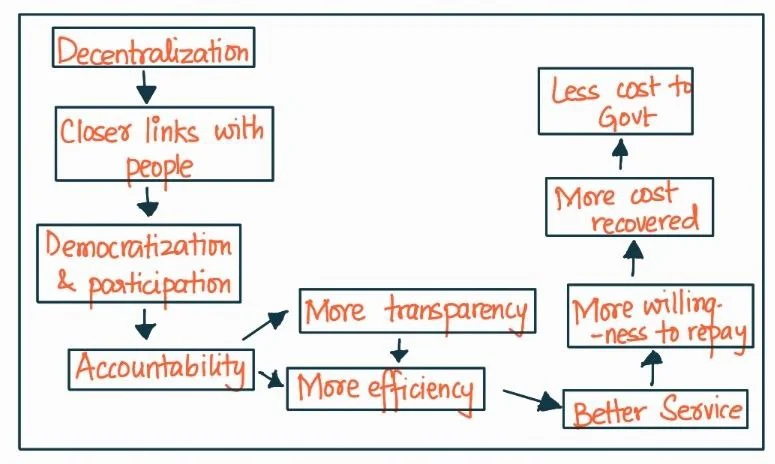
Body:
Decentralization has impacted the grassroots governance in India following ways:
- Enhanced participation: Decentralization has enabled people to be more involved in the planning, implementation, and monitoring of development programs and policies.
- Empowerment of marginalized groups: Decentralization has facilitated the inclusion of women and other marginalized groups in governance structures, promoting social justice and empowerment.
- Responsive governance: Decentralization has made local governments more responsive to people’s needs and demands.
- Strengthened accountability: The transfer of power and responsibilities to local government bodies has increased the accountability of elected representatives.
- Capacity building: Decentralization has paved the way for capacity building of local representatives, enabling them to acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to manage resources and address local issues more effectively.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Both Kerala and Tamil Nadu serve as examples of how decentralization can bring about positive change in governance, by empowering local bodies.
- Kerala has been a pioneer in decentralization and participatory governance in India. The People’s Plan Campaign (PPC) in 1996 was a groundbreaking initiative that aimed to transfer 35-40% of the state’s development budget to local bodies. This campaign promoted community participation in planning, implementation, and monitoring of development projects.
- Tamil Nadu empowered its Panchayati Raj Institutions with financial and administrative autonomy to manage development projects. The Tamil Nadu e-Governance Agency (TNeGA) digitalized various services, improving access to public services at the grassroots level and boosting the overall quality of life in rural areas.
However, there are challenges to the decentralization process as well:
- Lack of financial resources: Many local government bodies face a lack of financial resources and depend on higher levels of government for funding.
- Limited capacity: Some local representatives may lack the required skills, knowledge, or training to effectively manage resources and implement policies, which can hinder the overall governance process.
- Corruption and inefficiency: Decentralization can sometimes lead to increased corruption and inefficiency in local government bodies, especially in cases where there is a lack of accountability or proper monitoring mechanisms.
Conclusion:
By adopting measures like enhancing financial devolution, promoting transparency, strengthening accountability mechanisms, and investing in capacity building for local representatives, India can create a more inclusive and responsive governance framework at the grassroots level.
| VALUE ADDITION POINTS:
● Kerala’s People’s Plan Campaign: Launched in 1996, this campaign aimed at devolving around 35-40% of the state’s development budget to local governments. The initiative encouraged participatory planning, which allowed local communities to identify their priorities and formulate projects accordingly. This led to increased involvement of people in decision-making and better alignment of development projects with local needs.
● Watershed Management in Maharashtra: The state of Maharashtra implemented a decentralized watershed management program, which empowered local communities to plan, execute, and manage watershed development projects. This led to better water conservation, increased agricultural productivity, and improved livelihoods for farmers. |
