Answer:
| Approach:
Introduction
- Provide a brief overview of the Indian parliamentary system and the importance of holding the executive accountable.
Body
- Discuss the mechanisms for ensuring executive accountability in the Indian Parliament.
- Write examples to better substantiate your views.
- Analyze the factors that can limit the effectiveness of these mechanisms.
Conclusion
- Write a relevant conclusion.
|
Introduction:
In a parliamentary democracy like India, the executive is responsible to the Parliament, which plays a crucial role in ensuring accountability and transparency in governance. The Parliament uses various mechanisms to scrutinize the executive’s actions, policies, and decisions, maintaining a system of checks and balances.
Body:
The Parliament has various mechanisms to ensure accountability, including the following:
- Question Hour: Members of Parliament (MPs) can pose questions to ministers about the functioning of their respective ministries. For instance, during the Question Hour in August 2021, MPs posed questions about the government’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic, including the vaccination strategy, lockdown impact, and economic measures taken.
- Parliamentary Committees: They scrutinize budgetary allocations, policy decisions, and implementation of government programs. For instance, The Public Accounts Committee (PAC), for example, plays a significant role in ensuring governmental accountability. In 2010, it scrutinized the 2G Spectrum Scam, leading to serious implications for those involved.
- No-confidence Motion: If a majority in the Lok Sabha (the lower house) votes in favor of the motion, the government has to resign, which ensures executive accountability. A notable instance is from 1999 when the then Atal Bihari Vajpayee-led NDA government fell short of one vote, leading to the fall of the government.
- Adjournment Motion and Calling Attention Motion: These motions allow MPs to bring urgent matters of public importance to the attention of the executive and seek their response. In 2019, the calling attention motion was moved in Rajya Sabha by opposition MPs to discuss the issue of air pollution and climate change.
- Debates and Discussions: The Parliament engages in debates and discussions on various issues, bills, and policy decisions, allowing MPs to voice their opinions and hold the executive accountable. An example would be the extensive debate in Parliament over the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019, wherein MPs voiced their support, concerns, and objections, leading to nationwide discussion on the topic.
However, certain factors may limit the Parliament’s effectiveness in ensuring executive accountability:
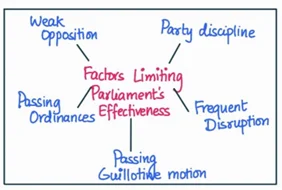
- Frequent disruptions: Disruptions and adjournments in the Parliament can limit the time available for scrutinizing the executive’s actions.
- Party discipline: MPs belonging to the ruling party may be reluctant to criticize their own government, which can undermine the Parliament’s role in holding the executive accountable.
- Weak opposition: If the opposition is weak or fragmented, it may not be able to effectively challenge the executive and hold it accountable.
- Bypassing the Parliament: Sometimes, the executive may bypass the Parliament and take decisions through ordinances or executive orders, which can limit parliamentary oversight.
Conclusion:
To maximize the Parliament’s ability to hold the executive accountable, it is crucial to address these challenges and promote a conducive environment for constructive debate, scrutiny, and oversight.
