![]() May 14, 2024
May 14, 2024
![]() 6287
6287
![]() 0
0
Assam, a land of rich history and diverse cultures, holds within it the roots of the Ahom Kingdom, tracing back to the legendary Kamarupa. From being a tributary to the Gupta Empire to the emergence of the Pralamba dynasty, Assam’s journey is marked by resilience and cultural amalgamation. The Ahom Kingdom, with its strategic isolation and assimilation of tribal influences, played a pivotal role in shaping Assam’s identity.
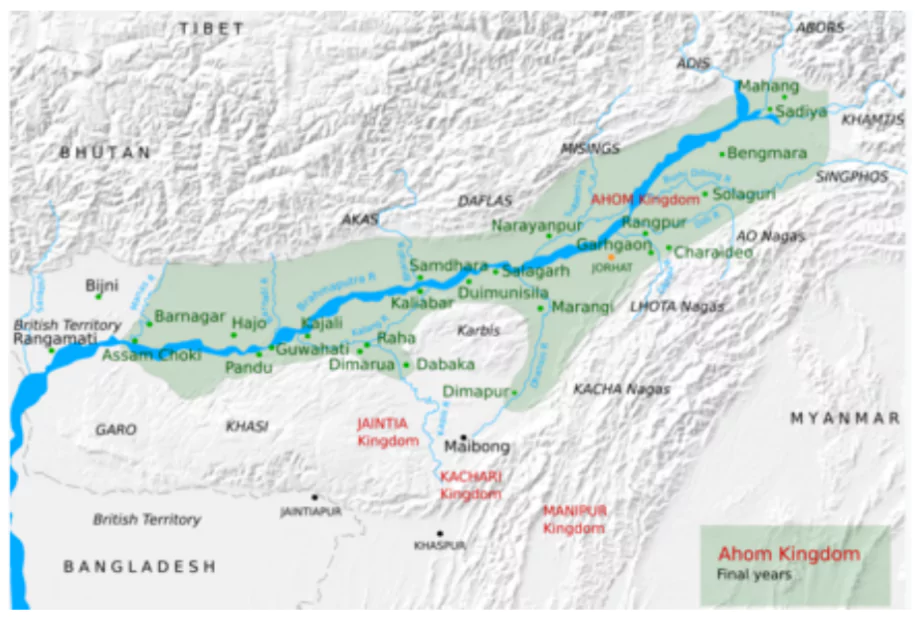 Area and Capital: Settled between the Burhidihing and Dikhau rivers, with Charaideo as the capital.
Area and Capital: Settled between the Burhidihing and Dikhau rivers, with Charaideo as the capital.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Through triumphs and challenges, Assam’s story reflects the resilience and diversity of its people. From the mighty Ahom rulers to the struggles against Mughal and Burmese invasions, each chapter adds depth to Assam’s vibrant heritage. Today, Assam continues to thrive, blending its ancient past with the aspirations of a modern era.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments