![]() June 5, 2024
June 5, 2024
![]() 2436
2436
![]() 0
0
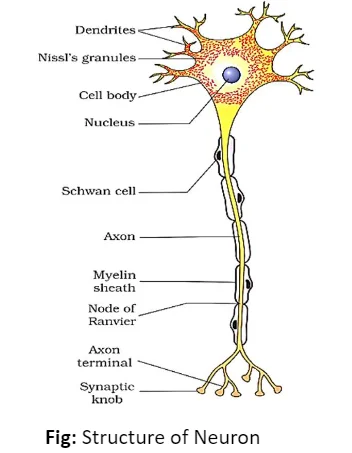
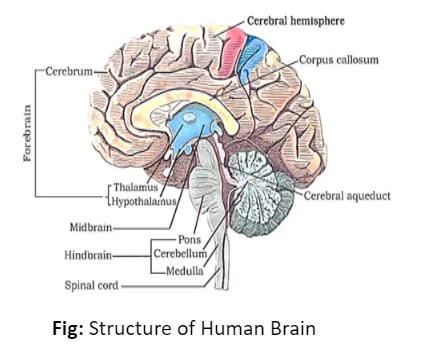
The nervous system helps our body by passing signals from our senses to where they need to go for a response. There are two main types: diffuse, found in lower invertebrates, and centralised, found in higher invertebrates and vertebrates like us. In our bodies, impulses travel to and from the central nervous system (CNS) through the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Our brain is like the command centre, with different parts handling different tasks.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
<div class="new-fform">
</div>

Latest Comments