![]() March 30, 2024
March 30, 2024
![]() 15948
15948
![]() 0
0
With only 2.4% of the world’s landmass and 4% of its water resources, India’s irrigation systems are critical in maximizing agricultural productivity and ensuring food security. Sustainable management practices are essential to address the disparity between water availability and the growing population’s demands, necessitating innovative irrigation approaches that prioritize water conservation and efficiency.
|
|
|
|
|
|
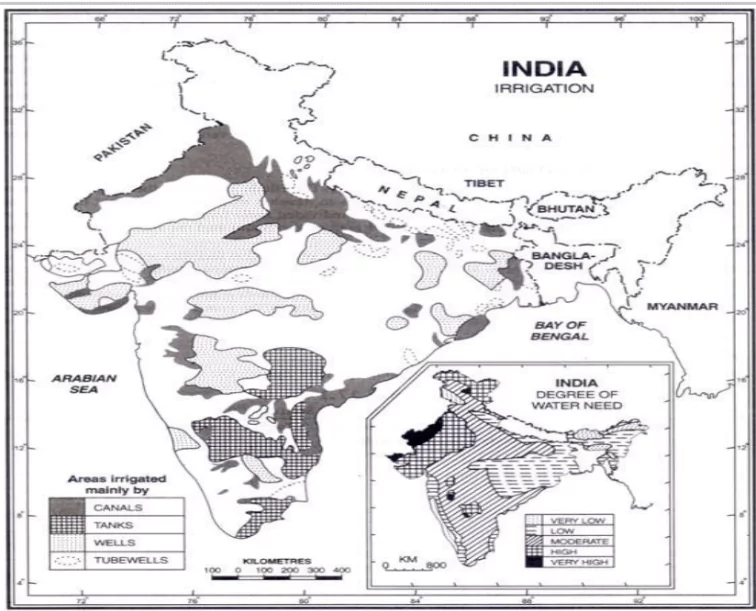
Net Irrigated area from various sources and their relative contribution
| Source (As Per ICAR data 2014-15) | NIA (Mha) | Contribution (%) |
| Canal | 16.18 | 23.66 |
| Tank | 1.72 | 2.52 |
| Well | 42.96 | 62.82 |
| Other | 7.52 | 11.00 |
Advantages of Drip Irrigation [UPSC 2016]
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
| Related Articles | |
| Indian Economy: Evolution | Basics of Money |
| Banks in India | Financial Market |
| Indian Insurance Sector | Financial Inclusion |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments