![]() June 5, 2024
June 5, 2024
![]() 5414
5414
![]() 0
0
The musculoskeletal system is crucial for our body’s movement and structure. Muscles, bones, and joints work together to support us and enable movement. Muscles make up a significant portion of our body weight and have unique properties like excitability and contractility. There are different types of muscles, including skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, each serving specific functions in our body.
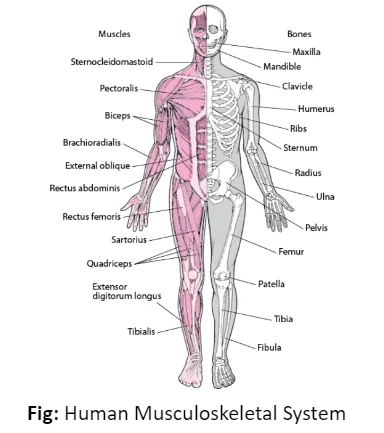
Skeleton
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
<div class="new-fform">
</div>

Latest Comments