![]() May 2, 2024
May 2, 2024
![]() 31517
31517
![]() 0
0
India’s population is a significant global demographic factor, surpassing China to become the world’s most populous nation. With a current population of 1.43 billion, India faces challenges such as resource pressure and socio-economic issues due to its immense size. Understanding population distribution, density, and growth trends is crucial for effective planning and development.
A. Distribution of Indian Population
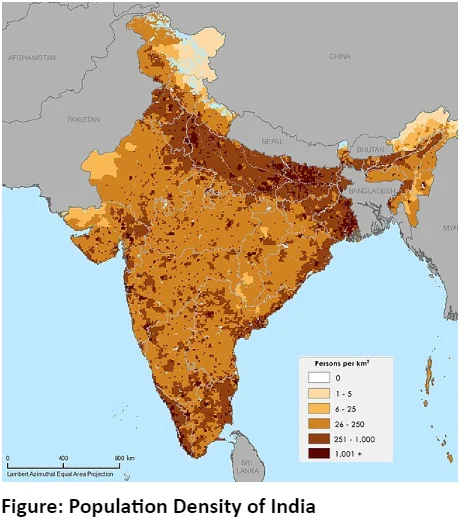
B. Population Density
|
C. Population Growth
| Phase | Key Characteristics |
| Phase I: Stagnant Phase (1901-1921) |
|
| Phase II: Steady Growth (1921-1951) |
|
| Phase III: Population Explosion (1951-1981) |
|
| Phase IV: Decelerating Growth (Post-1981) |
|
| Population Momentum: Tendency of a highly fertile population that has been increasing rapidly in size to continue to do so for decades even after a substantial decline in fertility. This results from the youthful age structure of such a population. |
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
| Related Articles | |
| Climate of India | Exploring the Density of Population, Distribution Patterns, Growth Trends |
| POPULATION IN INDIA | Northern Plains of India Importance, Features, Maps And States |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments