![]() June 24, 2024
June 24, 2024
![]() 15630
15630
![]() 0
0
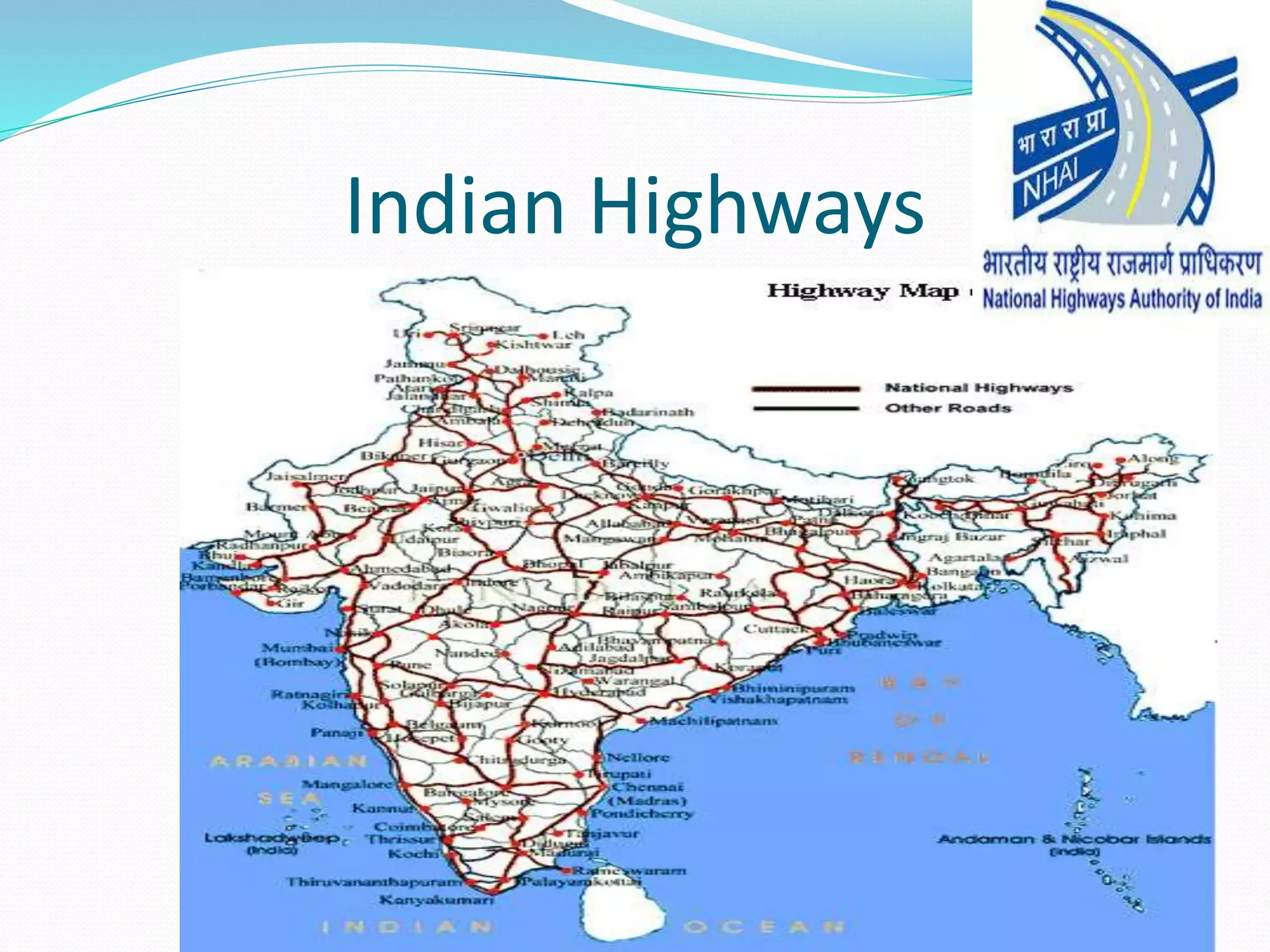
India boasts the world’s second-largest road network, covering approximately 63.73 lakh kilometers, consisting of various types of roads like national highways, state highways, district roads, and rural roads. Road transport plays a vital role in India, carrying around 87% of passenger traffic and over 60% of freight. With 100% foreign direct investment allowed in roads and highways, the sector holds significant potential for growth and development.
|
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
India’s road network, comprising national highways, state highways, district roads, and rural roads, forms the backbone of its transportation infrastructure, facilitating the movement of people and goods across the country. Through initiatives like the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) and projects like Bharatmala Pariyojana, the government is committed to enhancing connectivity, promoting economic development, and strengthening national security.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments