Introduction
- Definition: The service sector includes activities that do not produce physical goods but provide value through services.
- Examples: Finance, healthcare, education, hospitality, information technology, and more.
- Accounts for 54% of India’s Gross Value Added (GVA); Contributes over 50% to India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Comprises 38% of total exports and attracts two-thirds of foreign direct investment (FDI) into India.
- Employment Generation: Major source of employment, providing jobs to 30.7% of the Indian population.
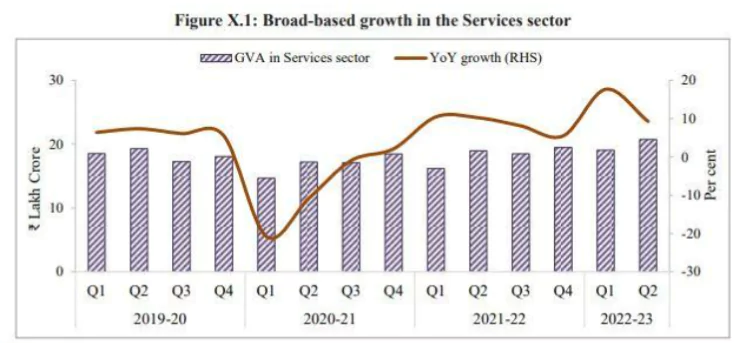
- Remarkable Recovery: In the fiscal year 2022-23, the services sector witnessed a significant recovery.
Service Sector Spread in India: Roles, Responsibilities, and Jurisdictional Insights
- Union List: Telecommunications, postal, broadcasting, financial services (including insurance and banking), national highways, mining services.
- State List: Healthcare and related services, real estate services, retail, services incidental to agriculture, hunting, and forestry.
- Concurrent List: Professional services, education, printing and publishing, electricity.
E-commerce Landscape in India: Models, Regulations, and Government Initiatives
- With a 10-15% share of the Indian retail market, it is a sunrise sector.
- Business Models
- Inventory-based Model: The e-commerce entity owns and sells goods and services directly to consumers.
- Marketplace-based Model: The e-commerce platform acts as a facilitator between buyers and sellers, providing a digital platform.
- Hybrid Model: A combination of both inventory-based and marketplace models.
- FDI Guidelines for E-commerce in India:
- 100% FDI is permitted in Business-to-Business (B2B) e-commerce in India. (Marketplace model)
- No FDI is permitted in Business-to-Consumer (B2C) e-commerce in India. (Inventory based Model)
- Initiatives Taken By The Government For The Promotion of E-Commerce Sector
- One District – One Product (ODOP): Under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry. It facilitates the onboarding of sellers of identified products on e-commerce platforms to provide greater visibility for small businesses from the rural sector.
- Government e-Marketplace: Launched in 2016 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry; helps government departments, organizations, and PSUs purchase common usage goods and services online.
- www.tribesindia.com Portal: Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India Limited (TRIFED) has been onboarding tribal artisans with their products for online sales.
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC): ONDC provides better market access to sellers and helps bring the country’s remotest corners into the e-commerce framework by empowering them with digitization.
- Consumer Protection (e-commerce) Rules, 2020
- Transparency in Pricing: The complete cost of the products and services being sold, as well as the breakdown of additional fees, must be shown by the e-commerce companies.
- Authority: It gives the Central Government the authority to take action against unfair trade practices in direct selling and online shopping.
- Grievance Officers: would need to be appointed by both sellers and marketplaces, and they would need to reply within a certain amount of time.
- Penalties for Violating Rules: The violation of the rules will attract penal action under the Consumer Protection Act 2019.
Startups: Growth, Regional Dynamics, and Job Creation
- India has the second-largest ecosystem for tech startups.
- Tier II and Tier III cities are home to about 40% of startups in India.
- Jobs created by startups are on constant increase since the past five years.
Initiatives Promoting Startups: Government Initiatives and Support Programs
- Startup India
- Launched in 2016.
- A startup is defined as an organization with its headquarters located in India, that was founded less than ten years ago, and that generates less than Rs 100 crore in revenue annually.
- To provide equity funding a corpus fund of INR 10,000 Cr managed by SIDBI has been created.
- Fund of Funds: The fund is in the nature of Fund of Funds, which means that the government participates in the capital of SEBI registered Venture Funds who invest twice the amount in startups.
- The flow of funds is Government > SIDBI > Venture Capitals > Startups.
- Fast Track Firms: The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has notified Startups as ‘fast track firms’, enabling them to wind up operations within 90 days vis-a-vis 180 days for other companies
- Incentives for New Businesses: Freedom from inspections for the first 3 years of operation, freedom from Capital Gain Tax for the first 3 years of operation, and freedom from tax for the first 3 years of operation have been provided.
- Compliance Mechanism: Startups are allowed to self-certify their compliance.
- DPIIT recognised startups can now get listed as sellers on the Government of India’s largest e-procurement portal – Government e-Marketplace (GeM).
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme: Launched by the Ministry of Commerce and the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- National Initiative for development and Harnessing Innovation (NIDHI)
-
- Launched by the Department of Science and Technology.
- Fostering Innovation: Under this initiative, programmes for setting up of incubators, seed funds, accelerators, and ‘Proof of concept’ grants for innovators and entrepreneurs are launched for nurturing ideas and innovations (knowledge-based and technology-driven) into successful startups.
- Ranking of States on Support to Startup Ecosystems (RSSSE)
-
- Carried out by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Prarambh
-
- The Startup India International Summit has been organized by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- National Startup Awards
-
- The initiative was launched by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry in 2016.
Evolution and Reform in India’s Insurance Sector: Key Players and Initiatives
- Life Insurance Corporation: LIC was created in 1956; LIC has a share of around 70% in terms of first-year premium income.
- However, the government has announced the IPO of LIC shares in the budget 2020-21.
- General Insurance Corporation: Government-owned insurance company under the Ministry of Finance.
- Agriculture Insurance Company of India: A central public sector undertaking under the ownership of the Ministry of Finance.
- It was incorporated under Indian Companies Act 1956, in 2002.
| Insurance sector reforms in India started with the formation of the Malhotra Committee in 1993. |
Insurance schemes backed by the Government
- Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana
-
- Healthcare Coverage: It provides a 5 lakh rupee sum insured for secondary and tertiary care per family.
- Health Benefits Packages: Pay for diagnostics, medications, surgery, medical care, and daycare expenses.
- The National Health Authority, registered under the Society Registration Act 1860, is the nodal implementing agency. At the state level, the State Health Agency implements the scheme.
- Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data is used to identify the beneficiaries.
- Funding Pattern: 60 : 40 for all states and UTs with their own legislature.; 90 : 10 in Northeast states and Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal and Uttarakhand; 100% Central funding for UTs without legislature.
- Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana
-
- It was launched by the Ministry of Finance, in 2015.
- It is accessible to anyone with a bank account who is between the ages of 18 and 50.
- Premium is 436 per annum, excluding service tax.
- 2 Lakh will be given in case of death for any reason.
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana
-
- It was launched by the Ministry of Finance in 2015.
- It is accessible to anyone with a bank account who is between the ages of 18 and 70.
- The premium is 20 per annum.
- The scheme provides one lakh rupees for partial disability and two lakhs rupees for accidental death and total disability.
- All Public Sector General Insurance Companies and other insurers willing to participate in the program and collaborate with banks towards this end will offer the scheme.
Boosting Tourism in India: Government Initiatives and Programs
Tourism Initiatives by Government of India
- Swadesh Darshan 2.0
-
- Central sector scheme by the Ministry of Tourism.
- The implementing agency is to be designated by the Central or State government.
- The center gives financial assistance to states and UTs for 13 theme-based tourist circuits with a focus on sustainability and responsible tourist destinations.
- Major themes under the scheme: Culture and Heritage; Adventure Tourism; Eco-Tourism; Wellness Tourism; MICE Tourism; Rural Tourism; Beach Tourism; Cruises – Ocean and Inland.
- National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation And Spiritual Augmentation Drive Scheme (PRASAD)
-
- Initiated in 2014–15 by the Ministry of Tourism.
- For Restoration and spiritual enhancement of significant national and international tourist destinations and historical sites.
- Implementing agencies would be identified by the respective State/ Union Territory Government.
- ‘Dekho Apna Desh’ Campaign
-
- This initiative was launched by the Ministry of Tourism in 2020.
- It is an effort to motivate people to travel extensively within their own nation.
- NIDHI (National Integrated Database of Hospitality Industry)
-
- A portal maintained by the Ministry of Tourism is being used to register lodging units across the nation.
- SAATHI (System for Assessment, Awareness, and Training for Hospitality Industry)
-
- The objective of the scheme is to sensitize the industry to the Covid-19 regulations of the government.
- Incredible India 2.0
-
- The Incredible India 2.0 campaign is centered on products for niche markets, such as yoga, wellness, luxury, and wildlife cuisine.
- RCS-UDAN 3.0
-
- The program covered a number of routes in the Northeast Region in addition to seaplanes that connected water aerodromes.
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
Transforming India’s Telecom Sector: Policies, Projects, and Innovations
National Digital Communication Policy 2018
Objectives
- Broadband for all
- Creating four million additional jobs in the Digital Communications sector.
- Enhancing the contribution of the Digital Communications sector to 8% of India’s GDP from ~ 6% in 2017
- Propelling India to the Top 50 Nations in the ICT Development Index of ITU from 134 in 2017
Features
- Provide universal broadband connectivity at 50 Mbps to every citizen.
- Provide 1 Gbps connectivity to all Gram Panchayats by 2020 and 10 Gbps by 2022.
- Attract investments of USD 100 billion in the Digital Communications Sector
- Train one million manpower for building New Age Skill.
Telecom Technology Fund
- The goal of TTDF is to create partnerships between academia, start-ups, research institutions, and industry to foster innovation
- Under the scheme, Indian entities will receive grants to support and introduce indigenous technologies that are specifically designed to meet domestic needs.
BharatNet Project
- It is the largest optical fiber-based rural broadband connectivity program in the world and a flagship project carried out by Bharat Broadband Network Ltd. (Special purpose vehicle under the Companies Act, 1957)
- The Universal Service Obligation Fund is providing funding for the entire project (USOF).
- Viability Gap Funding: Union Cabinet has approved a Viability Gap Funding support for the implementation of the BharatNet project through the Public-Private Partnership model.
PM WANI (Wi-Fi Access Network Interface)
- This will enable the establishment of public Wi-Fi hotspots through public data offices (PDOs) across the nation.
- The PDOs won’t have to apply for a license or pay a fee.
Digital Financial Services
Initiatives taken to promote Digital Financial Services
- JAM (short for Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile) trinity refers to the government of India initiative to link Jan Dhan accounts, mobile numbers and Aadhaar cards of Indians to plug the leakages of government subsidies.
- Account Aggregator Framework
- Account Aggregator is a Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) providing the service of retrieving or collecting financial information concerning the customer. It also facilitates the transfer of data from one financial institution to another.
- Regulated by RBI; As of now, RBI has granted a Certificate of Registration to six companies as AAs
- Information retrieval, sharing and transfer is done with the consent of the customer.
- Registering with an AA is entirely voluntary for consumers.
- Entities can enroll themselves on the AA framework in two roles:
- Financial Information Provider (FIP): Entities like banking companies, non-banking financial companies, asset management companies, depositories, depository participants, insurance companies, insurance repositories, pension funds, etc.
- Financial Information User (FIU): Entities registered with and regulated by any financial sector regulator.
- National e-Governance Services Limited (NeSL: An Information Utility registered with and regulated by the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India.
Conclusion
- The service sector in India has emerged as a significant contributor to the economy, demonstrating robust growth and offering employment opportunities across various segments.
- It contributes significantly to GDP growth, employment generation, and foreign exchange earnings.
- Its continued expansion, fueled by advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences, reinforces its pivotal role in driving India’s economic development and global competitiveness.

