![]() April 29, 2024
April 29, 2024
![]() 7801
7801
![]() 0
0
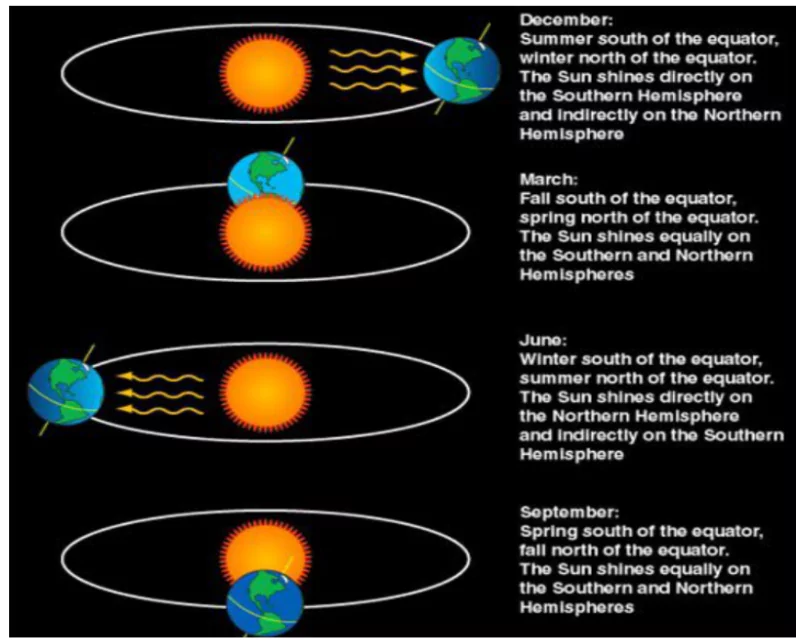
Solar insolation, the incoming solar radiation, varies globally due to factors like Earth’s rotation, distance from the sun, and atmospheric conditions. These factors influence the angle and intensity of sunlight, impacting temperatures and climate patterns across different latitudes and landforms. Understanding how sunlight is distributed across the Earth is important for understanding how weather works and how our environment functions.
| The red colour of the rising and setting sun and the blue colour of the sky are the result of scattering of light within the atmosphere. |
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
| Related Articles | |
| Solar Insolation: Heat Budget, Temperature Regulation & Distribution | ROTATION OF EARTH |
| Latitudes, Longitudes and Heat Zones | Speed of Sound: Pitch, Amplitude, & Wavelength |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments