Temperate cyclones, also known as extratropical cyclones, are big storms in the atmosphere that can cause various types of weather, like light rain, strong winds, thunderstorms, snowstorms, and tornadoes. These storms are common in the middle parts of the world and bring rain to many populated areas when different masses of air meet between 30° and 70° latitude and move eastward with the westerly winds. Predicting their weather mainly focuses on looking westward.
Mid-Latitude Cyclones Or Temperate Cyclones
Temperate Cyclones characteristics and understanding these differences is crucial for effective disaster preparedness, response, and mitigation efforts. Below are the characteristics of Temperate Cyclones:
Characteristics of Temperate Cyclone
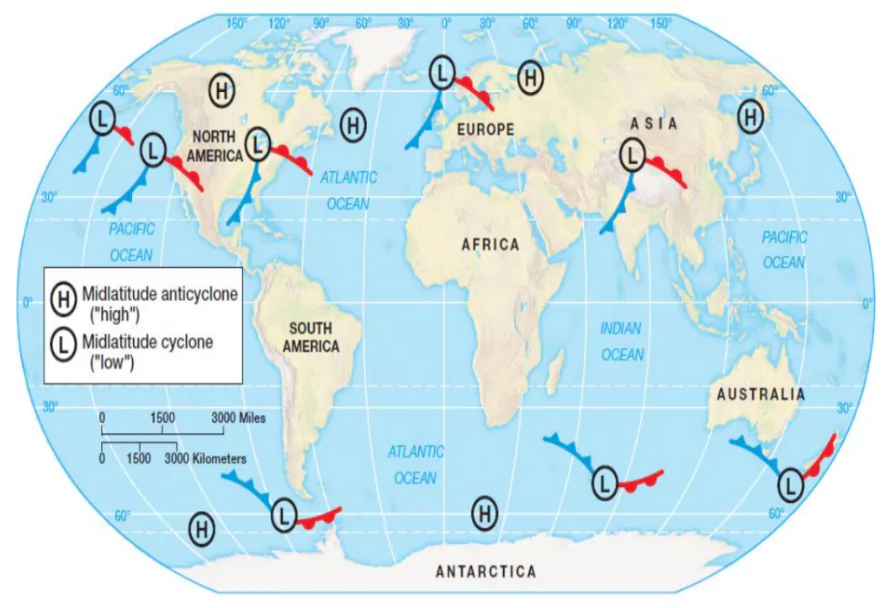
- Low-Pressure System: The low-pressure systems developing in the mid-and high latitudes, beyond the tropics are called the Temperate/ Extra-Tropical/ Mid-Latitude/ Frontal/ Wave Cyclones.
- Formation: Most commonly formed at the polar fronts, where warm and moist air masses meet cold and dry air masses from poles.
- Occur mostly in winter, late autumn and spring.
- Size: They stretch over large areas under the influence of westerlies.
- Indicators of Approaching Temperate Cyclones: The approach of a temperate cyclone is marked by a fall in temperature and pressure and a thin veil of cirrus clouds.
- Direction: These cyclones move from west to east under the influence of westerlies.
- Western Disturbances: The western disturbances arriving in North West India during winter are remnants of such cyclones.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Life Cycle of Temperate Cyclone
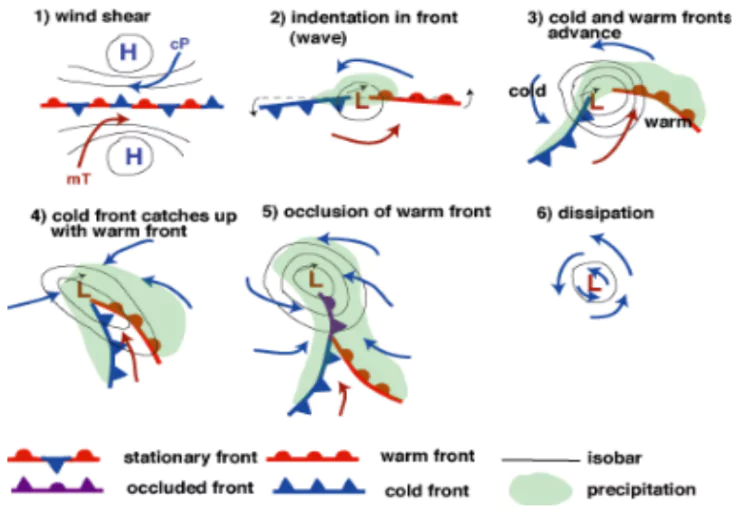
- Process of Formation: Temperate cyclones typically develop along the polar front, where cold polar easterlies meet warm westerlies.
- Pressure drop along the polar front initiates an anticlockwise cyclonic circulation.
- Warm air (from the south) moves northward, and cold air (from the north) moves southward.
- This circulation forms a well-developed extratropical cyclone with a warm and cold front.
- Waves along the Polar Front: Undulations called waves form in the upper-level jet stream, leading to disturbances along the polar front.
- Upper-Level Airflow Influence: The behaviour of upper-level airflow, particularly meandering north-to-south patterns known as Rossby waves, influences cyclone development.
 Ground-Level Disturbances: Various ground factors such as topography, temperature contrasts, and ocean currents can initiate cyclone formation.
Ground-Level Disturbances: Various ground factors such as topography, temperature contrasts, and ocean currents can initiate cyclone formation.- Mountain Cyclogenesis: Cyclogenesis can occur on the leeward side of mountains, where air compression and expansion trigger spin and cyclonic development.
- Maturity and Occlusion: Midlatitude cyclones progress through stages of origin, maturity, and occlusion.
- Occlusion occurs when the cold front overtakes the warm front, leading to the dissipation of the cyclone.
- Occlusion Process: As the cold front catches up with the warm front, warm air is lifted aloft, forming an occluded front. This process intensifies precipitation and wind before the cyclone dissipates.
- Dissipation: During the occlusion process, there’s a brief period of stronger rain and wind.
- As the warm air is pushed upward the low-pressure centre is surrounded by cool air, bringing stability.
- This weakens the storm’s energy and stops it from producing clouds, leading to the end of the storm.
Impact Of Mid-latitude Cyclones on India
- Positive Impacts of Temperate Cyclones
- Known as ‘western disturbances’ in India, temperate cyclones are responsible for significant winter and pre-monsoon rainfall across North-West India.
- Beneficial for standing rabi crops like wheat, providing moisture is crucial for their growth.
- The slow and prolonged rainfall associated with temperate cyclones can alleviate drought conditions by replenishing water sources over many days or even weeks.
- Negative Effects
-
- While they typically cause less damage from winds, temperate cyclones can result in extensive destruction due to unusual rains and flooding.
- These cyclones can lead to various cloud formations at different altitudes and contribute to dense fog over the Indo-Gangetic plains.
Conclusion
- Temperate cyclones, though vital for replenishing water sources and supporting crops, can also bring destructive rains and flooding.
- In India, they’re known as ‘western disturbances’ and play a crucial role in winter and pre-monsoon rainfall, benefiting agriculture but also causing challenges like fog and extreme weather events.
- Understanding their lifecycle and impacts is key for preparedness and mitigating their negative effects.

 Ground-Level Disturbances: Various ground factors such as topography, temperature contrasts, and ocean currents can initiate cyclone formation.
Ground-Level Disturbances: Various ground factors such as topography, temperature contrasts, and ocean currents can initiate cyclone formation.