![]() April 5, 2024
April 5, 2024
![]() 9496
9496
![]() 0
0
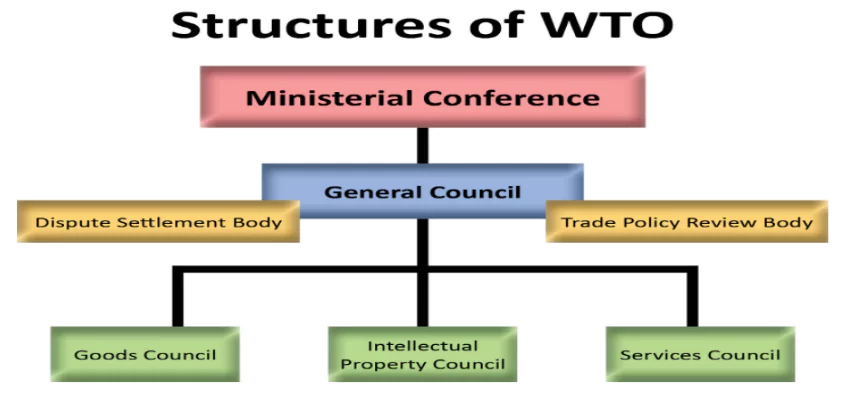
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is the sole global organization dedicated to establishing trade rules among nations. At its core are World Trade Organization (WTO) agreements, negotiated and adopted by the majority of the world’s trading nations, and ratified by their respective parliaments.
History Of World Trade Organization (WTO)
|
General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS):
Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS):
Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS Agreement):
Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade:
Agreement on Customs Valuation: Also known as the Agreement on Implementation of Article VII of GATT. Prescribes customs valuation methods for Members to follow.
G-33
|
Some Important Terms
|
| Aspect | Anti-Dumping Duty (ADD) | Countervailing Duty (CVD) |
| Purpose |
|
|
| Trigger |
|
|
| Nature of Practice |
|
|
| Focus |
|
|
| Determination |
|
|
UNCTAD, or the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development,
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
| Related Articles | |
| Indian Economy: Evolution | Basics of Money |
| Banks in India | Financial Market |
| Indian Insurance Sector | Financial Inclusion |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments