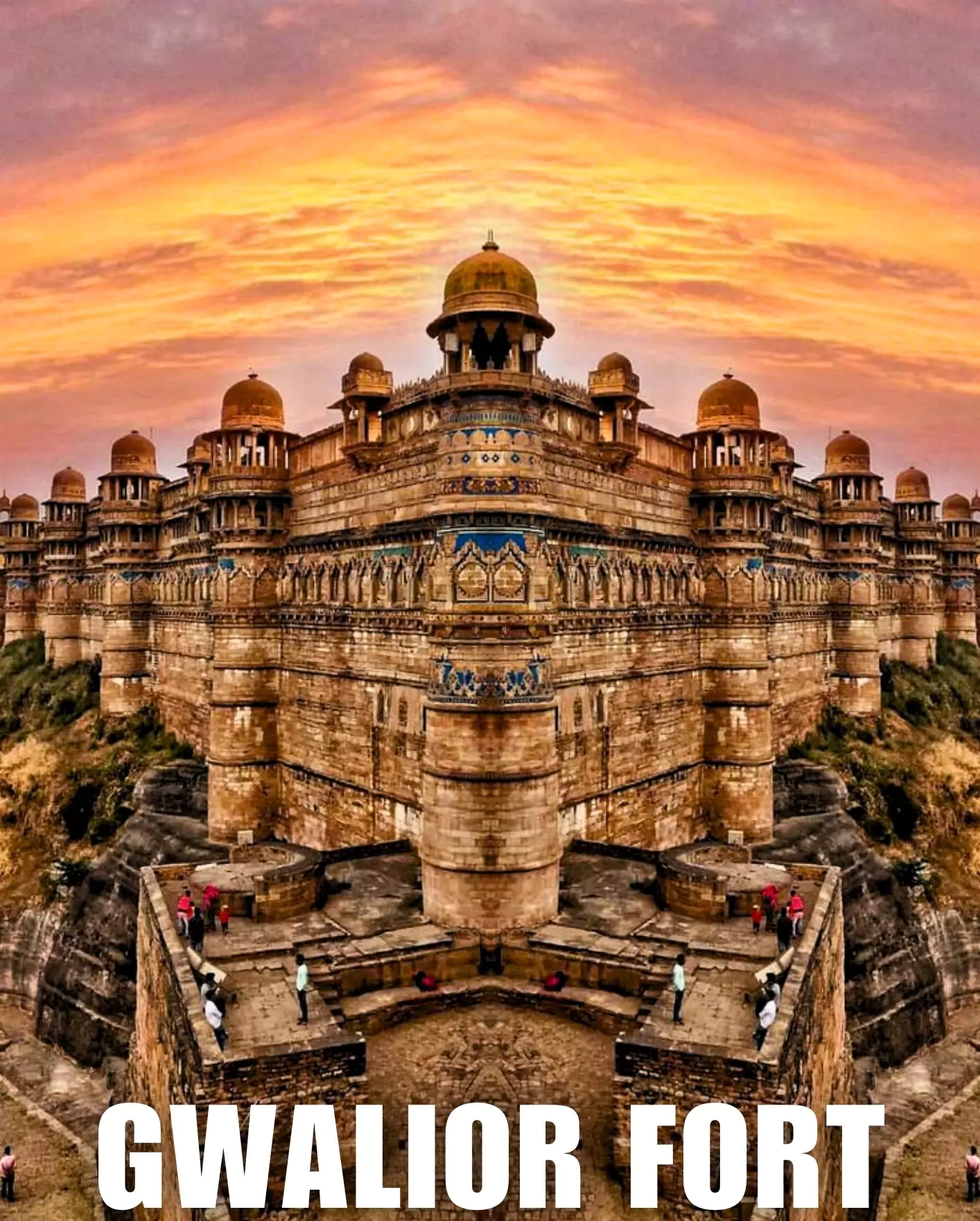
Gwalior Fort

|
- It is known as the ‘Gibraltar of India’.
- Location: A mountain named ‘Gopachal’ (Gop + Achal = Gop Parvat) Gwalior city, Madhya Pradesh.
- Built By: Suraj Sen of Tomar Dynasty from 525 CE
- Fort Architectural Style : The fort showcases a unique amalgam of Rajput, Mughal, and Hindu style of architecture.
- Famous Monuments & Artifacts located in Fort :
- Chaturbhuj temple: Zero (0) is carved on the wall of the temple (which is the second oldest known example of the writing of zero).
- Sas Bahu (Sahastrabahu) Temple: Dedicated to Lord Vishnu built by King Mahipal of the Kachhapaghat dynasty of Gwalior in 1092-93 CE
- Teli ka Mandir (Dravidian style architecture) : Built by the Pratihara King Mihira Bhoja.
- Gurudwara ‘Data Bandi Chhor’: where 6th Sikh Guru Hargobind Sahib was arrested and held captive by Mughal Emperor Jahangir.
- Siddhachal Jain Temple Caves were built in the 7th to 15th century. There are eleven Jain temples inside Gwalior fort dedicated to the Jain Tirthankaras.
- Famous Mahal & Palaces: Gujari Mahal, Man Mandir
- Impressive Ramparts and Gateways
|
The Historic Ensembles of Dhamnar

|
- Location : Dhamnar caves are situated near Dhamnar village of Mandsaur district, Madhya Pradesh.
- Built in: the 5th-7th century CE.
- Historical Accounts: Explored by James Tod in 1821, James Furgusson in 1845, and Alexander Cunningham in 1864-65.
- Expansion :
- Spread across 5.2 hectares, they comprise 51 caves ( 14 larger caves and 37 smaller caves) carved into a laterite hill.
- Two main groups exist: Series of Buddhist caves and the Hindu temple complex known as the Dharmrajeshwar temple.
- Cave Characteristics:
- Bari Kacheri (large courtyard) and Bhima Bazaar are outstanding caves.
- The Bari Kacheri cave is 20 feet square and consists of a stupa and chaitya.
- The verandah consists of a stone railing with wooden architraves.
- The caves vary in size and function, with dwellings, halls, stupas, and statues of Buddha.
- This place has huge statues of Gautam Buddha sitting and in Nirvana posture.
- Other Notable features include large doorways, window elements.
- Temple Complex: Located 170 feet north of cave number 12,include a large hall, pillars resembling wood, and a stupa in the rear.
- Outstanding Universal Value:
- Remarkable workmanship : Constructed between the 5th-7th century CE, the caves demonstrate remarkable workmanship.
- Symbolizing tolerance : They showcase elements of Buddhist and Hindu architecture, symbolizing tolerance.
- Comparable with other similar Sites: Ellora, Bhimbetka, Lalibela of Ethiopia, Rangiri Dambulla of Sri Lanka , and Yungang grottoes of China.
|
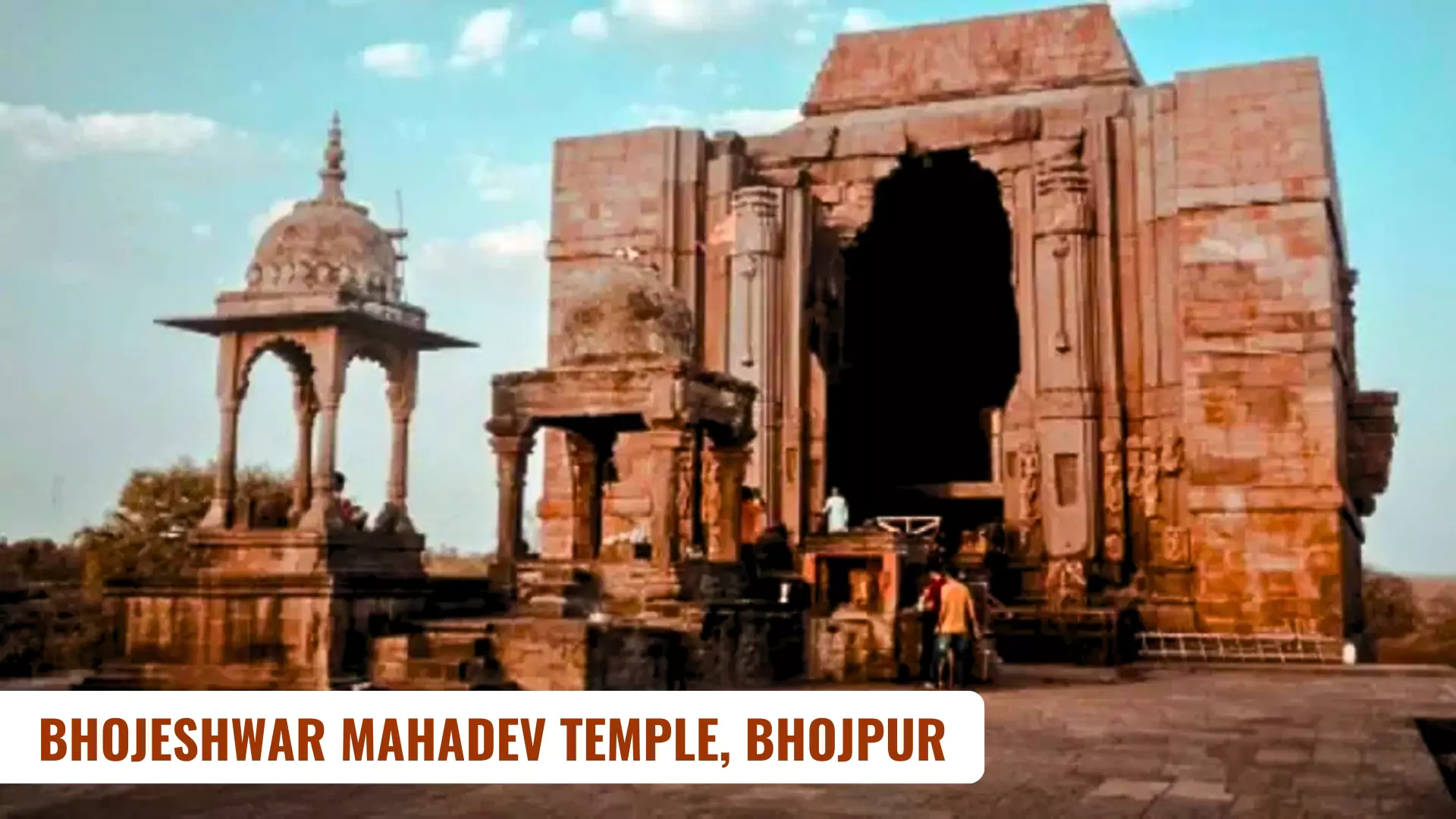
The Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple, Bhojpur
|
- It is known as Somnath of the East, named after the Paramara King Bhoj
- (Raja Bhoj was known for his architectural treatise, Samaranganasutradhara.
- Paramara Dynasty: Ruled the Malwa region and adjacent areas during the 9th -14th century. )
- Located: On the banks of Betwa River in Raisen District of Madhya Pradesh
- Built by: Raja Bhoj on a hill between : 1010-1053 AD.
- Temple dedicated to : Lord Shiva
- About Temple Architecture:
- Bhumija Style of Temple (influenced by Dravida style, they have towering shikharas and ornate carvings)
- Massive lingam : The most notable feature of the temple is its massive lingam, measuring approximately 2.3 meters in height and 5.4m in circumference that sits on a square pedestal approx. 8m high.
- Features :
- Exemplifies exceptional architectural creativity and grandeur, reflecting Paramara dynasty’s engineering prowess.
- Providing insights into socio-cultural and religious practices of ancient India.
- Comparison with Similar Properties:
- Resembles Brihadisvara temple of Thanjavur in scale and grandeur.
|
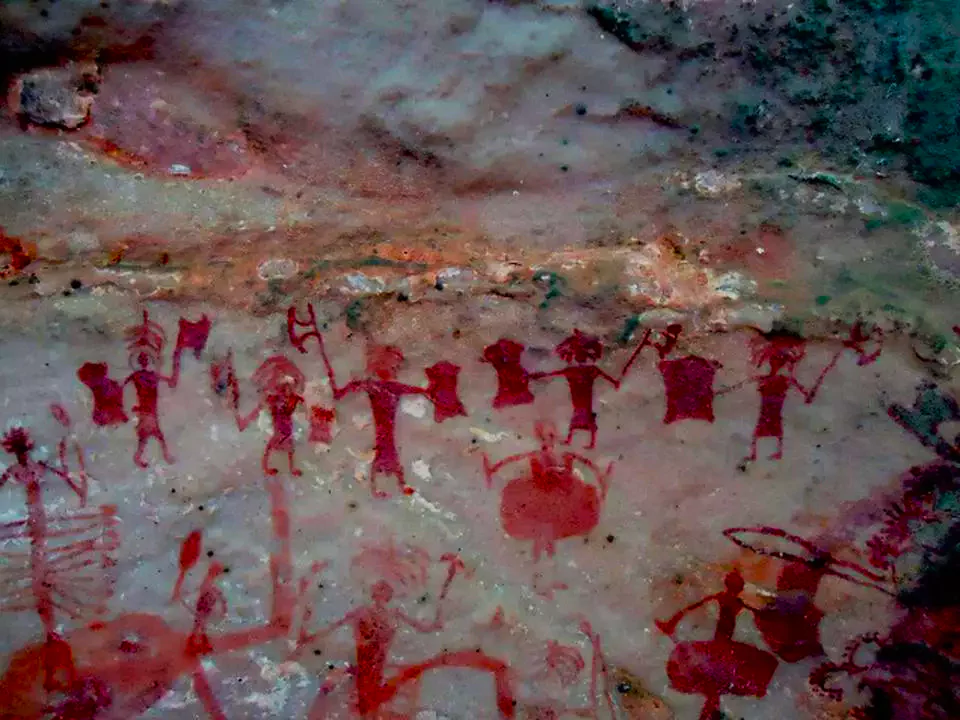
Rock Art Sites of the Chambal Valley (Serial Nomination)

|
- It is categorized on the basis of Serial Nomination by UNESCO that means it extends to boundaries of two or more states parties.
- Therefore, many rock art sites are expanded in 9 clusters of various districts of Madhya Pradesh & Rajasthan.
- Historical Background and Geographical Features:
-
- The Chambal River originates from the Malwa trap zone, with tributaries flowing from the Aravali and Vindhya hills.
- The Basin covers parts of Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, featuring diverse geology and geomorphological conditions.
- Archaeological Significance:
- The Basin has yielded evidence from the Middle Pleistocene period onwards. Rock art themes depict scenes from various historical periods, including the Mesolithic, Chalcolithic, and Early Historical periods.
- Features of Chambal Valley Rock Arts :
- Civilizational Testimony: The Chambal Valley region spans civilizations from the Palaeolithic to the Early Historical period.
- Evolution of Rock Art Themes: Rock art themes in the region evolve over time, reflecting shifts in societal structures, economic activities, and religious beliefs
- Continuity in Traditional Practices: Modern semi-nomadic pastoral communities continue traditional practices depicted in the rock art of the Basin.
- Threats to Rock Art Sites: Human-related activities, such as quarrying and deforestation, pose significant threats to the preservation of rock art sites in the Chambal Valley region.
- Comparison with Similar Properties:
- Similar UNESCO World Heritage Sites, such as Gobustan and Bhimbetka rock shelters, share criteria related to the archaeological significance of rock art.
- Other designated sites like Tadrart Acacus, Kondoa Rock-Art Sites, and the Ḥimā Cultural Area highlight diverse rock art traditions worldwide.
|
Khooni Bhandara, Burhanpur
|
- Underground water management system : One of its kind water supply system Khooni or Kundi Bhandara
- Situated in: Burhanpur, which was constructed 407 years ago and is still operational and useful for the local people.
- Built in: 1615 by Abdul Rahim Khankhana, the ruler of Burhanpur.
- Purpose and Construction: The system was constructed to address water scarcity faced by the growing settlement of Burhanpur due to its strategic importance during Mughal rule.
- Technological Innovation: Inspired by Persian qanat systems, the Khooni Bhandara utilized sophisticated engineering to capture groundwater from nearby Satpura hills and store it in underground conduits and reservoirs.
|
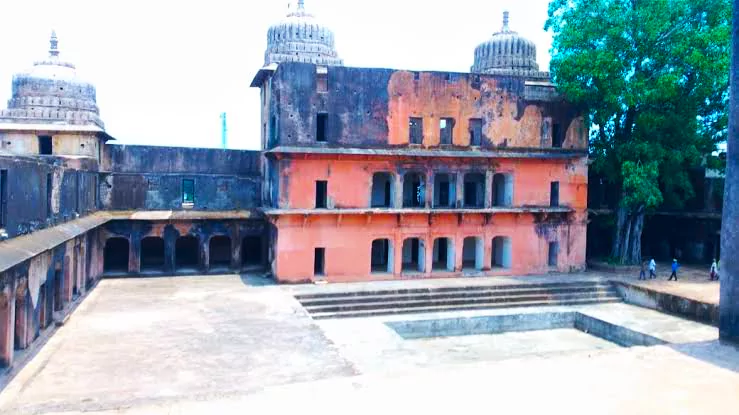
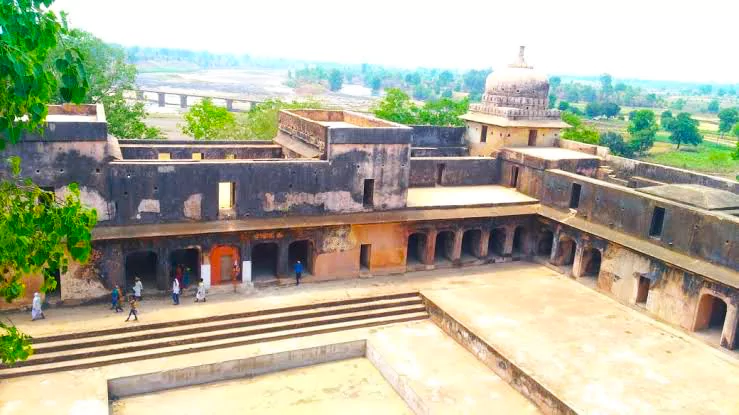
The Gond monuments of Ramnagar, Mandla


|
Historical Background:
- Gondwana, historically home to the Gond tribe, encompassed parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Maharashtra.
- Major kingdoms like Garha-Mandla, reigning from 1300 AD to 1789 AD, emerged within Gondwana, blending Gond culture with political governance.
- Gond Memorial, Mandla, Ramnagar Ramnagar in Mandla district used to be the stronghold of Gond kings.
Architectural Complexes:
- Notable monuments built by Gond ruler Hirday Shah: include Moti Mahal, Raibhagat ki Kothi, Vishnu Mandir, Begum Mahal, and Dalbadal Mahal.
- Moti Mahal: Built-In 1667 by Gond king Hriday Shah, situated on the Narmada river bank, showcases Mughal and Rajput architectural influences, with a central courtyard, arched colonnades, and elaborate drainage systems.
- The five-storeyed palace testifies to the willpower of the king despite limited resources and technology. Over time, two floors have been buried underground but three floors are still visible.
|
![]() 16 Mar 2024
16 Mar 2024