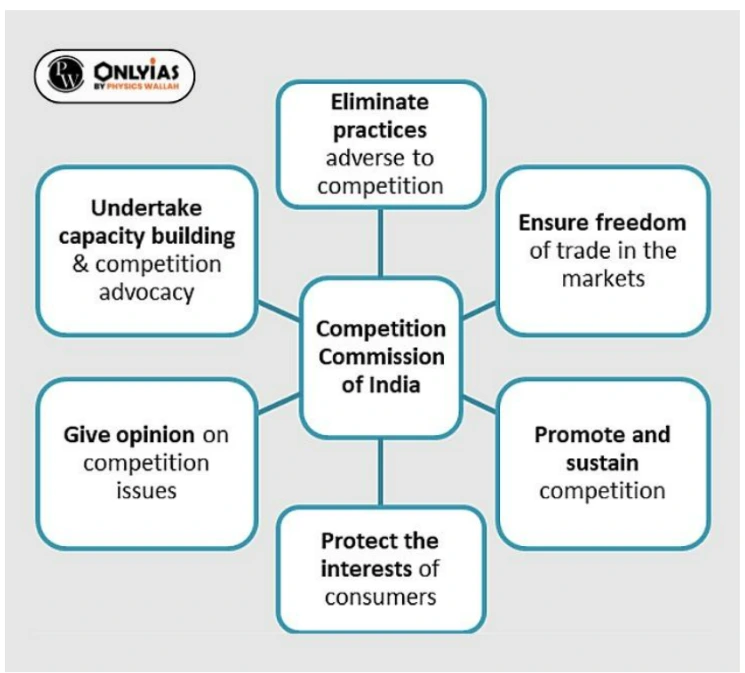
The Competition Commission of India (CCI) is a statutory body set up under the provisions of the Competition Act 2002. It works within the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.

Provision: The Competition Commission of India (CCI) is a statutory body set up under the provisions of the Competition Act 2002. It works within the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
Must Read: Patents Act Overrides The Competition Act
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Competition Commission of India (CCI) is a statutory body set up under the provisions of the Competition Act 2002. It works within the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
The CCI was set up to ensure competition by enforcing the Competition Act, of 2002. It seeks to prevent activities that have an appreciable adverse effect on competition in India.
Based on the Raghavan Committee report, the Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 (MRTP Act) was repealed and replaced by the Competition Act 2002.
The chairperson and members of the commission are appointed by the central government. The CCI consists of a chairperson and not less than two and not more than six other members.
The Competition Appellate Tribunal (COMPAT) is a statutory organization set up under the provisions of the Competition Act, 2002.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
