The National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) recently completed five years.
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
Non-Attainment Cities:
Difference Between PM2.5 and PM10:
|
|---|
News Source: DTE
The study, published in the journal Nature, highlights decline in Snow Cover is expected to accelerate with further warming.
What is Snow Water Equivalent (SWE)?
|
|---|
News Source: Down to Earth
Recently, an Indian delegation visited Mauna Kea, situated in Hawaii, USA to address the challenges faced by the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) project.

Is Mauna Kea the highest mountain in the world?
|
|---|
India’s Role and Contribution:
|
|---|
News source: The Hindu
Indian Army develops end-to-end encrypted mobile ecosystem SAMBHAV (Secure Army Mobile Bharat Version).
News Source: Business Standard
The Himalayan Wolf has been assessed for the first time in the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s Red List.

News Source: Down to Earth
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
The 14th ministerial-level meeting of the India US Trade Policy Trade Policy Forum (TPF) was held in New Delhi.
India US Trade policy and Economic Relations:
|
|---|
Trade Margin Rationalization (TMR): It is a mode of price regulation by way of capping trade margins in the supply chain.
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
According to a new study published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, the amount of heat stored in the upper 2,000 meters of the global ocean reached 286 Zetajoules (ZJ) in 2023 relative to the 1981–2010 average.
| Year | Ocean heat content trend |
| 1958-1985 | 3.1 ± 0.5 ZJ per year |
| 1986 -2007 | 9.2 ± 0.5 ZJ annually. |
| 2007-2023 | 10.8 ± 1.2 ZJ per year |
Zeta Joules
|
|---|
Ocean stratification: A Dive into the Layers of Global Waters
|
|---|
News Source: Down to Earth
Recently, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) conducted a successful flight test of the New Generation Akash Missile (AKASH-NG) from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur off the coast of Odisha.

News Source: The Hindu
Recently, the World Economic Forum (WEF) has released the 19th Edition of Global Risks Report 2024, titled as “From Life to Lab: Science in Action”.
Global Risk: Definition & Feature
World Economic Forum: Shaping the Global Agenda for Positive Change
|
|---|
News Source: World Economic Forum
The Indian government plans to launch an HPV immunisation campaign to curb cervical cancer cases in the second quarter of the year.
| A quadrivalent vaccine is a vaccine that works by stimulating an immune response against four different antigens, such as four different viruses or other microorganisms. |
|---|
About Human Papillomavirus:
|
|---|
Transformative Healthcare: Success and Impact of India’s Universal Immunization Programme (UIP)
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
Recently, the Prime Minister visited the Kalaram Mandir of Nashik, Maharshtra.

News Source: The Indian Express
The World Health Organization (WHO) has certified Cabo Verde as a malaria-free country, becoming the third country to acquire the status in the African region.
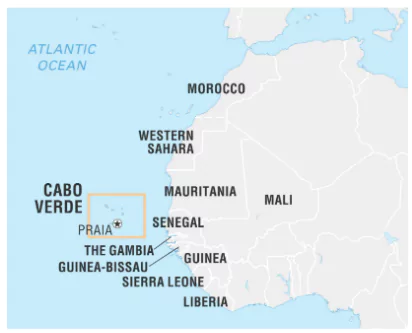
Additional Information: World Malaria Report 2023: By WHO
News Source: DTE
This editorial is based on the news “Green Hydrogen: Enabling Measures Roadmap for Adoption in India” which was published in WEF. The Report, Green Hydrogen: Enabling Measures Roadmap for Adoption in India has been released by the World Economic Forum.
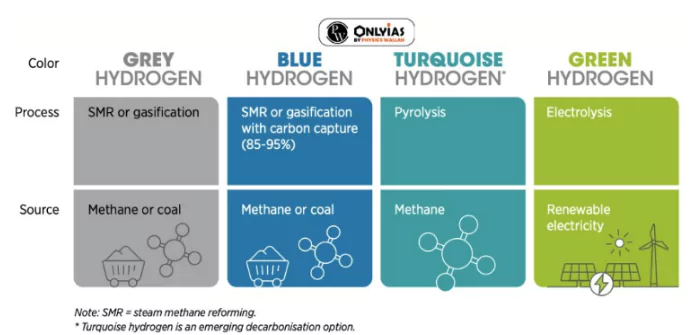
Advantages of using hydrogen as a fuel:
|
|---|
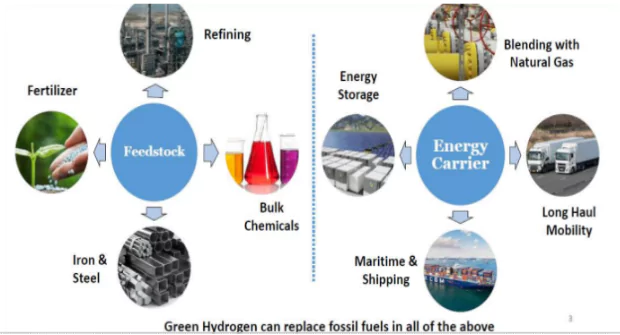 Green hydrogen can abate at least 50 MMTPA of greenhouse gases by 2030.
Green hydrogen can abate at least 50 MMTPA of greenhouse gases by 2030.
Initiatives for Green Hydrogen Production In India: Policies and Alliances Shaping the Future
|
|---|
This editorial is based on the news “Iran-backed Houthis warn of ‘serious consequences’ after US, UK strikes hit Yemen” which was published in Indian Express. The United States-backed coalition including the United Kingdom launched airstrikes in Yemen, targeting Houthi rebels.
Operation Prosperity Guardian: Multinational Response to Houthi Threats Lead the Red Sea Crisis
|
|---|
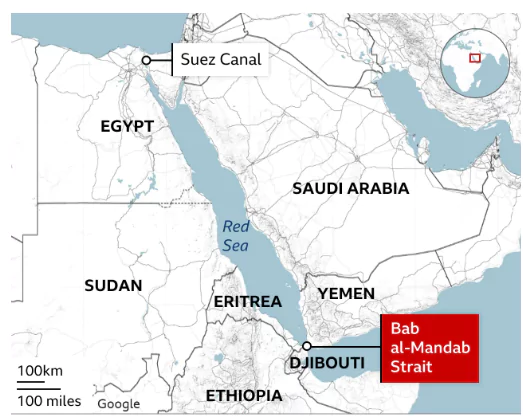
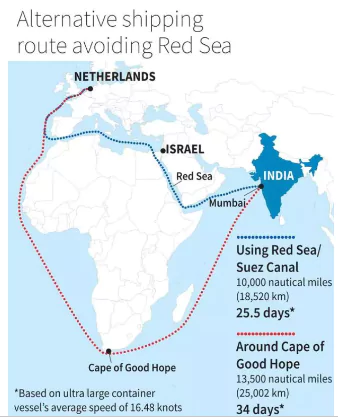 For instance, the ship Galaxy Leader and its crew were seized by the Houthis.
For instance, the ship Galaxy Leader and its crew were seized by the Houthis.
Maharashtra Withdraws GRs on Hindi as Third Langua...
Statistical Report on Value of Output from Agricul...
Skills for the Future: Transforming India’s Work...
National Turmeric Board HQ Inaugurated in Nizamaba...
ECI Moves to De-List 345 Inactive Registered Unrec...
MNRE Issues Revised Biomass Guidelines Under Natio...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>