The South Pacific nation of Nauru recently announced its decision to switch its diplomatic ties from Taiwan to China.
Nauru Country Location
News Source: NDTV
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
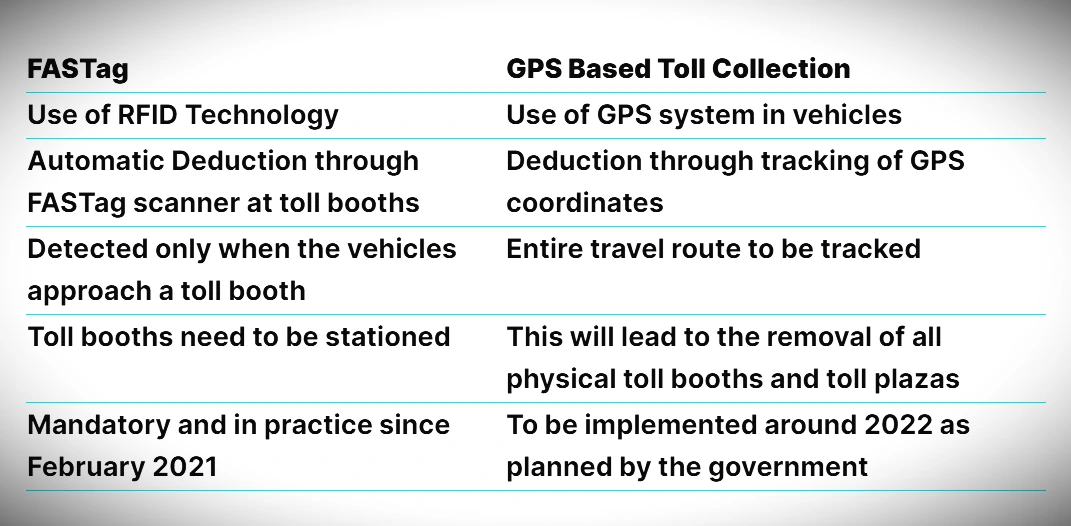
The National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) has undertaken the ‘One Vehicle One FASTag initiative to discourage using single FASTag for multiple vehicles.
About FASTag:
|
|---|
Also Refer: India’s First National Highway Steel Slag Road Section on NH 66
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) will be putting in place GPS based toll collection on various routes across India with an aim to cut toll booth congestion.
Also Refer: NHAI’s One Vehicle One FASTag Initiative
News Source: Times of India
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Thiruvalluvar Day was celebrated on January 16.

About Sangam Literature
Continue To Read: Sangam Age – Political History Of South India |
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
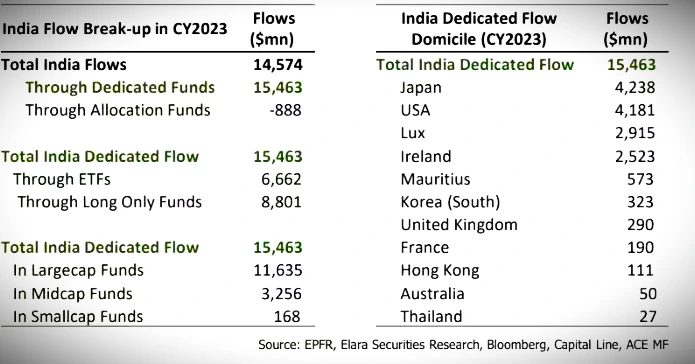
India becomes the 2nd largest destination for foreign capital of around $15 billion. The Report is being released by Elara Capital.
Also Read: India Tops Global Remittance Flows At $125 Billion In 2023
News Source: Business Standard
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
The Indian Army is launching Operation Sarvashakti to counter terrorist activities in Jammu and Kashmir.
Also Refer: Why Terrorist Activity Shifted From Kashmir to Poonch-Rajouri
Source: LiveMint
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has started revising the National Essential Diagnostics List (NEDL).
Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS) 2022
|
|---|
Also Refer: New Class Of Antibiotic Against A Drug-Resistant Bacterium
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
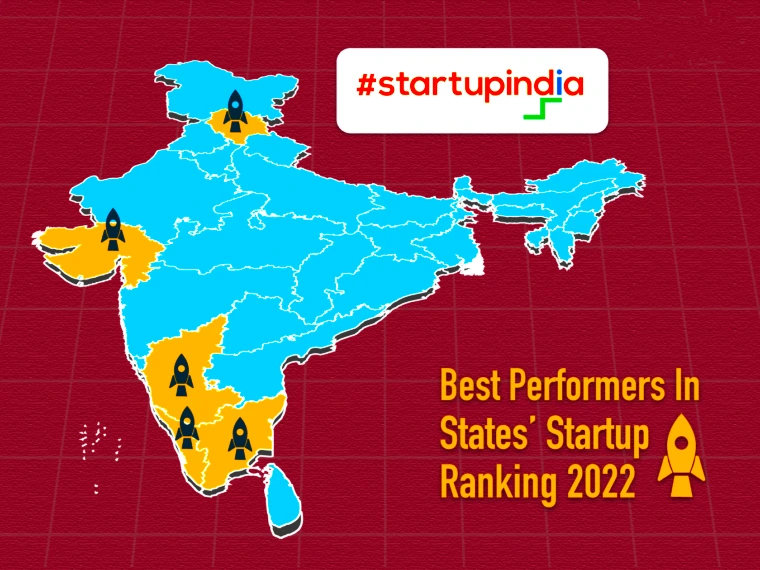
National Startup Awards 2022: Gujarat, Kerala and Karnataka have emerged as the best-performing states in developing startup ecosystems, as per the States’ Startup Ranking 2022.
Startup India Initiative:
|
|---|
Also Refer: Startup Ecosystem In India
News Source: Live Mint
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
A joint study by the Indian Institute of Technology (Kharagpur) has discovered evidence of cultural continuity in Vadnagar indicating the likelihood of the concept of a “Dark Age” being a myth.
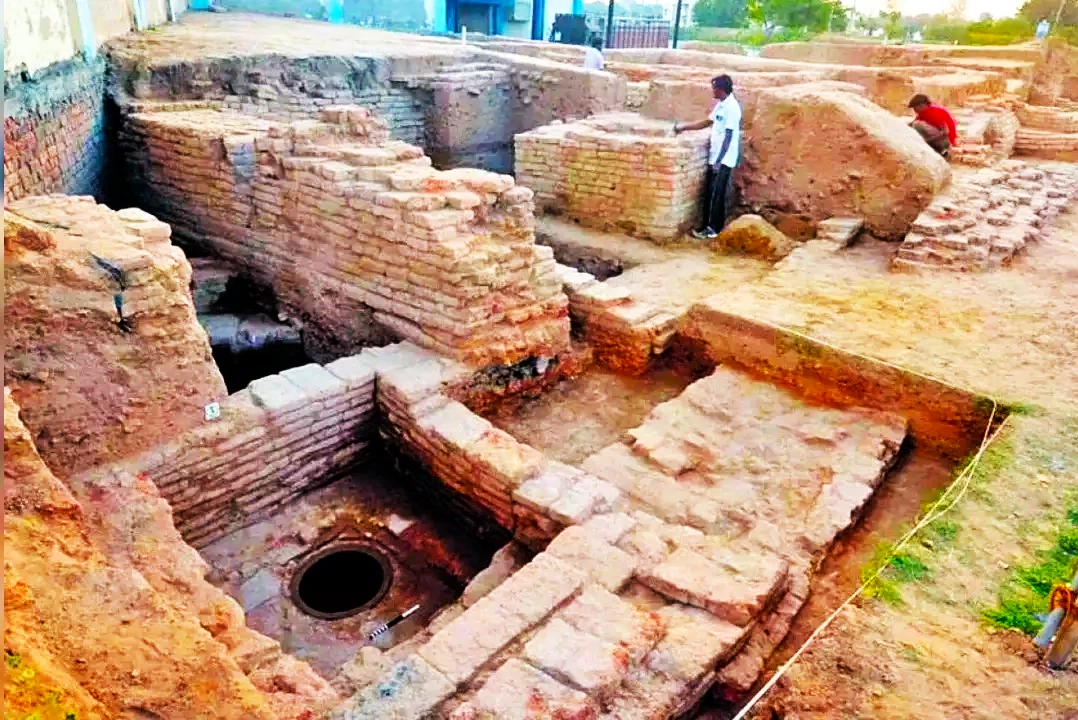

| Dark Age: The period between the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilisation and the emergence of the Iron Age and cities like Gandhar, Koshal, and Avanti is often depicted as a Dark Age by archaeologists. |
|---|
About Vadnagar
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
The Delhi High Court in a recent judgment specified that the right to reside in India under Article 19(1)(e) of the Constitution of India cannot be claimed by foreigners.
|
Fundamental Rights of Foreigners |
|
| Article 14: | Legal equality and equal protection under the law. |
| Article 20: | Protection in respect of conviction for offenses. |
| Article 21: | Protection of life and liberty. |
| Article 21(A): | Right to primary education. |
| Article 22: | Protection against arrest and imprisonment in certain circumstances. |
| Article 23: | Prohibition of human trafficking and forced labor. |
| Article 24: | Prohibition of child labor in factories. |
| Article 25: | Freedom of conscience and free profession, practice, and propagation of religion |
| Article 26 | Freedom to manage religious affairs. |
| Article 27: | Freedom from payment of taxes for promotion of any religion. |
| Article 28: | Freedom from religious instruction or worship in certain educational
institutions |
Also Refer: Fundamental Rights(Article 12-35) Of Indian Constitution
About Writ Petitions:
|
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has issued notices to the governments of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala following a report by the Indian Institute of Science (IISC) over a reduction of green cover in the Cauvery basin.
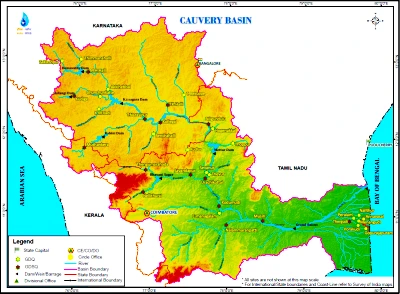
Cauvery Basin Map
About Biodiversity HotspotsTo qualify as biodiversity hotspot, an area must meet two strict criteria:
Biodiversity Hotspots in India
|
|---|
About National Green Tribunal (NGT):
Benches of National Green Tribunal (NGT):
|
|---|
Also Refer: Protected Areas, Biosphere Reserve, National Park
News Source: DTE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Recently, the maiden bilateral maritime exercise named “Ayutthaya” was conducted between the Indian Navy (IN) and Royal Thai Navy (RTN).
 SAGAR and Engagement in IOR: As part of India’s vision of SAGAR (Security And Growth for All in the Region), the Indian Navy has been proactively engaging with countries in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) towards enhancing regional maritime security.
SAGAR and Engagement in IOR: As part of India’s vision of SAGAR (Security And Growth for All in the Region), the Indian Navy has been proactively engaging with countries in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) towards enhancing regional maritime security. 
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) to succeed the incandescent bulbs and fluorescent lamps of previous centuries as the world’s light source of choice.
Also Refer: Nobel Prize Winners 2023 List, Name And Fields
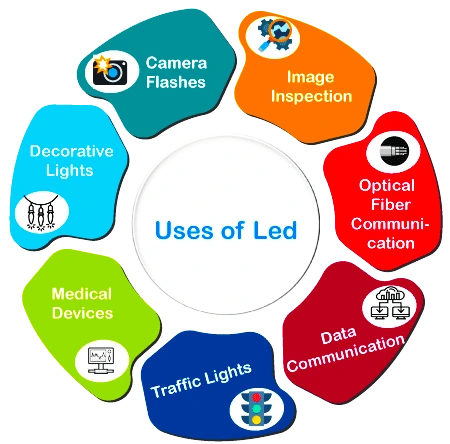
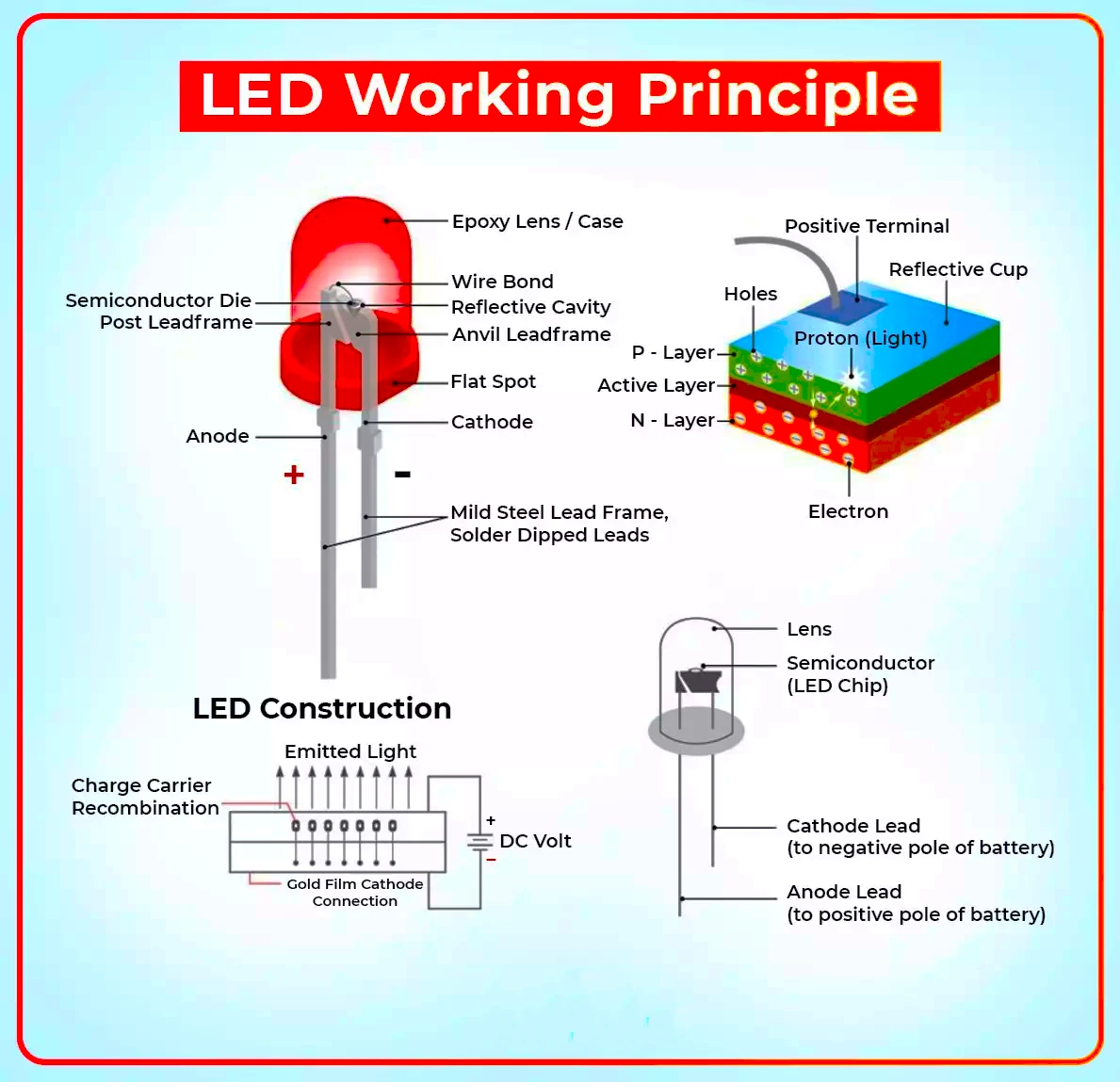
About Compact Fluorescent Lighting (CFL)
About Incandescent bulbs
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |