The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) regained contact with its Mars helicopter Ingenuity on January 21.
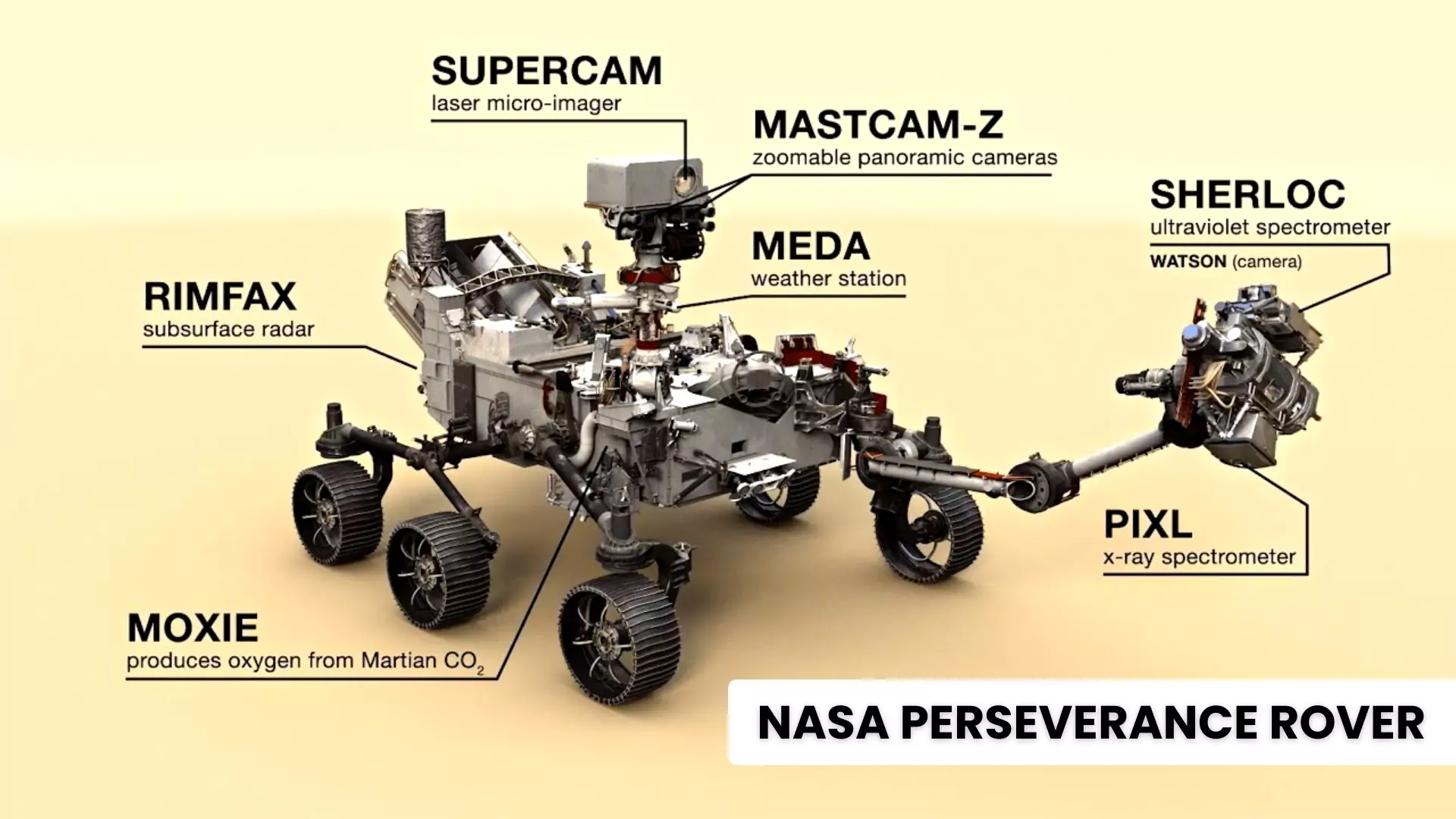
NASA Perseverance Rover
Mars Missions |
Space Agency (Country) |
|
USSR |
|
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (USA) |
|
European Space Agency (ESA) |
|
Indian Space Research Organization (India) |
|
Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre (UAE) |
|
China National Space Administration (China) |
About Mars
Red Planet Mars and Its Moons |
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
StartupShala has been introduced by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
Additional Reading: Startup Ecosystem in India
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Neuralink has successfully implanted a brain chip in its first human patient.
About Neuralink
|
|---|
News Source: Business standard
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
An anti-piracy operation off the East Coast of Somalia was conducted by INS Sumitra recently.
INS Sumitra
|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
First India-Saudi Arabia Joint Military Exercise ‘SADA TANSEEQ‘ officially began from January 29th to February 10th, 2024 in Rajasthan.
Other Joint Exercises Between India and Saudi Arabia
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
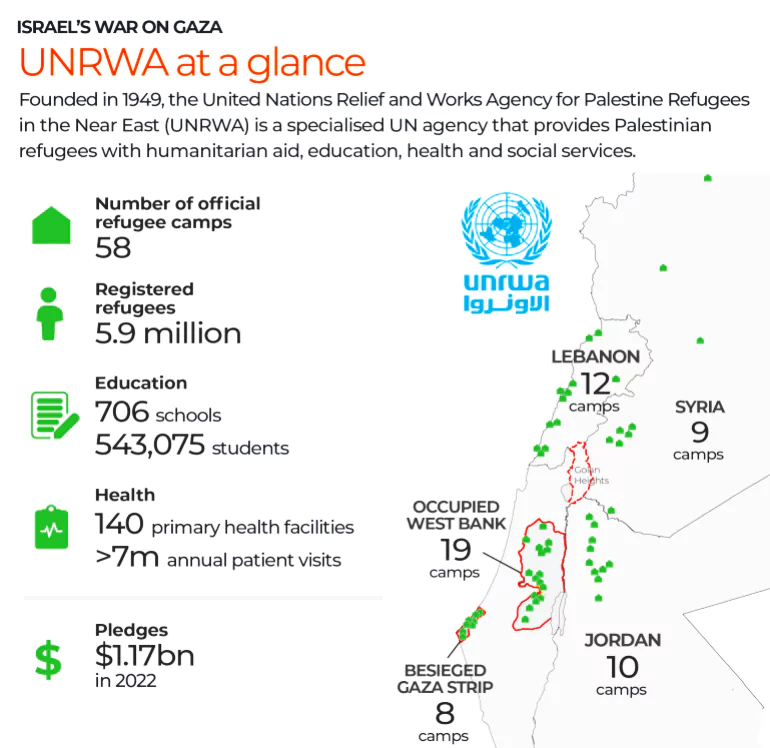
Several donor countries have recently announced a halt to their funding to the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA).
News Source: Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
India has put “Maratha Military Landscapes of India” as its nominee for inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage List for 2024-25.
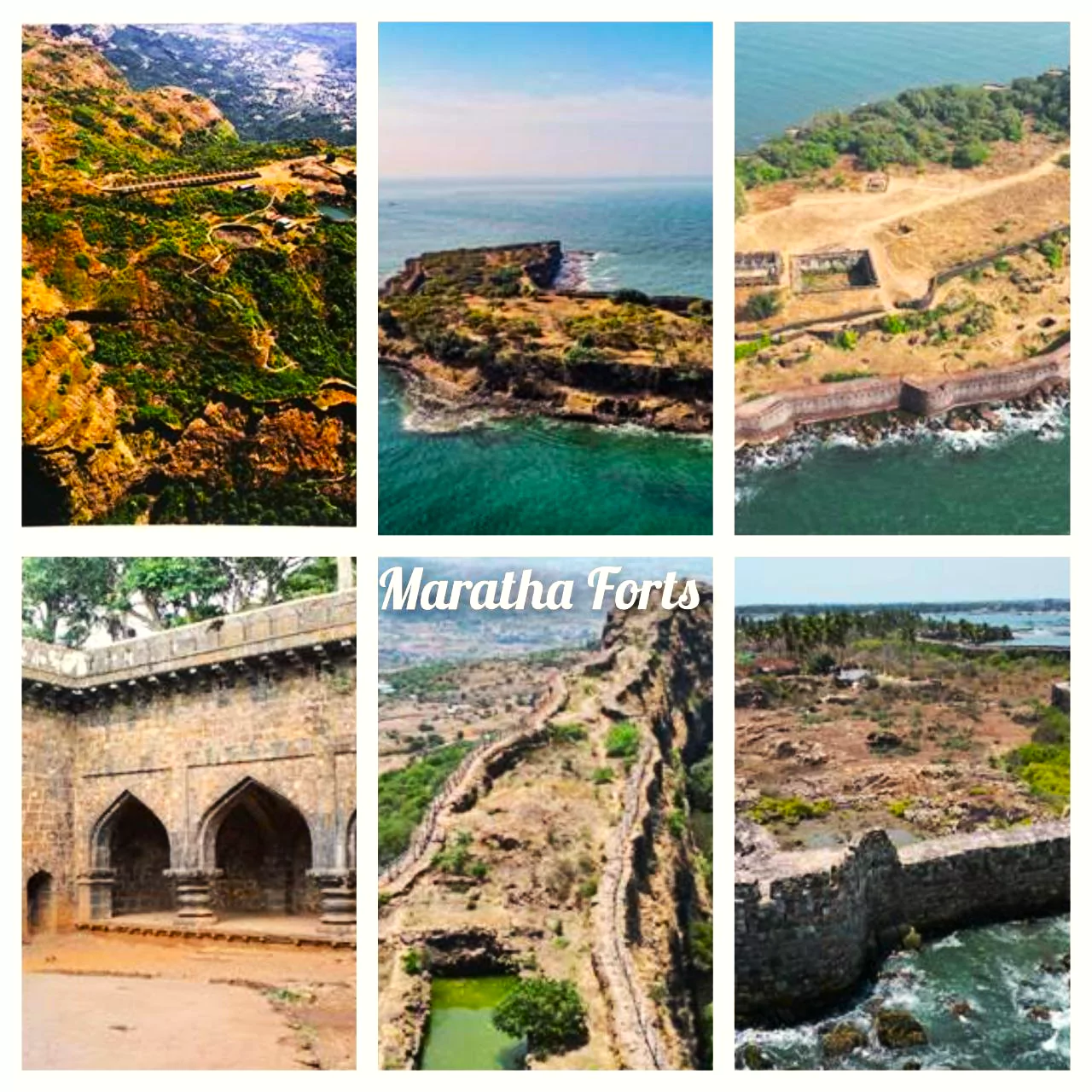

Criteria under World Heritage List Nomination by UNESCO: The nomination process for the World Heritage List involves two categories: Cultural and Natural criteria.
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Department of Fertilizers (DoF) issued detailed guidelines for evaluating the “reasonableness” of the MRPs for all non-urea fertilizers covered under NBS.
Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme:
|
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A MoU was signed between Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti to implement the Modified Parbati Kalisindh Chambal ERCP Link Project.
Modified PKC ERCP Link Project
|
|---|
Chambal River
|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “What is Humboldt’s enigma and what does it mean for India?” which was published in the Hindu. Explorers and naturalists have been curious about the biodiversity of different regions.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Biodiversity, Earth’s Latitude, Physiography Of India, and Climate Change In India.
Relevancy for Mains: Humboldt’s Enigma and Its Meaning For India. |
|---|
Biodiversity Richness
|
|---|
Humboldt’s enigma is perhaps one of many puzzles of mountain biodiversity, offering opportunities for study and insights into global climate and landscape change issues. To gain more, the national programmes need to be strengthened, bolstered by the will to support basic research on diversity.
| Mains Question: How does biodiversity vary in India? How is the Biological Diversity Act,2002 helpful in conservation of flora and fauna? [250 Words, 15 Marks] |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Launch of Framework for Voluntary Carbon Market in Agriculture Sector and Accreditation Protocol of Agroforestry Nurseries” which was published in the PIB. The Union Minister of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare and Tribal Affairs launched the Framework for Voluntary Carbon Market in Agriculture Sector and Accreditation Protocol of Agroforestry Nurseries.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Agriculture In India, Climate Smart Agriculture, Green Credit Program (GCP), COP28 Climate Summit, and Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs).
Relevancy for Mains: Voluntary Carbon Market in Agriculture Sector: Need, Significance, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Agroforestry
National Agroforestry Policy
|
|---|
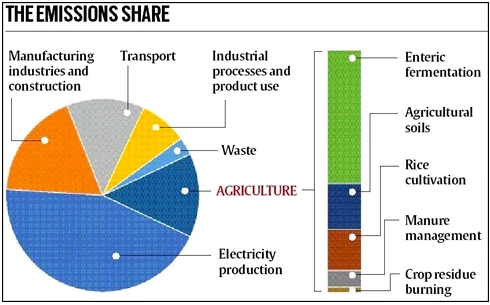
Status of Voluntary Carbon Market
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>