Amid a downturn in the software-as-a-service (SaaS) market, marked by declining sales and delayed purchases, innovation-led differentiation has emerged as a key challenge for most SaaS firms.

| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has decided to delist 18 centrally protected Monuments because it has assessed that they do not have national importance.
Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) working group for Planetary System Nomenclature recently approved the name ‘Statio Shiv Shakti’ for the landing site of Chandrayaan-3‘s Vikram lander.
Previous Names of Crash Sites
|
|---|
Location:

Nomenclature Criteria by IAU
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently a political party filed a complaint with the Election Commission of India (ECI) against a prominent opposition leader for hurting Hindu sentiments with his remark on ‘shakti’.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
India’s External Affairs Minister recently had an important meeting with the Foreign Minister of Singapore, Vivian Balakrishnan, to discuss trade issues.
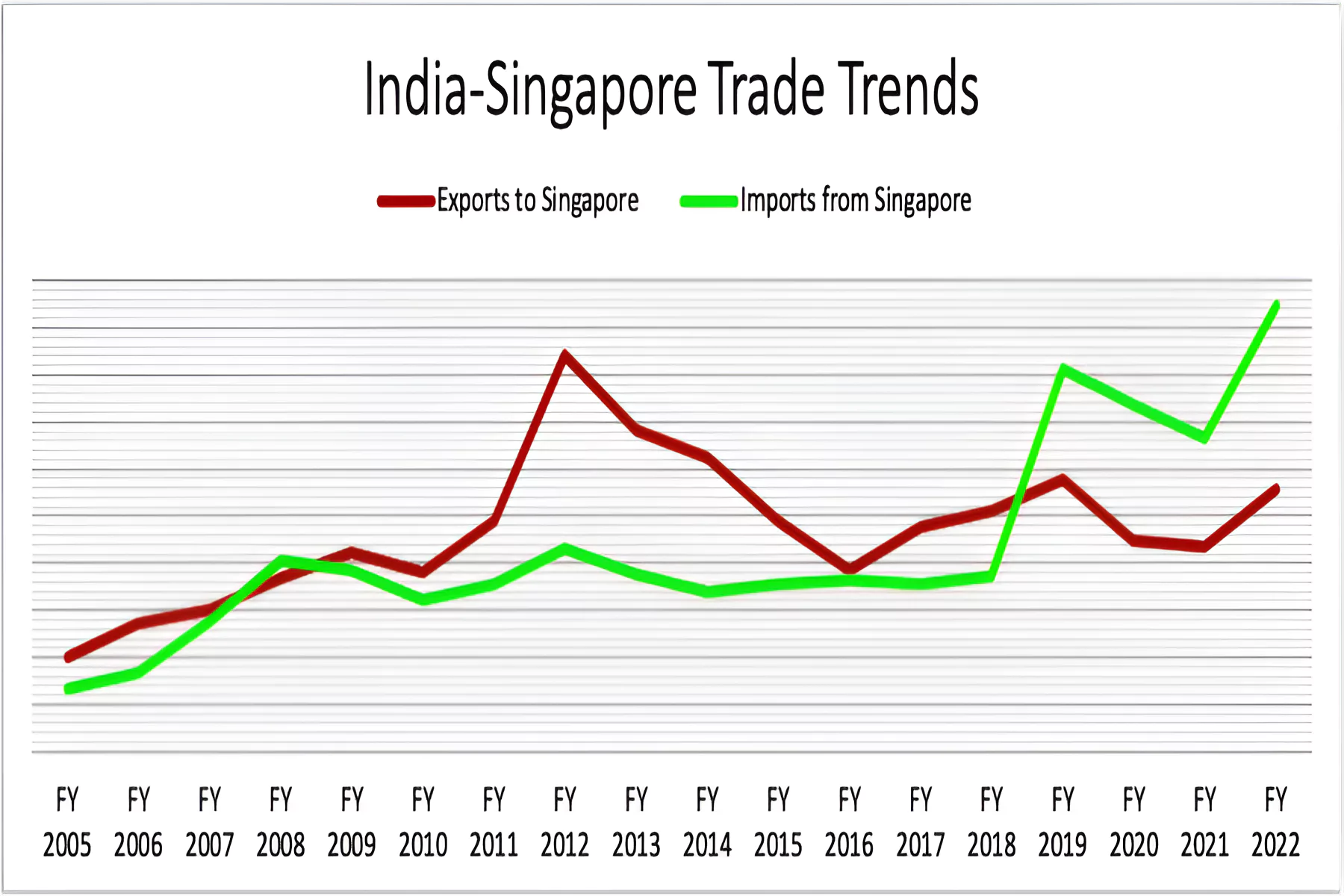
| Positives | Negatives |
|
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Kerala government has moved the Supreme Court against the President for withholding assent to bills passed by the state legislature without disclosing any reasons.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
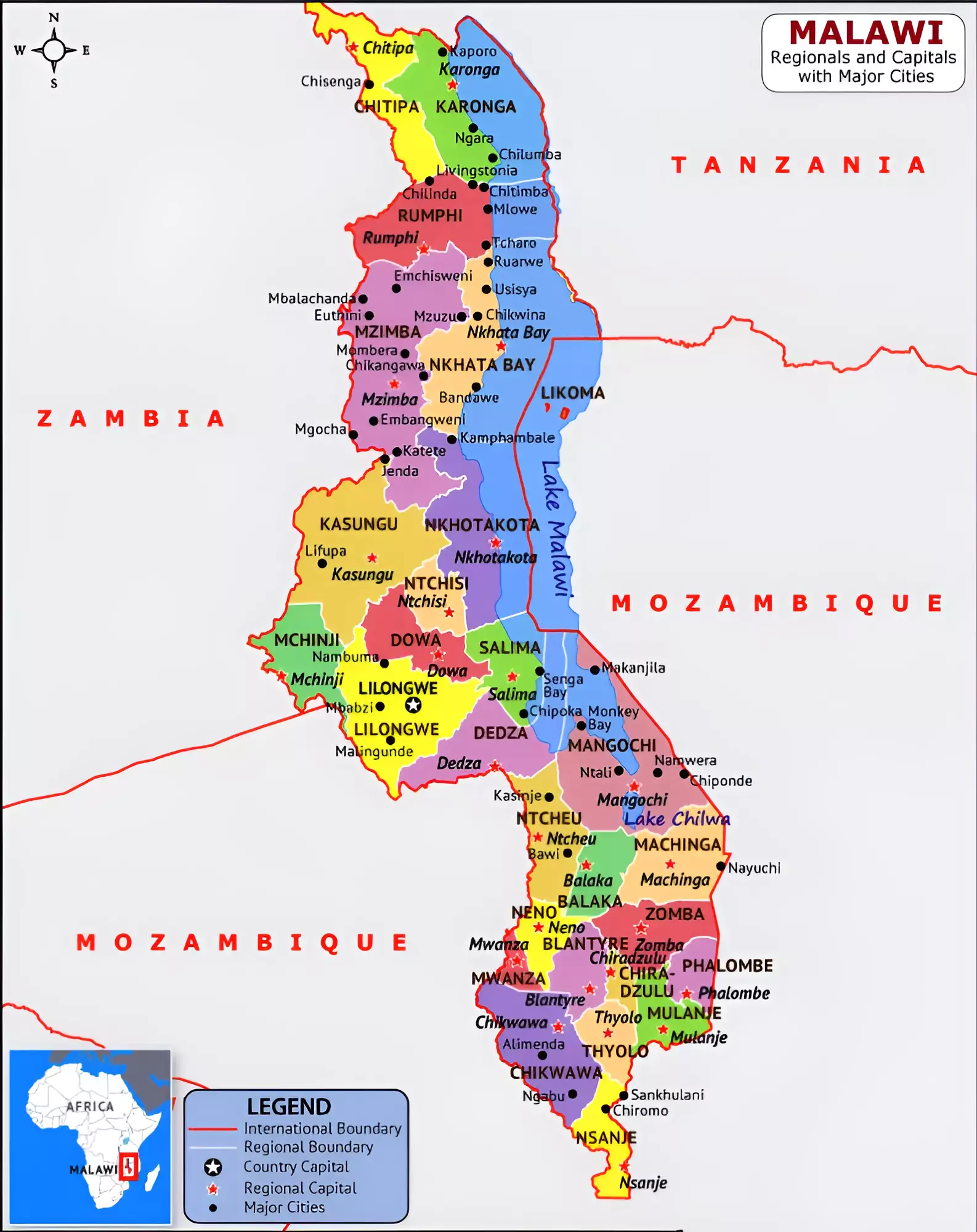
Malawi has declared a state of disaster in 23 out of its 28 districts due to severe drought.
 Highest peak: Sapitwa.
Highest peak: Sapitwa.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Central Government has approved a simple reversionary bonus for the Postal Life Insurance Scheme and Rural Postal Life Insurance Scheme for fiscal year 2024-25 without changing the rate.
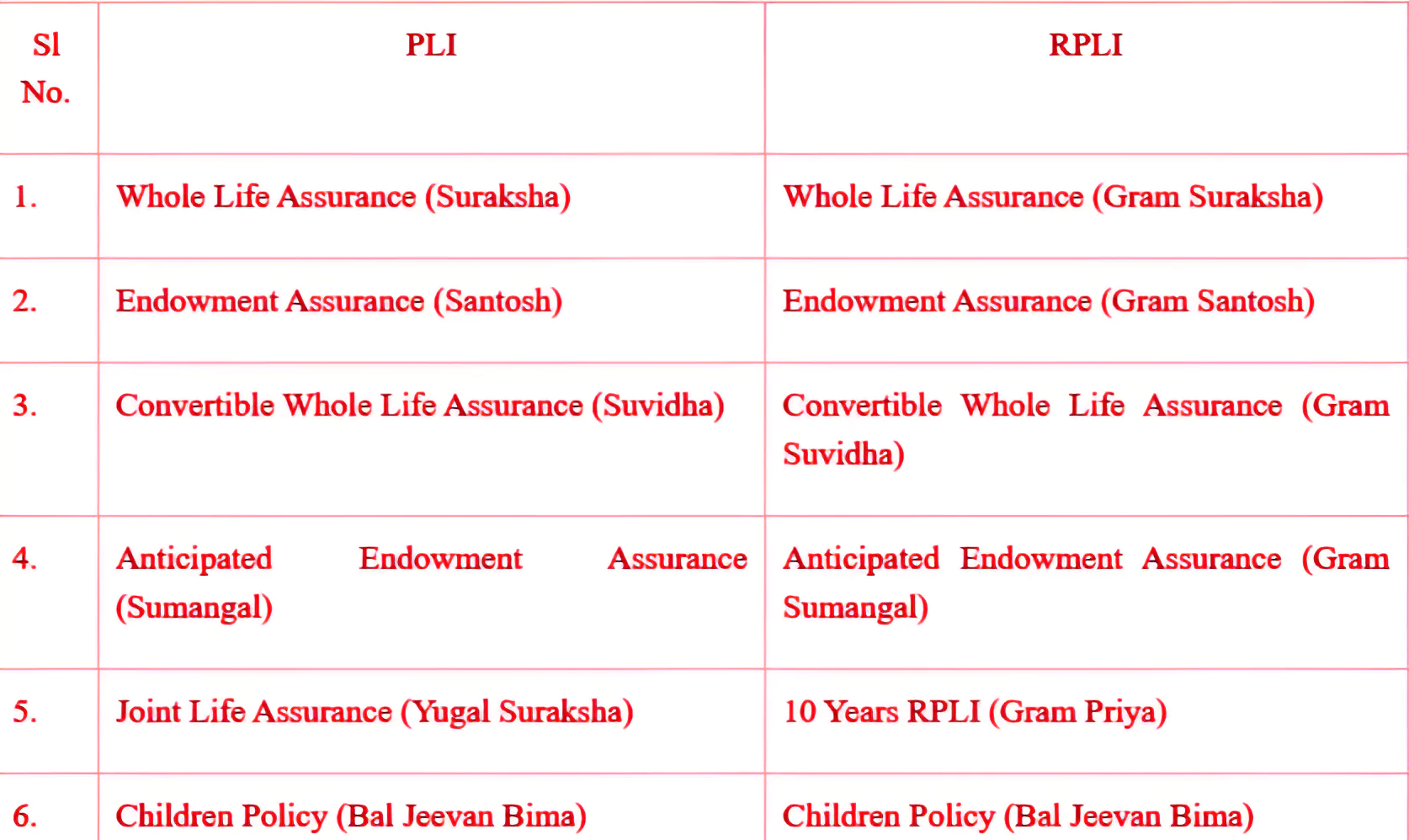 However, a period of consecutive 5 years should not have passed from the date of first unpaid premium.
However, a period of consecutive 5 years should not have passed from the date of first unpaid premium.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
World TB Day is celebrated annually on 24 March to raise awareness about the tuberculosis disease.
| Relevancy for Prelims: World TB Day 2024, India Has Set The Target To Eliminate TB By 2025, and Global TB Report 2023 By World Health Organization (WHO).
Relevancy for Mains: Tuberculosis (TB) Control in India, and Role Of Government In Health. |
|---|
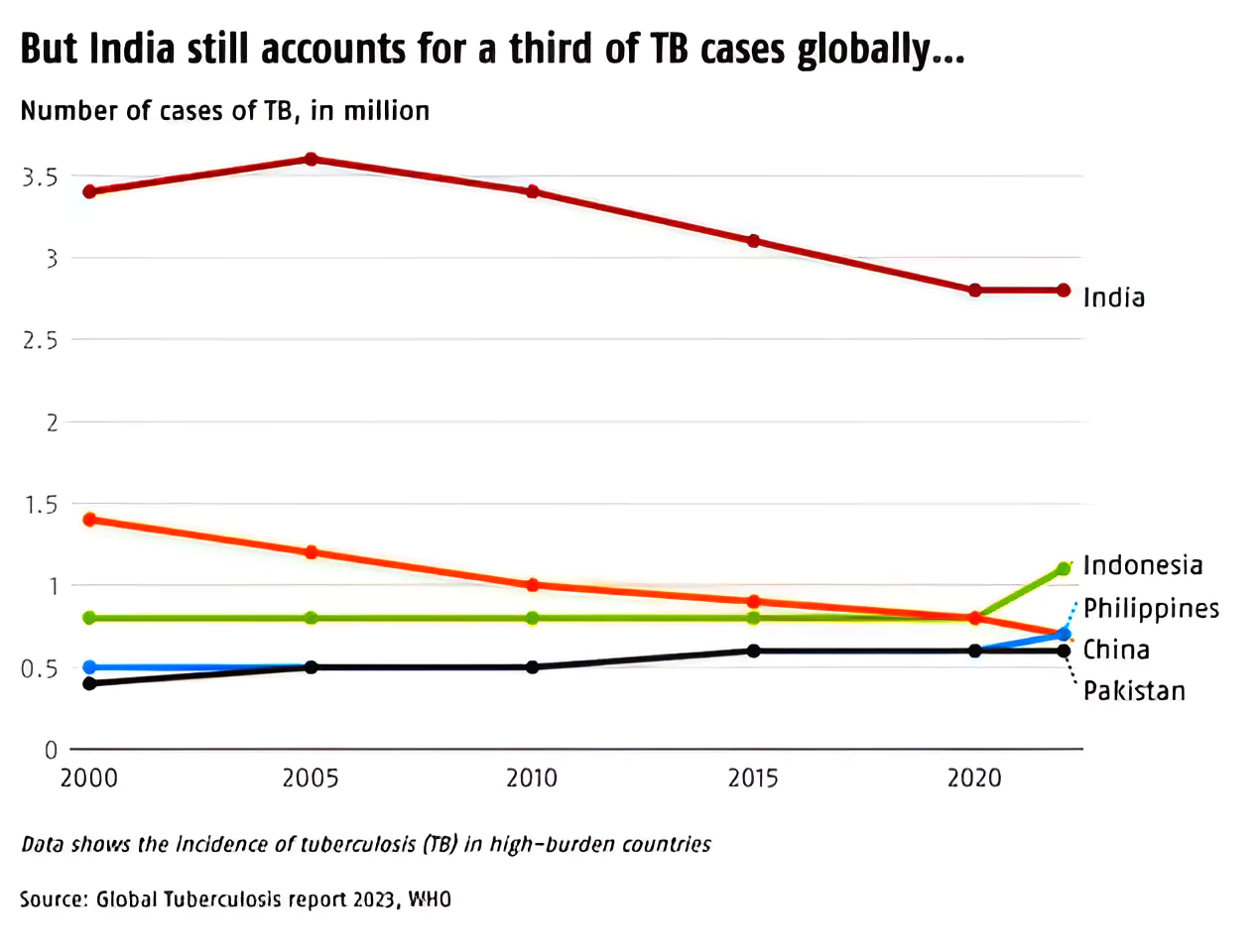 However, with treatments, recommended by WHO, about 85% of TB patients can be cured.
However, with treatments, recommended by WHO, about 85% of TB patients can be cured.How Does Drug Resistance Happen?
|
|---|
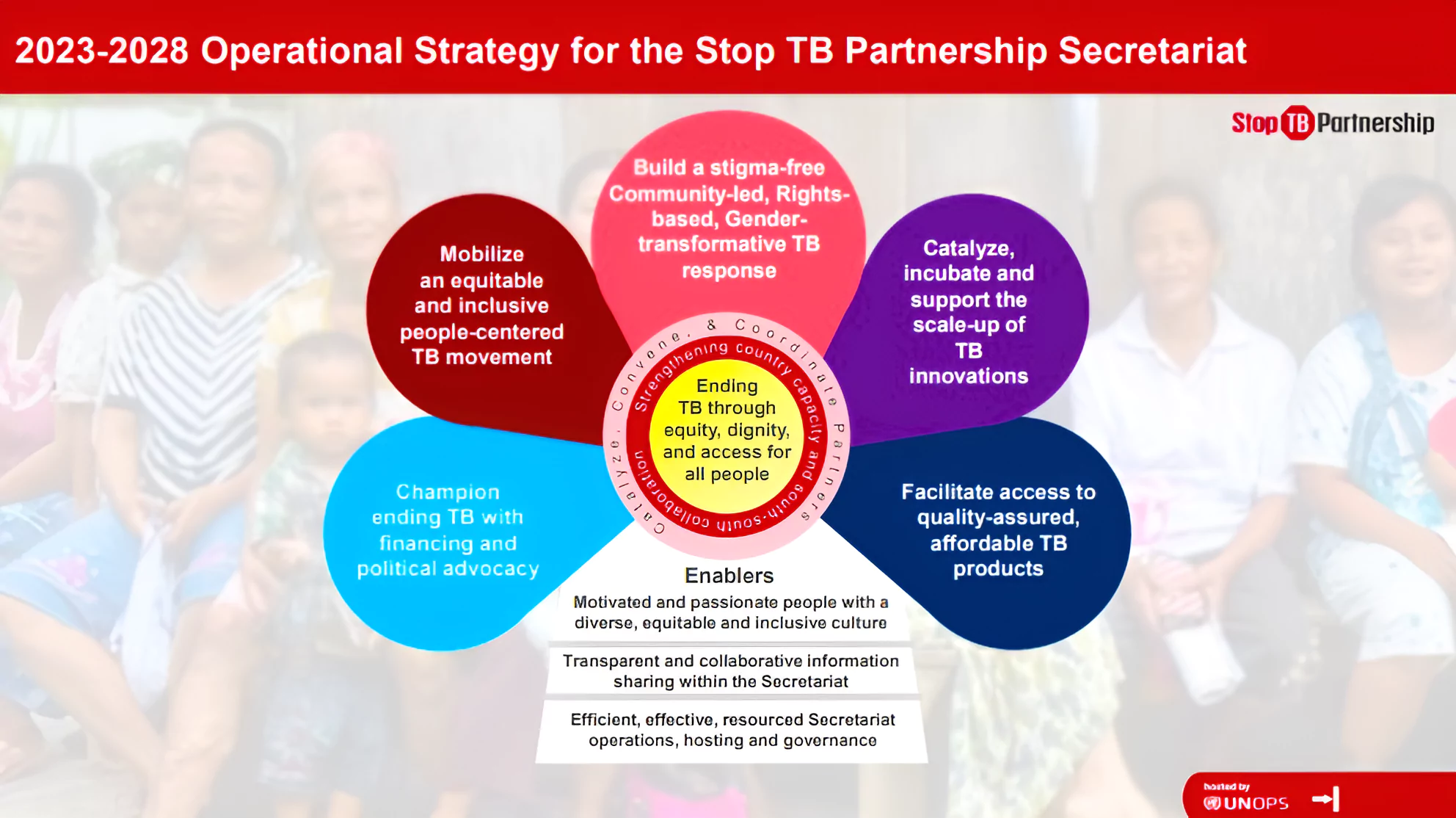
Achievement By India
|
|---|
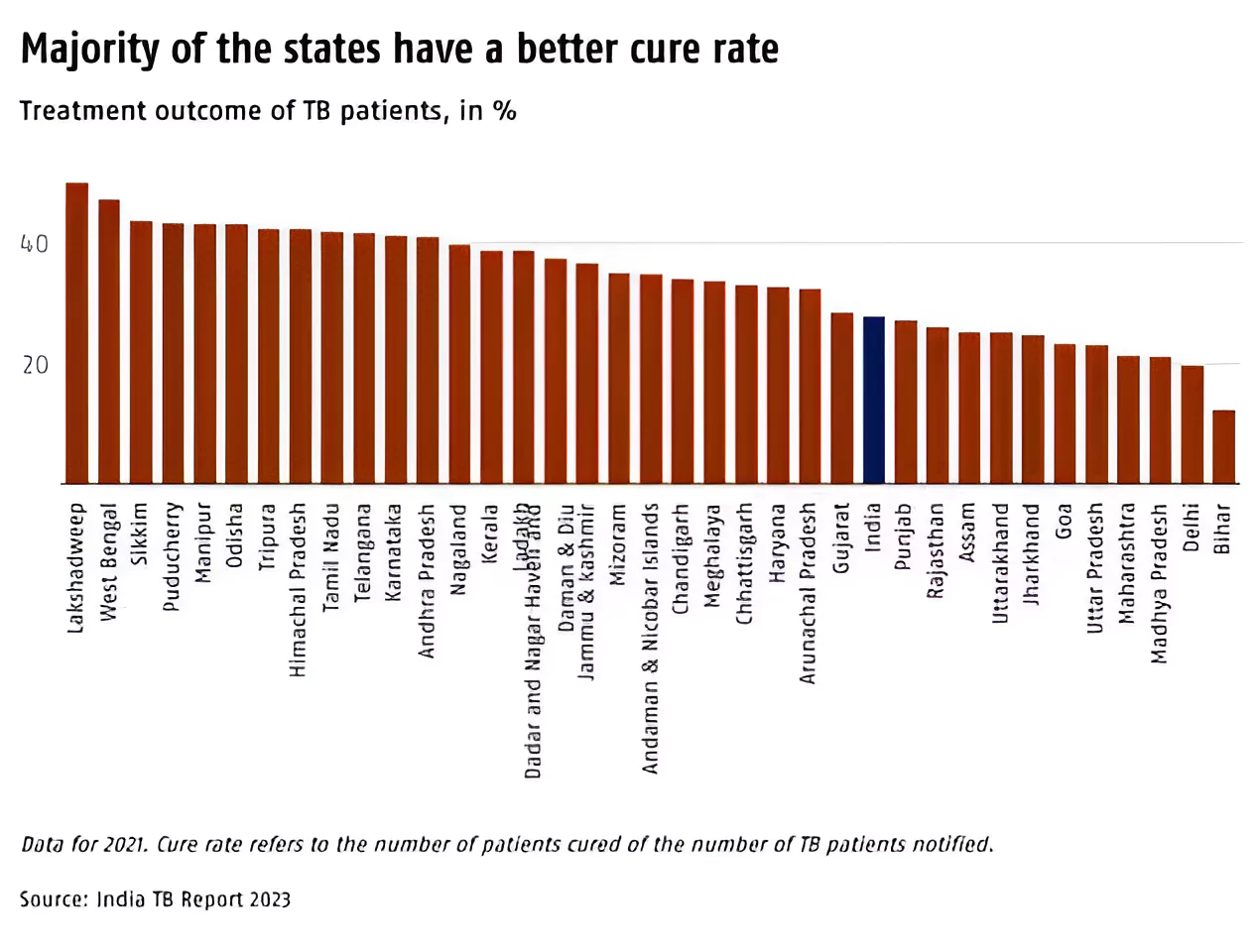
| Bimaru: It was coined in the 1980s, to refer to states lagging in key economic and other indicators, including the availability of health services needed to address diseases like TB. |
|---|
The path to TB elimination requires a concerted effort to prioritise person-centred care, address social determinants of health, and embrace innovation. By adopting a holistic and person-centred approach, India can overcome the barriers and create a healthier future for all its citizens.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Mixed reality headsets have gained widespread attention with the reveal of the Apple Vision Pro headset.
| Relevancy for Prelims: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, and Information Technology. |
|---|
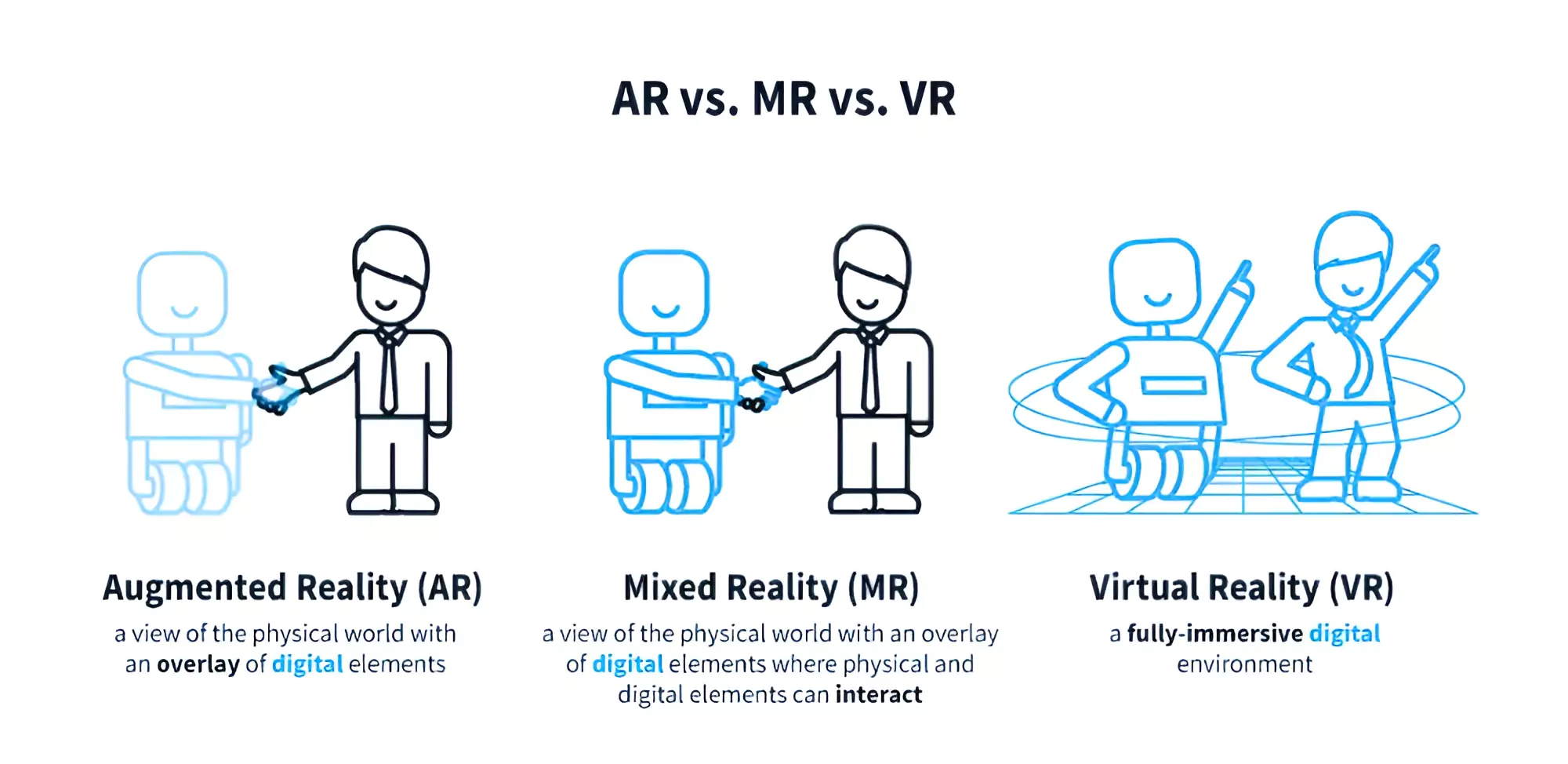 Spatial Computing: According to mixed reality researcher Louis Rosenberg, spatial computing “is a great overarching term for AR, MR, and VR, along with other immersive experiences such as 3D movies and telepresence.
Spatial Computing: According to mixed reality researcher Louis Rosenberg, spatial computing “is a great overarching term for AR, MR, and VR, along with other immersive experiences such as 3D movies and telepresence.Extended Reality:
|
|---|
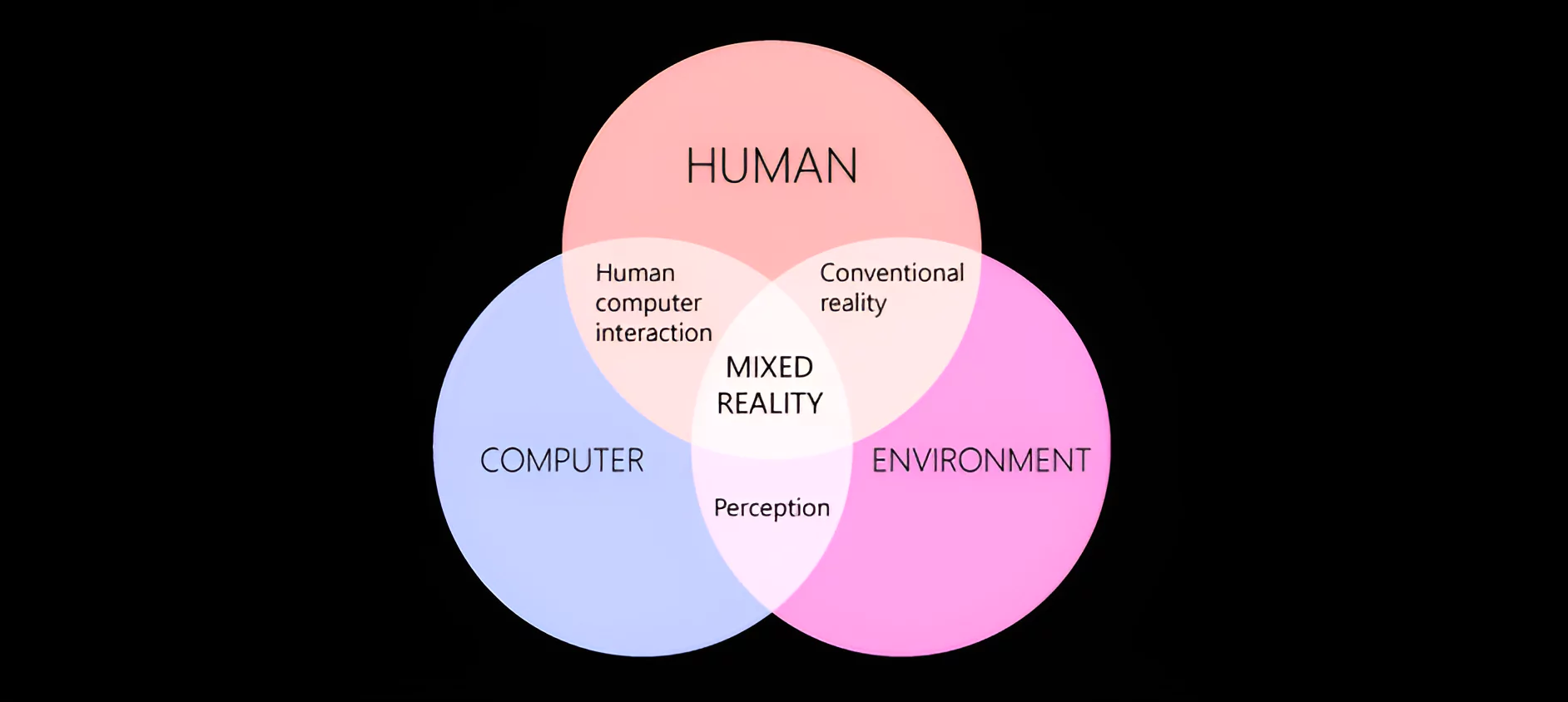 Collaboration: MR can facilitate collaboration by allowing multiple users to interact with the same virtual environment from different locations.
Collaboration: MR can facilitate collaboration by allowing multiple users to interact with the same virtual environment from different locations. 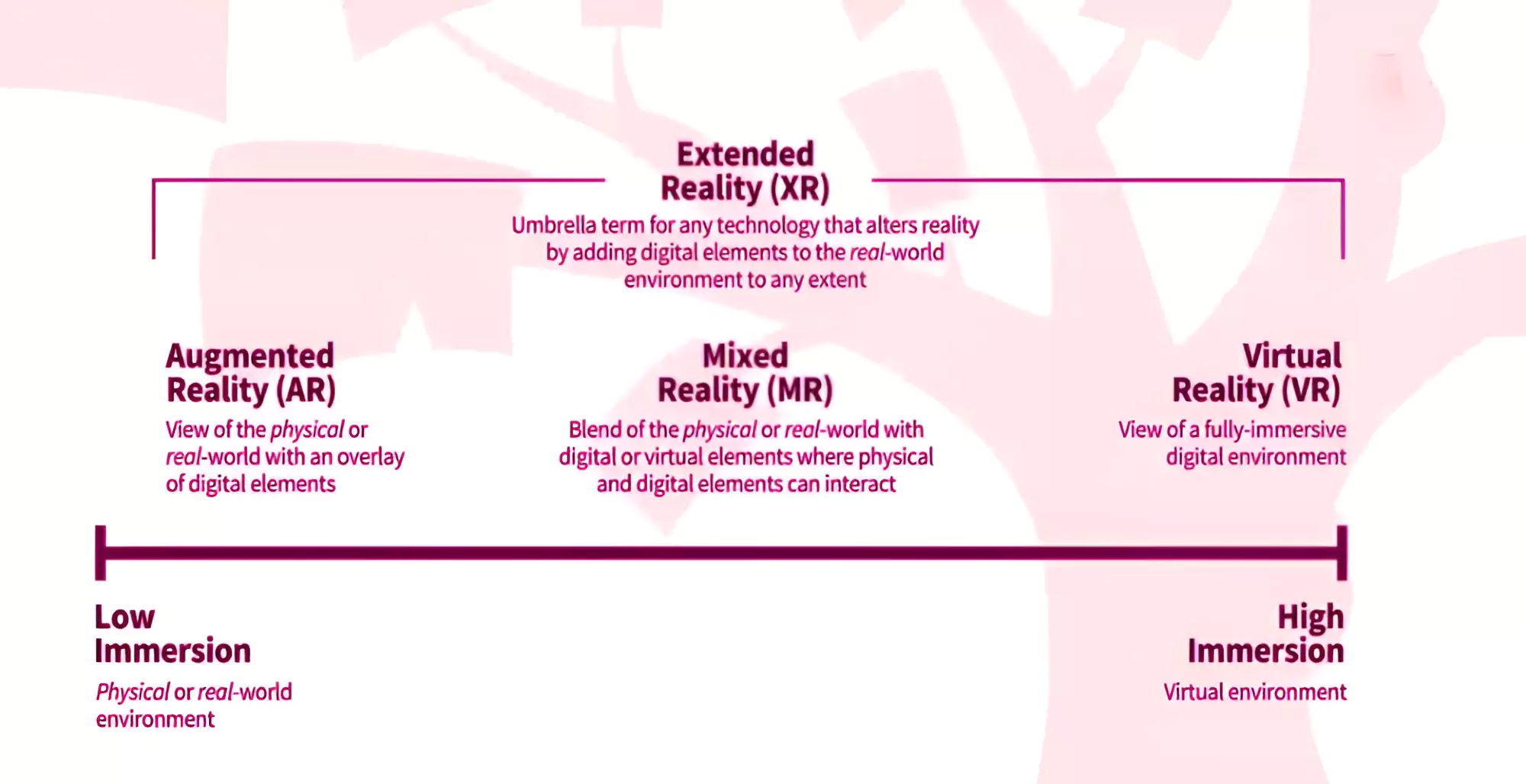 Mixed Reality Spectrum: It is a way of describing how physical and digital worlds can be combined in different ways to create immersive experiences.
Mixed Reality Spectrum: It is a way of describing how physical and digital worlds can be combined in different ways to create immersive experiences. 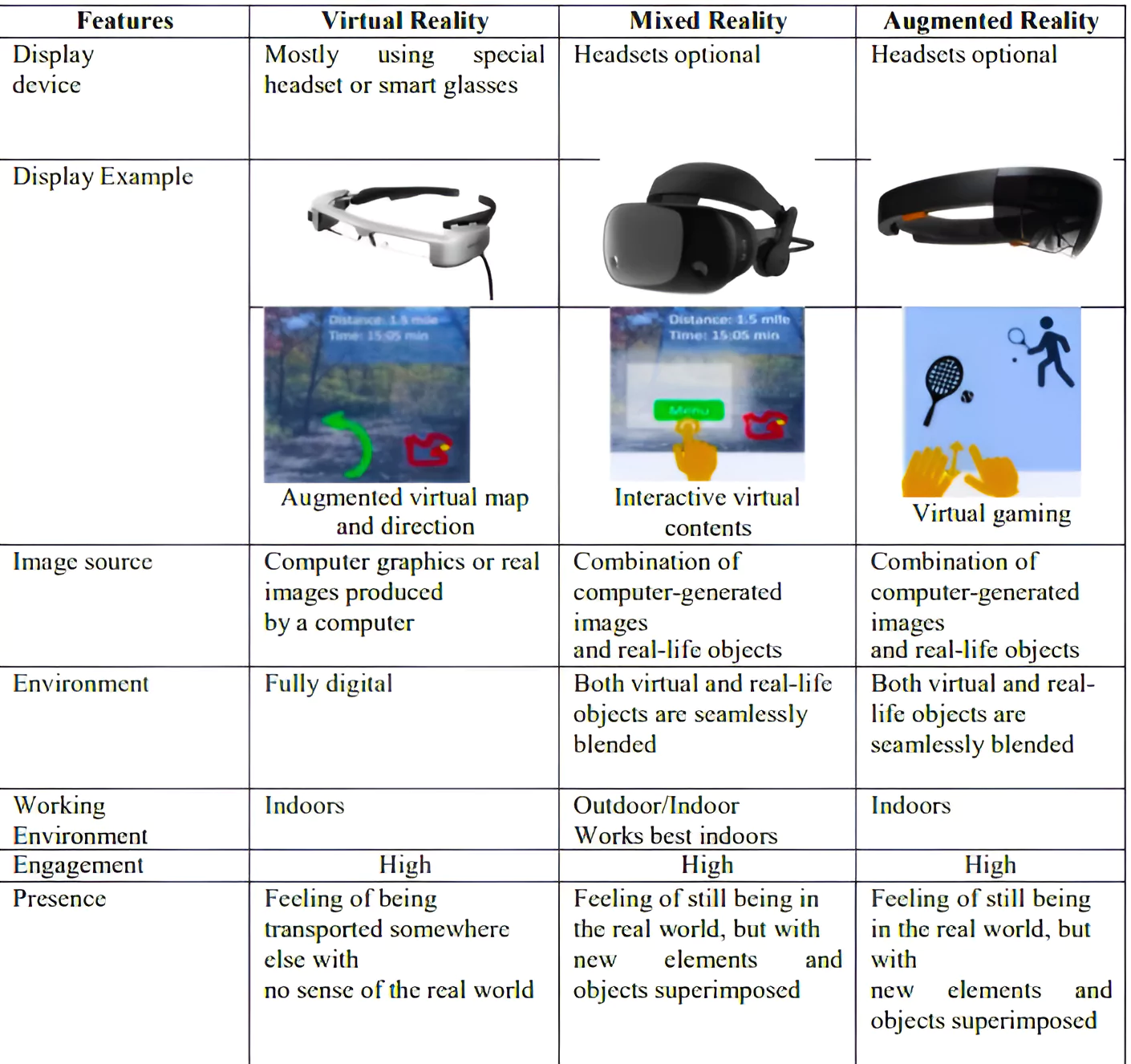
Mixed Reality Program in India:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>