Recently, the Indian government has introduced a new platform called CDP-SURAKSHA for disbursing subsidies to horticulture farmers under the Cluster Development Programme (CDP).
About Cluster Development Program (CDP)
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Global Hepatitis Report 2024 was released by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
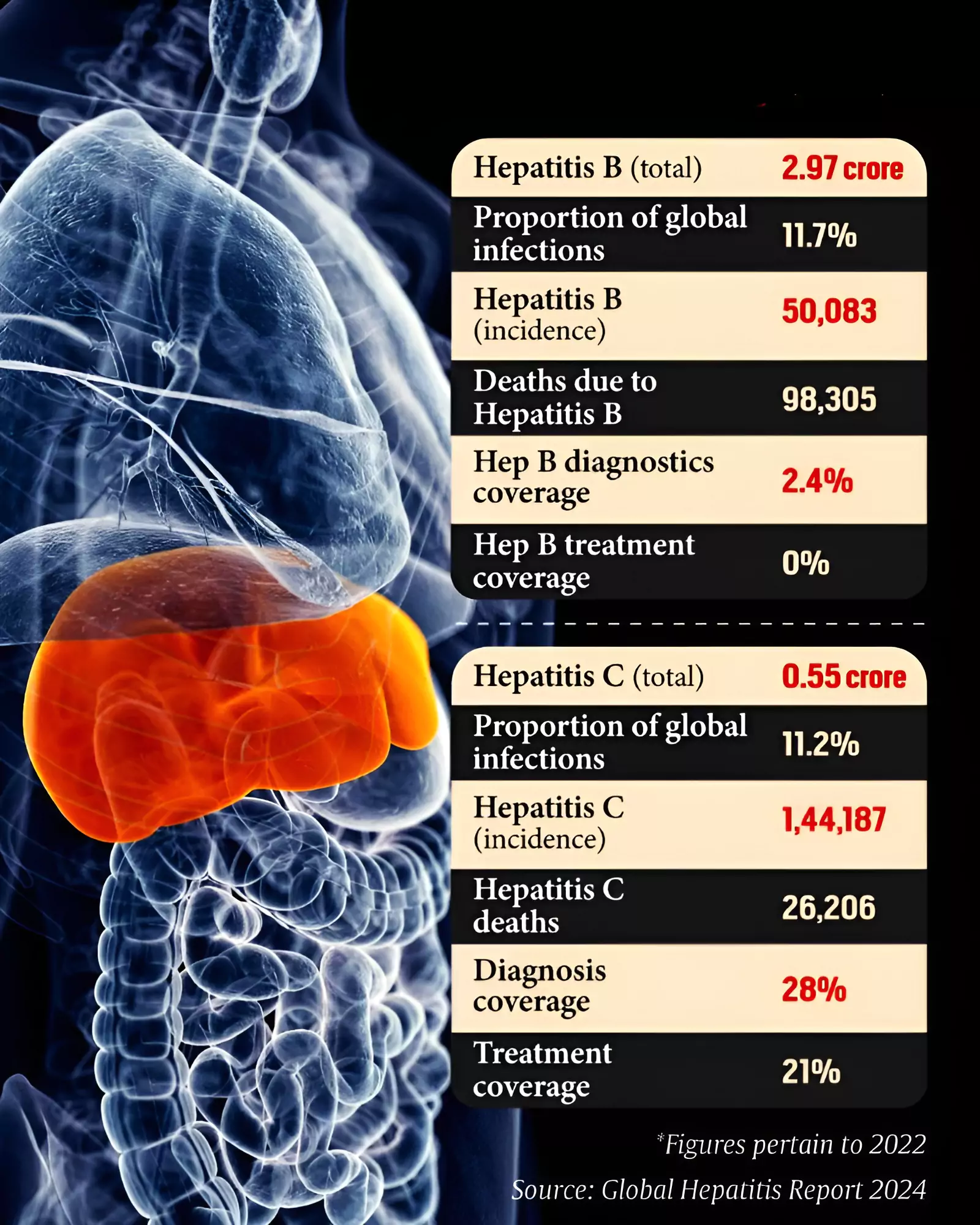 Largest killer: A global death rate of 1.3 million annually, viral hepatitis with tuberculosis were the second biggest infectious killer in 2022, behind only the deaths caused by the Covid-19 pandemic.
Largest killer: A global death rate of 1.3 million annually, viral hepatitis with tuberculosis were the second biggest infectious killer in 2022, behind only the deaths caused by the Covid-19 pandemic.
 Hepatitis B: It is known to cause acute infection with nausea, vomitting and yellowing of the eye and skin for several weeks.
Hepatitis B: It is known to cause acute infection with nausea, vomitting and yellowing of the eye and skin for several weeks.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, In response to a petition filed by an MLA from Arunachal Pradesh legislative assembly), Supreme court observed that Candidates are not required to disclose every item of moveable assets except “High value” asset, citing a candidate’s Right to privacy.
Grounds For Filing an Election Petition or Declaring an Election Void:
|
|---|
| Section 123 of the Representation of the People Act, 1951
Corrupt Practices:
Undue Influence :
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
An international team of researchers released the most comprehensive “three-dimensional” map of the universe.
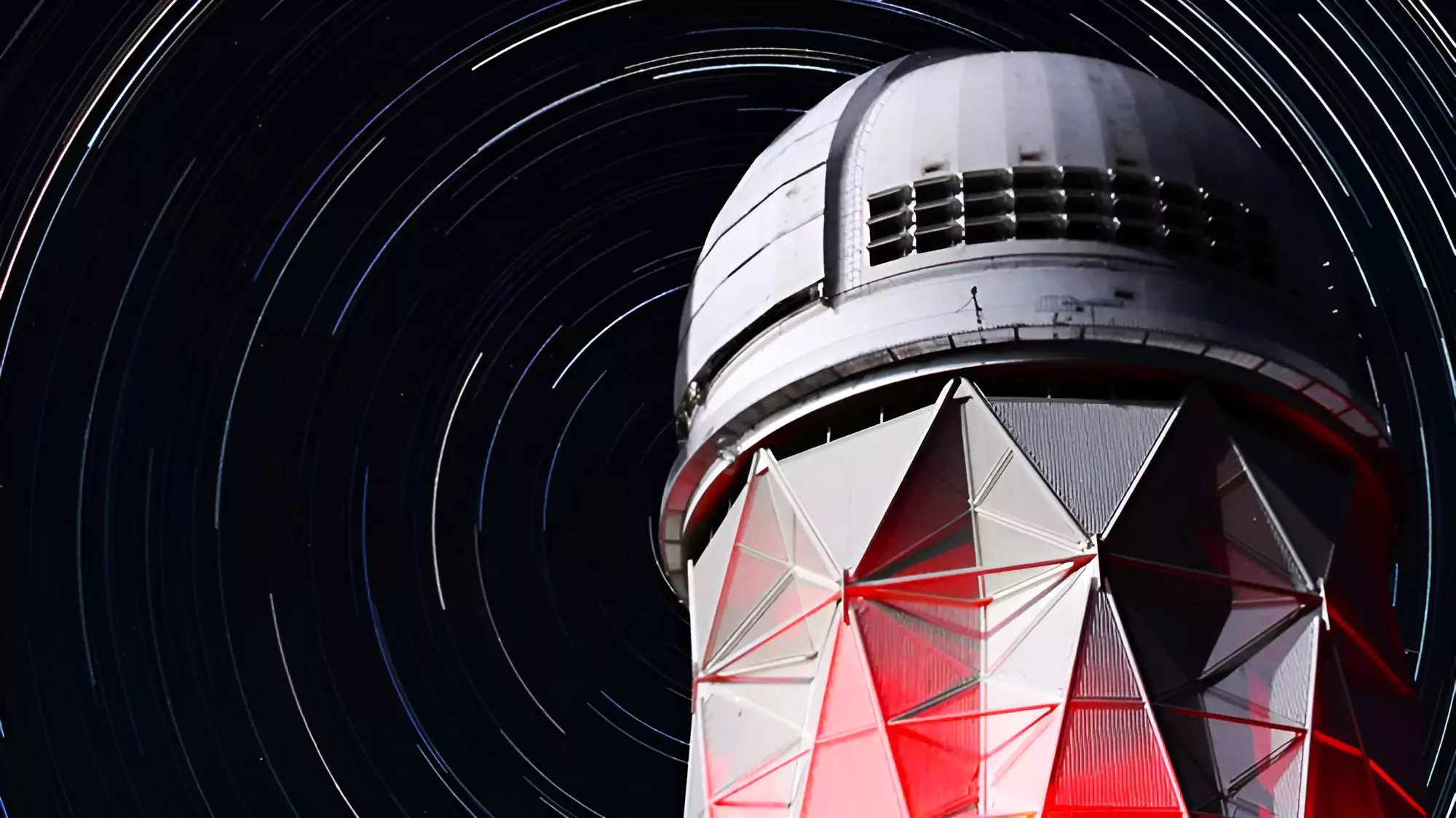 Mapping of the Distribution and Movement of these Galaxies: The precise distances calculated have resulted in the mapping of the distribution and movement of these galaxies over time.
Mapping of the Distribution and Movement of these Galaxies: The precise distances calculated have resulted in the mapping of the distribution and movement of these galaxies over time.

| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The set of “womenomics” reforms implemented during the “Abenomics” era by Japan are now yielding positive outcomes.
According to an OECD paper, key determinants of low participation of women in the job market in India are:
After nearly declining continuously for five decades, India’s WFLPR has begun showing a rising trend, increasing from 23 per cent in 2017-18 to 37 per cent in 2022-23.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
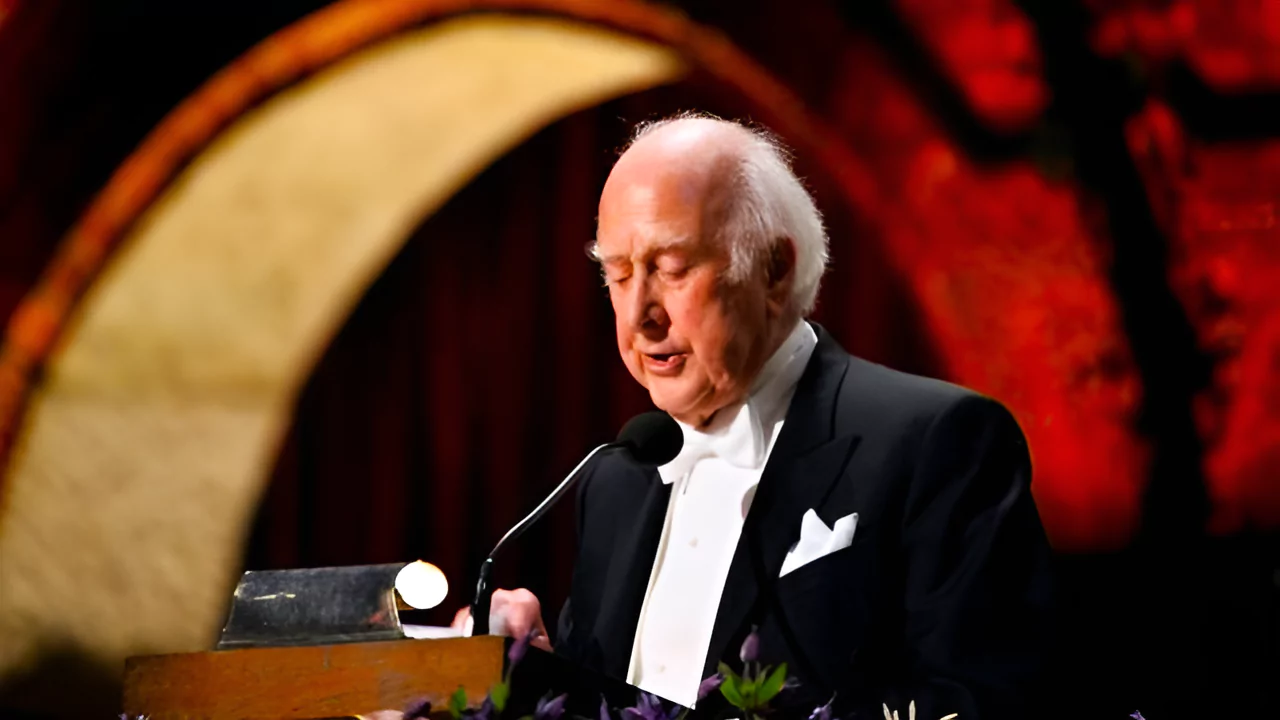

Recently, Nobel laureate and noted Physicist Peter Higgs, known for predicting God’s Particle has passed away.
What is a Boson?
|
|---|
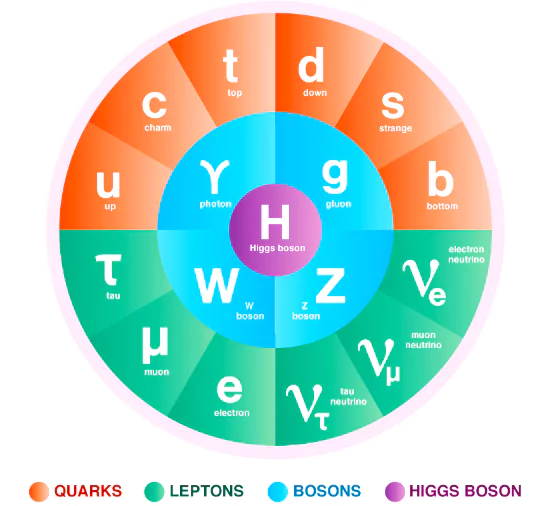 It also explains how force carrying particles, which belong to a broader group of bosons, influence the quarks and leptons.
It also explains how force carrying particles, which belong to a broader group of bosons, influence the quarks and leptons.
CERN (European Council for Nuclear Research):
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The 2024 QS World University Rankings by Subject have been released recently.
About QS World University Rankings
|
|---|
 It is behind only China’s 4.5 million, the United States’ 4.4 million, and slightly less than the United Kingdom’s 1.4 million.
It is behind only China’s 4.5 million, the United States’ 4.4 million, and slightly less than the United Kingdom’s 1.4 million.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) has deployed its sub-metre resolution optical satellite, TSAT-1A, into space.

| Sector | Application | Description |
| Agriculture | Monitoring Crop Health and soil condition |
|
| Disaster Management | Real-Time Data for Preparedness |
|
| Environmental Monitoring | Land Cover and Land Use Mapping |
|
| Infrastructure Planning | Urban Development / construction |
|
| Security and Defense | Border Surveillance |
|
| Scientific Research | Environmental Studies |
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Aadhaar-based age tokens can solve privacy problem as per experts.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
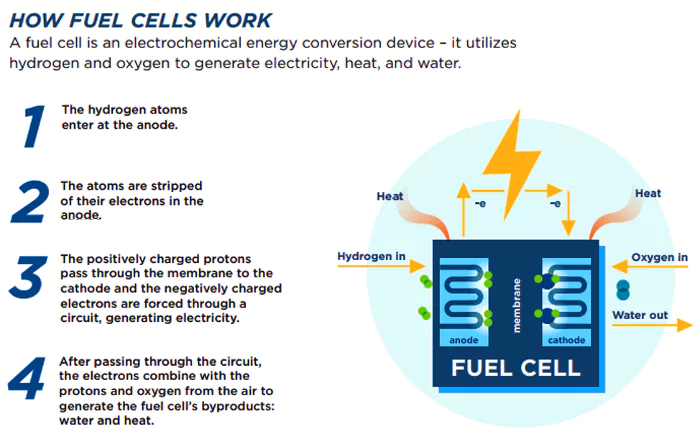
Researchers at the University of Kerala have devised an eco-friendly fuel cell that generates power mainly using air and seawater.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
According to the Hurun Global Unicorn Index 2024, India for the first time recorded a decline in unicorn creation since 2017.
Global Unicorn Index
Hurun Global 500s: It is a list of the 500 most valuable non state-controlled businesses in the world. |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the ‘India Employment Report 2024’ has been released by the Institute for Human Development (IHD) and International Labour Organisation (ILO).
| Relevance For Prelims: Unemployment In India, How Unemployment Is Measured, India Employment Report 2024- Outlook On Women, International Labour Organisation (ILO), Human Development, and Poverty In India.
Relevance For Mains: Unemployment In India: Current Status, Causes, Challenges, Government Initiatives, and Way Forward. |
|---|
About Unemployment
Calculation of Unemployment Rate in India
Or,
|
|---|
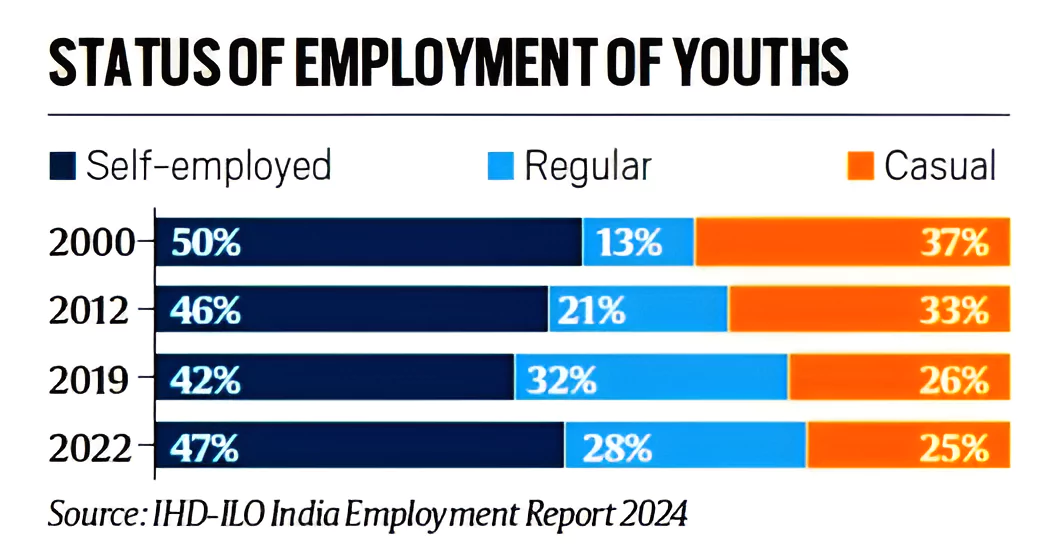
About Labour Force:
|
|---|
| Usual Principal and Subsidiary Status (UPSS): It determines a person’s employment status based on their engagement for a substantial period (over 182 days) in one or more work-related activities during the 365 days preceding the survey. |
|---|
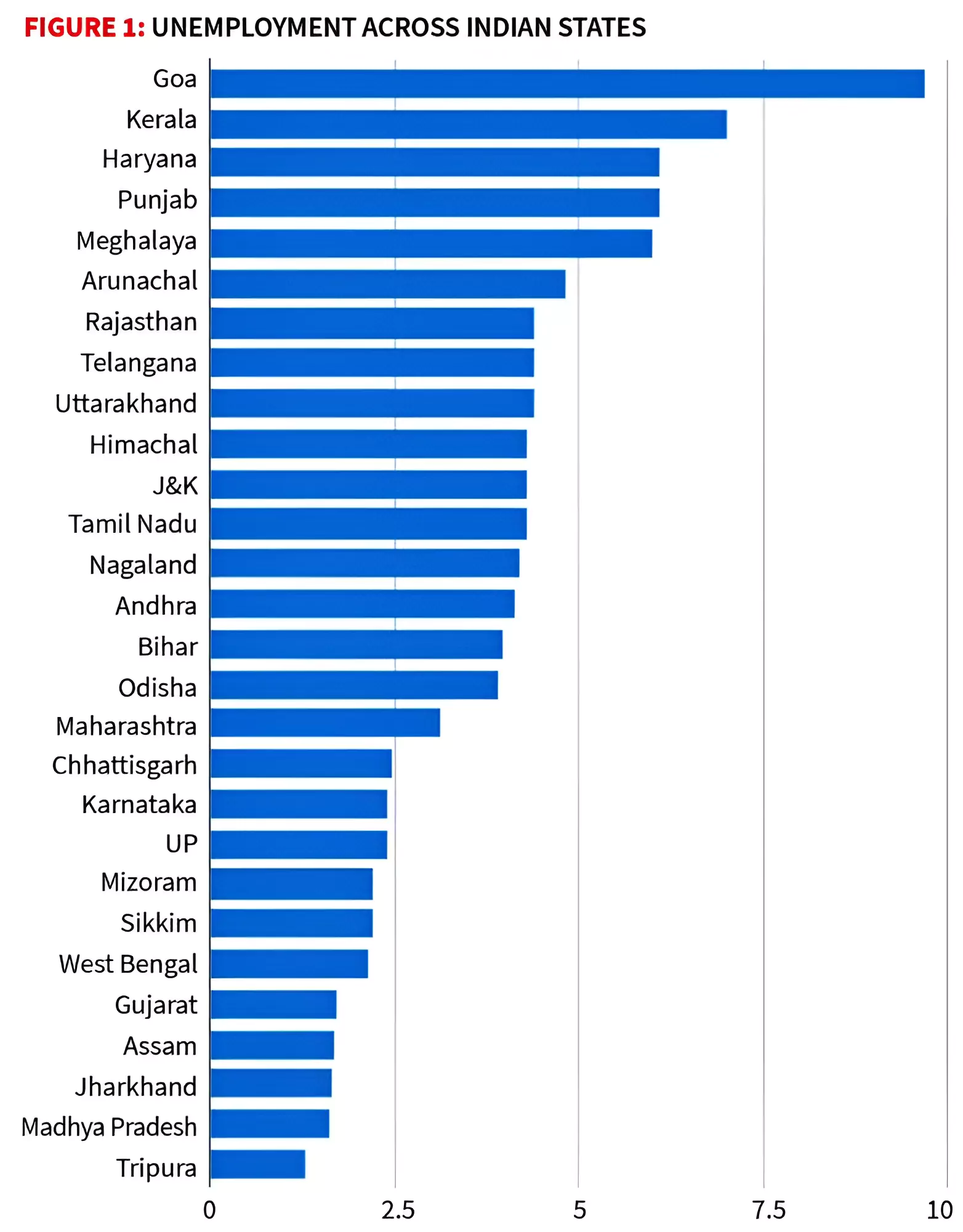 But this presents a conundrum, barring Maharashtra and Gujarat, many States with unemployment rates lower than the national average also have per capita incomes lesser than the national average.
But this presents a conundrum, barring Maharashtra and Gujarat, many States with unemployment rates lower than the national average also have per capita incomes lesser than the national average.
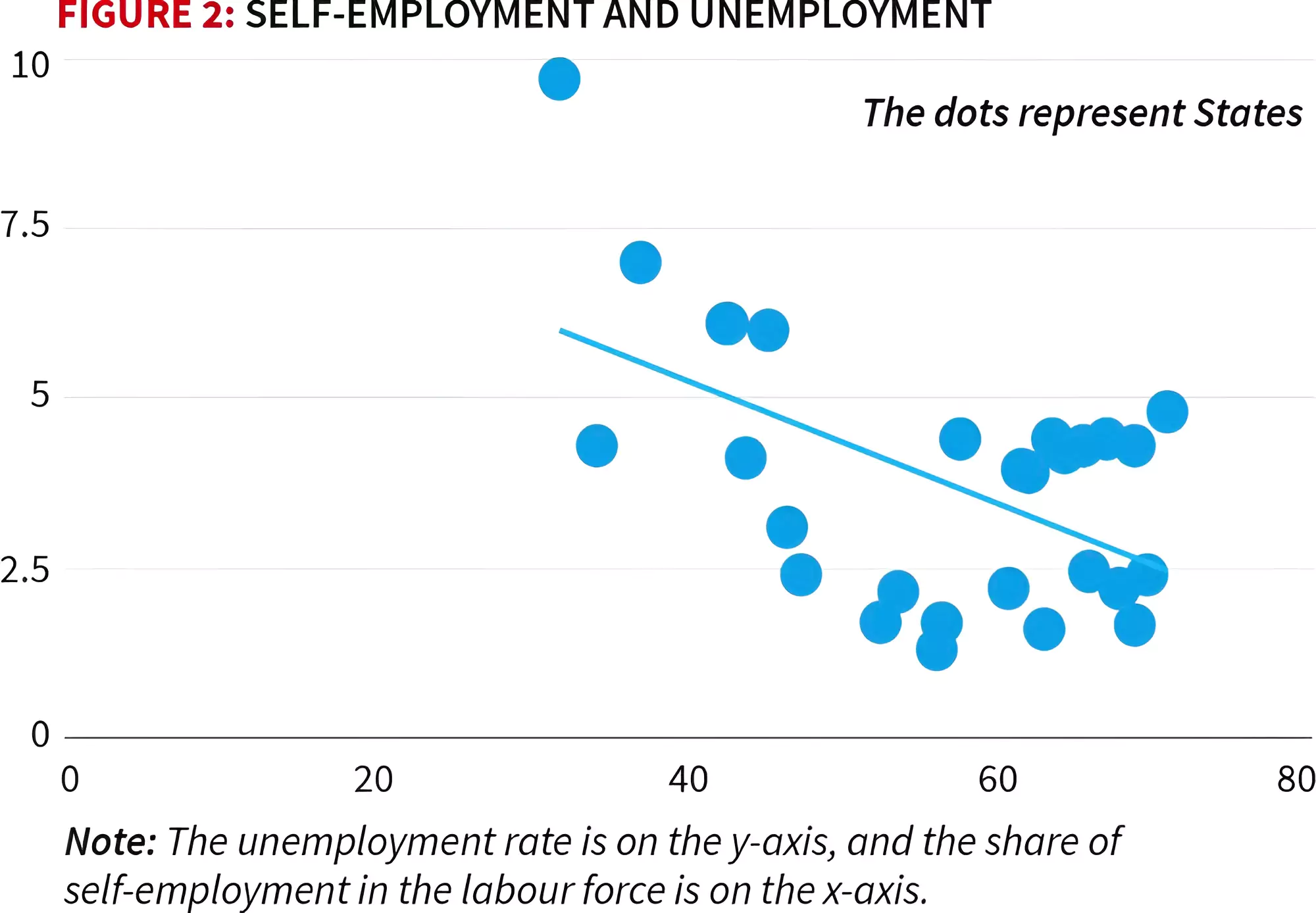
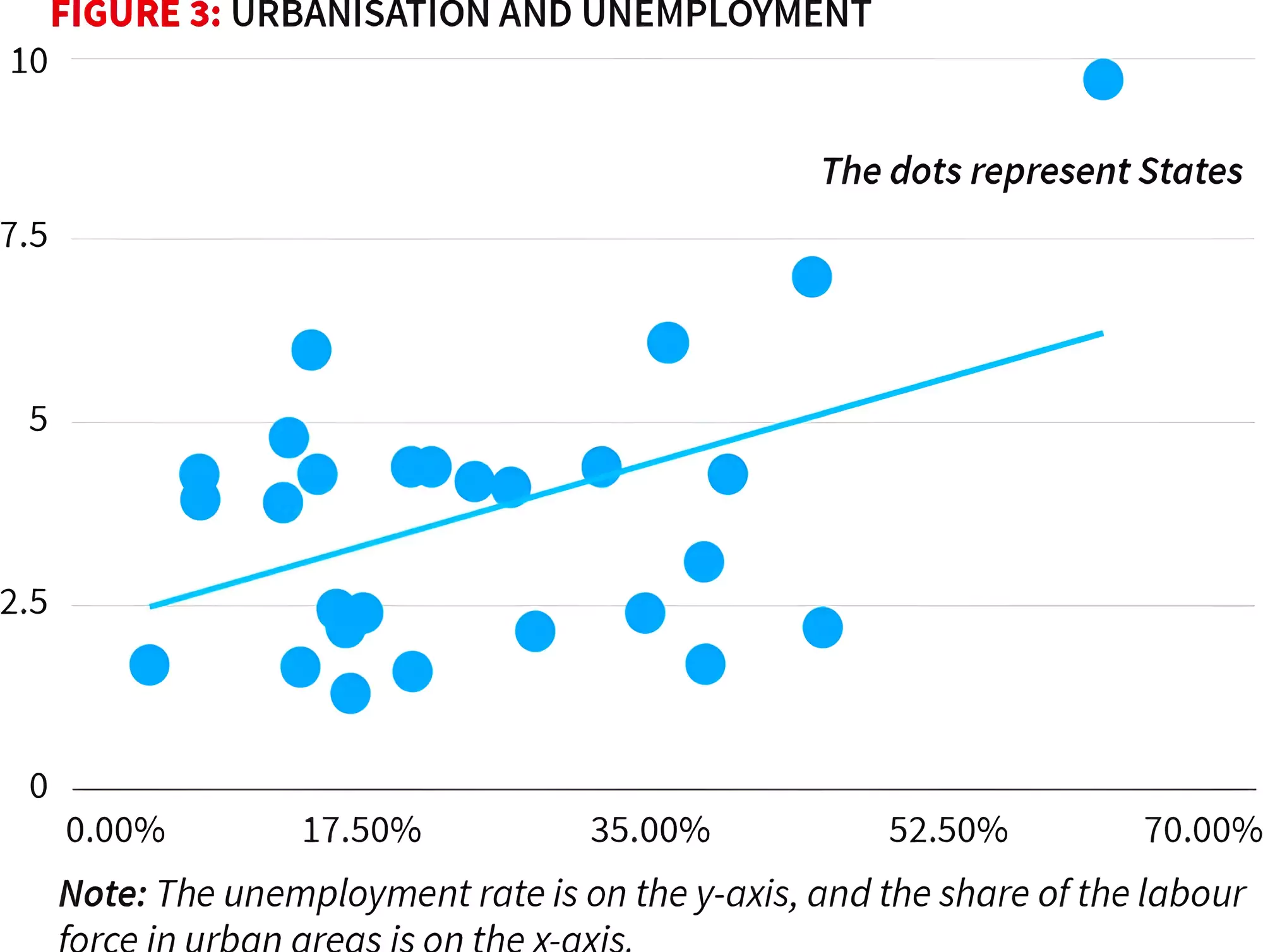 Informal Self-employment Sector: A large proportion of informal self-employment is accounted for by agriculture and the rural economy.
Informal Self-employment Sector: A large proportion of informal self-employment is accounted for by agriculture and the rural economy.
Indicators Used in Employment Condition Index:
|
|---|
Initiatives Taken by the Government
|
|---|
| Prelims PYQ (2018):
Consider the following statements: Human capital formation as a concept is better explained in terms of a process which enables 1. individuals of a country to accumulate more capital. 2. increasing the knowledge, skill levels and capacities of the people of the country. 3. accumulation of tangible wealth. 4. accumulation of intangible wealth. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 4 (d) 1, 3 and 4 Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Mains Question: PM Vishwakarma Yojana will push people on the path of self-reliance, and create better employment opportunities for the youth. Critically Discuss. (10 M, 150 Words) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>