Diplomats met in Paris to raise humanitarian aid for the northeast African country of Sudan grappling with a year-long period of conflict.
| Darfur Region: It is a western region of Sudan. It is bordered by Libya to the northwest, Chad to the west, the Central African Republic to the southwest, South Sudan to the south, and the Nile River to the east. |
|---|
Talks led by Saudi Arabia and the United States in Jeddah in 2023 aimed to mediate a ceasefire between the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) and the Sudanese army.
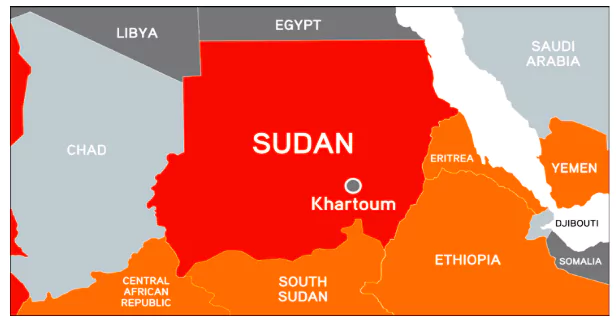
Sudan is a country in Northeast Africa with the capital city Khartoum.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
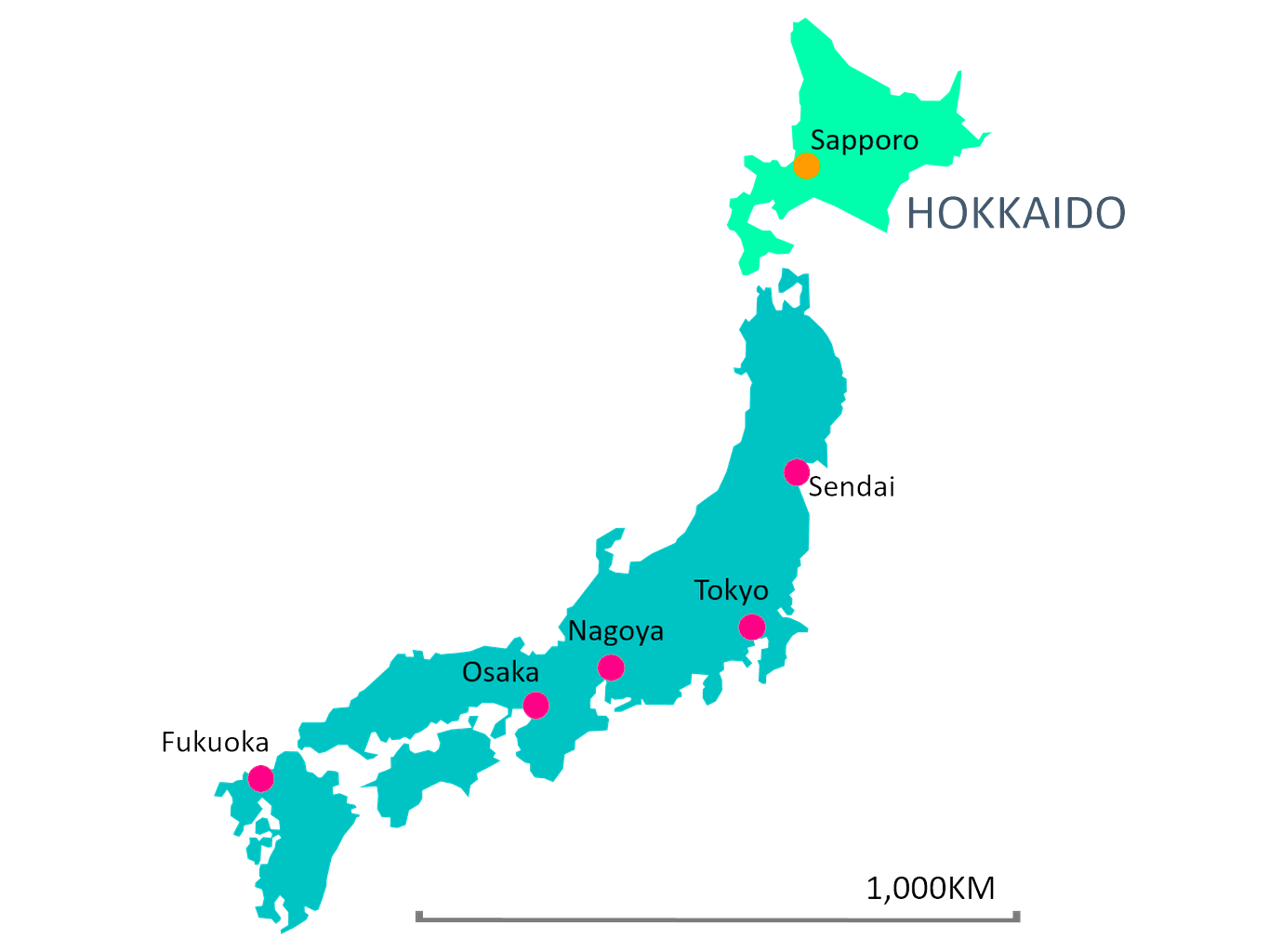
According to the Japanese Meteorological Agency (JMA), Sapporo, the main city of Japan’s second-largest island of Hokkaido, recorded 26 degrees Celsius on April 15, 2024.
Climate of Hokkaido:
|
|---|
| Urban Heat Island [UHI] effect:
It refers to the observable occurrence of markedly higher temperatures in urban regions relative to adjacent rural areas, primarily as a result of human activities. Typically, the mean temperature in urban heat islands can be 8 to 10 degrees Celsius higher than in the surrounding rural zones. |
|---|
The Ainus:
|
|---|
As Japan confronts its own challenges related to a swiftly declining population, the recent temperature recorded in Sapporo serves as a stark reminder of the accelerating impact of climate change on the archipelago.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The utilization of hydrocarbons for powering large engines polluting the air and water contributed to the phenomenon of global warming.
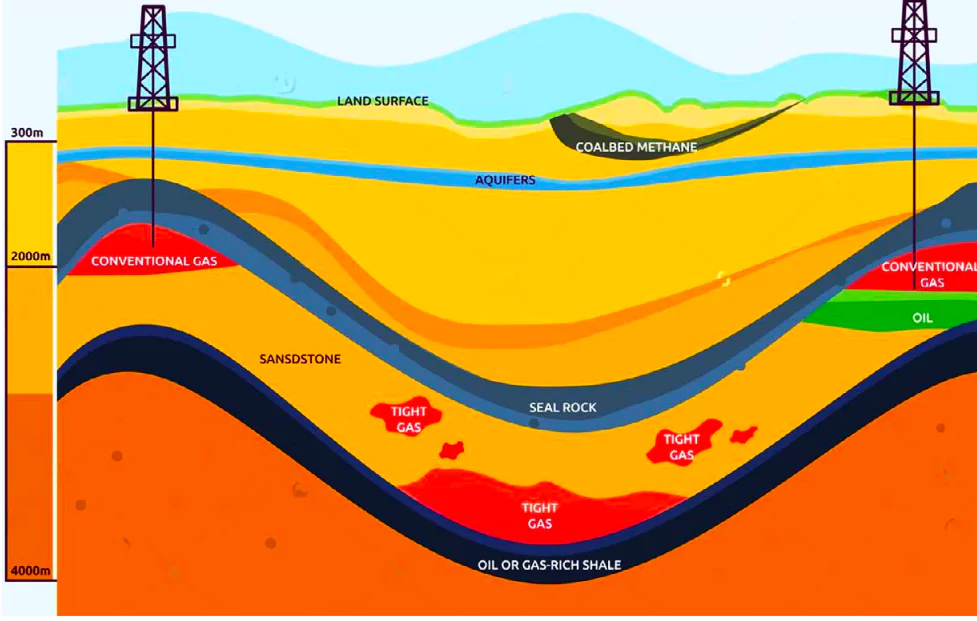
The term ‘hydrocarbon’ means compounds of carbon and hydrogen only. Hydrocarbons are the critical energy storage molecules within all major types of fossil fuels (including coal, oil, and natural gas) and biofuels.
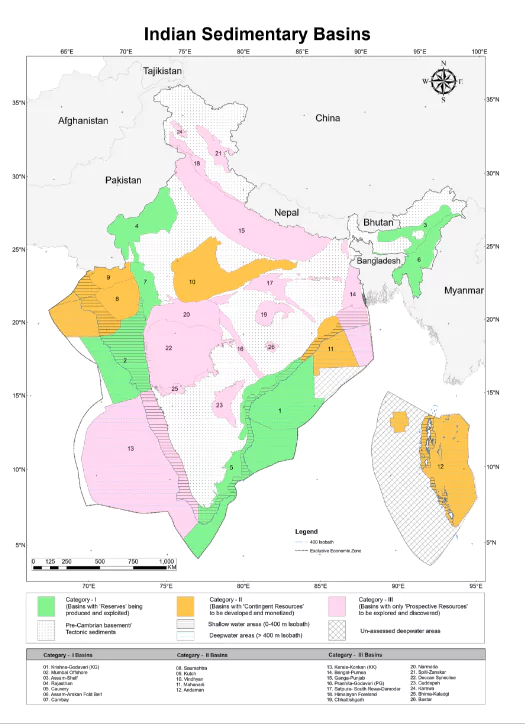
HELP is an exploration and production policy of the Government of India that replaced the New Exploration Licensing Policy (NELP).
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
IMD in a press briefing has forecast that the rains in June-September will be 6% more than these months, an annual average of 87 cm.
Indian Monsoon
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
In a newly published research, a new genetic variant linked to Parkinson’s disease has been discovered that sheds light on the evolutionary origin of multiple forms of familial parkinsonism.
| Parkinsonism: Parkinsonism is an umbrella term that refers to conditions with similar, movement-related effects.
Difference between parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
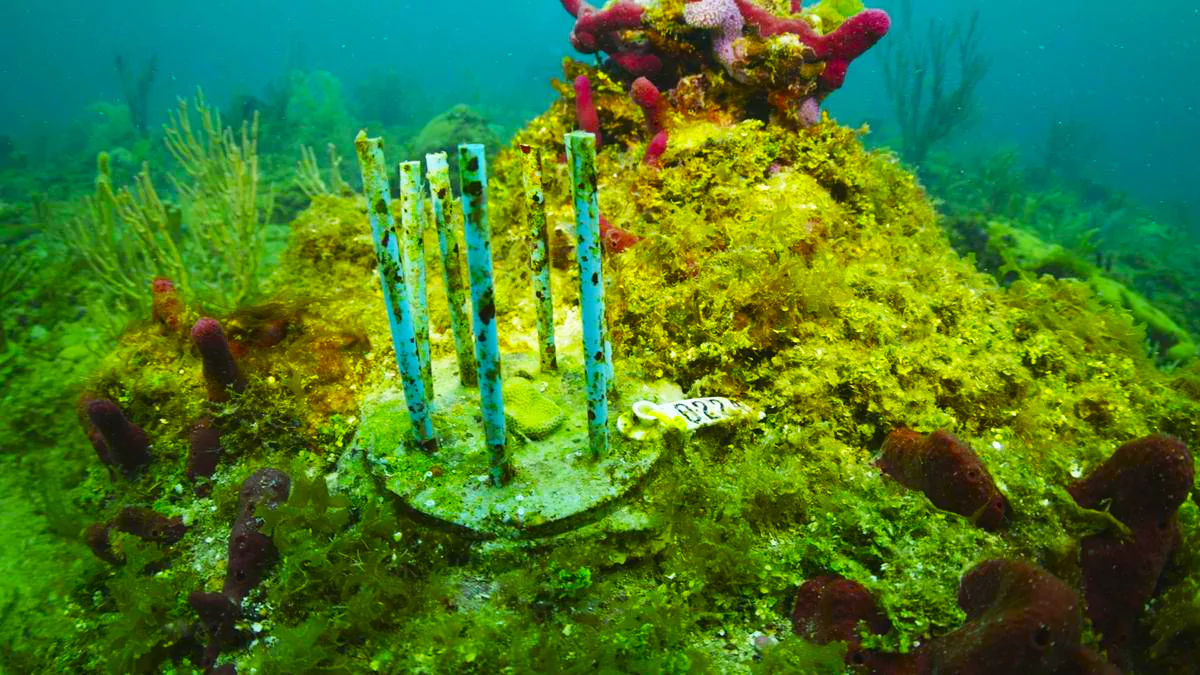

Researchers in South Florida are pioneering an innovative approach to safeguarding laboratory-grown coral from predatory fish, utilizing biodegradable materials to aid in coral reef restoration efforts.
Parrot Fish Relationship with Corals
|

| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
In March 2024, India completed its first-ever winter expedition successfully in the Arctic.
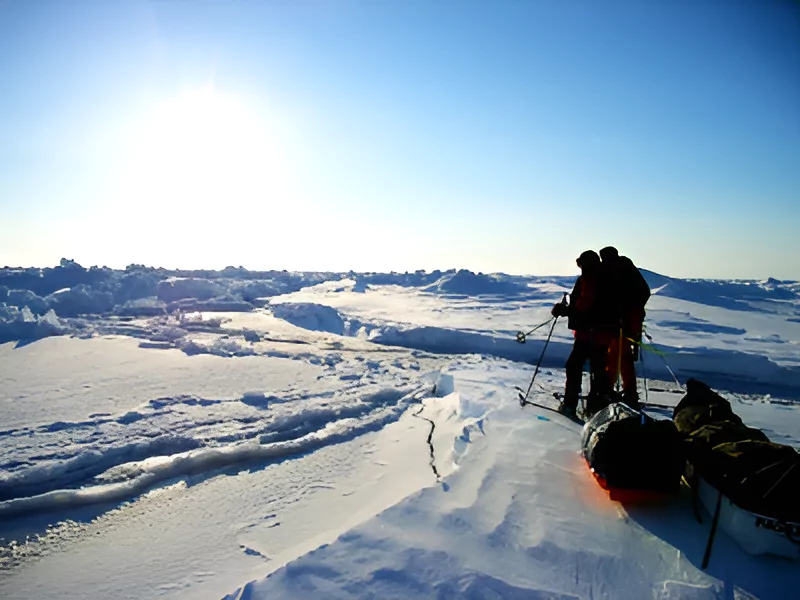

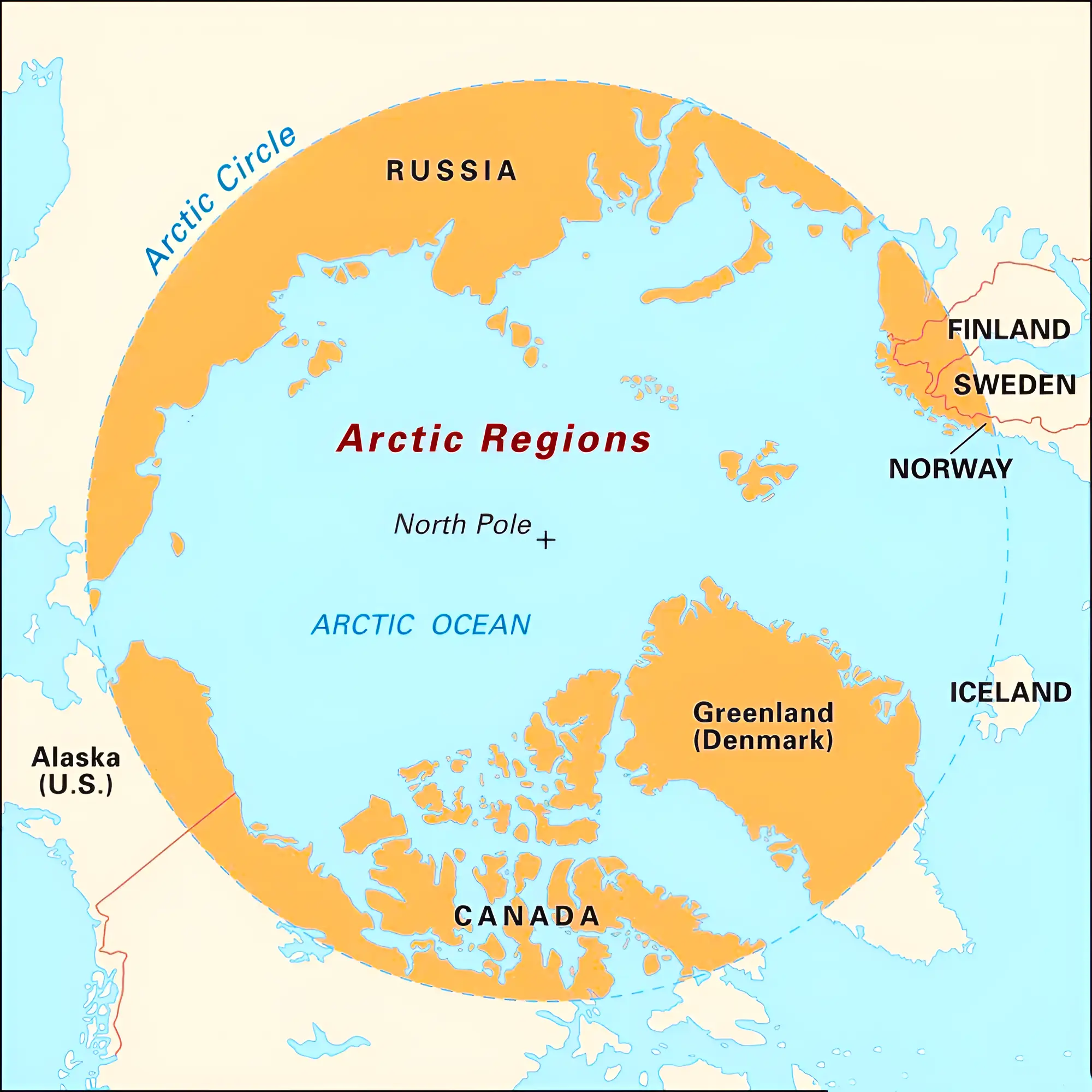
India has been involved in Arctic affairs since 1920, starting with the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in Paris.
Key Provisions of India’s Arctic PolicyThis policy lays down six central pillars
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The annual rate of inflation based on the All India Wholesale Price Index (WPI) number is 0.53% (Provisional) for the month of March, 2024 (over March, 2023).
Reason for Positive rate of Inflation: Positive rate of inflation in March, 2024 is primarily due to increase in prices of food articles, electricity, crude petroleum & natural gas, machinery & equipment and other manufacturing etc.
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) represents the price of goods at a wholesale stage i.e. goods that are sold in bulk and traded between organizations instead of consumers.
GDP Deflator and Implicit Price Deflator: It is the ratio of the value of goods and services an economy produces in a particular year at current prices to that of prices that prevailed during the base year.
OR
|
|---|
Wholesale Price Index |
Consumer Price Index |
| It measures the changes in the prices of goods sold and traded in bulk by wholesale businesses to other businesses. | Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures price changes from the perspective of a retail buyer. |
| Publication: Ministry of Commerce and Industry. | Publication: National Statistical Office (NSO). |
| Base Year: 2011-12 | Base Year: 2012 |
| It keeps track of the wholesale price of goods | It measures the average price that households pay for a basket of different goods and services. |
| Even as the WPI is used as a key measure of inflation in some economies, the RBI no longer uses it for policy purposes, including setting repo rates. | RBI currently uses CPI or retail inflation as a key measure of inflation to set the monetary and credit policy. |
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
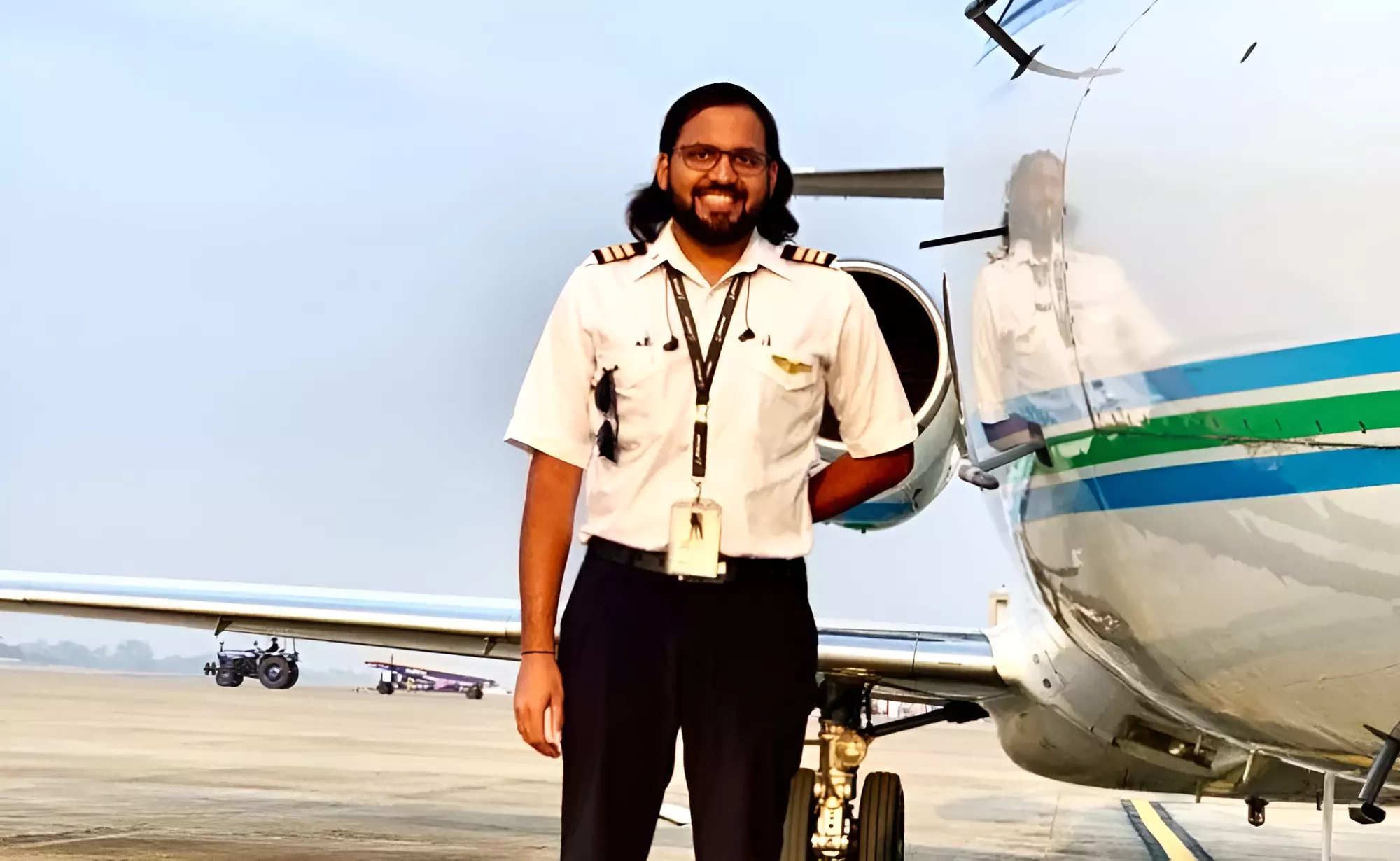
Entrepreneur and pilot Gopi Thotakura is set to become the first Indian to venture into space as a tourist on the NS-25 mission of Blue Origin Company.

| Kármán Line: It lies nearly 100 kilometres above our heads and is considered to be the boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space. |
|---|
Space tourism is a section of the aviation sector which seeks to provide tourists with the opportunity to become astronauts and experience space travel for recreational, leisure, or business purposes.
Global Space Tourism Efforts:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, a new bill has been introduced in the US Congress aims to force AI companies to disclose their use of copyrighted material in training their generative AI models.
| Relevance For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence, AI-Generated Content And Copyright Infringement, ILO Report On Generative AI, and Copyright Law In India.
Relevance For Mains: Copyright Infringement and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Arguments in Favour/Against for Use of Copyrighted Content, and Regulation in India on AI Copy Infringement. |
|---|
India’s Initiatives for Developing AI
|
|---|
| Prelims PYQ (2023):
Consider the investments in the following assets: 1. Brand recognition 2. Inventory 3. Intellectual property 4. Mailing list of clients How many of the above are considered intangible investments? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) Only three (d) All four Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Union Cabinet Approves National Sports Policy 2025...
What are Altermagnets? A Breakthrough in Magnetism...
India’s 7-Point Strategy for Sustainable Gro...
Cabinet Approves Employment Linked Incentive Schem...
INS Udaygiri Delivered Under Project 17A to Indian...
SC Issues Implemented Reservation Roster for SC/ST...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>