New Caledonia
|
Recently, massive protests and riots broke out in New Caledonia following the French parliament’s decision to modify the voters’ list.
|
AIM – ICDK Water Challenge 4.0 |
Recently, NITI Aayog’s Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) unveils the ‘AIM – ICDK Water Challenge
|
National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) |
A meeting of the National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) was chaired by the Union Cabinet Secretary to review the preparedness to deal with heat waves and forest fires.
About : The NCMC is set up by the Government of India for disaster preparedness and effective coordination and implementation of relief measures and operations and providing support to states during a natural calamity.
|
Recently, Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) releases Images of the Sun Captured by Aditya-L1 Payloads.
The images were taken by the remote sensing payloads Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) and Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) aboard the Aditya-L1 spacecraft.
Lagrange Point (L1)
|
Recently, the Health Ministry and the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) are working together to launch the National Health Claim Exchange (NHCX).
Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI)The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) is a statutory body established under the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 1999, tasked with the overall supervision and development of the insurance sector in India.
|
|---|
Recently, President Mohamed Muizzu of the Maldives was one of seven neighboring leaders who attended Indian Prime Minister’s wearing-in ceremony at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
Neighbourhood First PolicyNeighbourhood First Policy (NFP) was conceived in 2008 wherein the principles of engagement under NFP were 5S (Samman, Samvad, Shanti, Samriddhi and Sanskriti).
SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region)SAGAR, a concept introduced by PM Modi in 2015 during his visit to Mauritius, emphasizes the blue economy.
|
|---|
Indian Highways Management Company Limited has invited Global Expression of Interest (EOI) from innovative and qualified companies to develop and implement GNSS-based Electronic Toll Collection system in India.
It is a toll collection method without barriers, using Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technology.
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
|
|---|
Recently, the Indian Ocean has been under a lot of attention due to its rapid warming and the outsized influence on other oceans.
World Oceans Day 2024World Oceans Day 2024 is celebrated on June 8th.
|
|---|
Indian Ocean is the Third-largest ocean, covering 70,560,000 km², about 20% of Earth’s water surface.
Heat Absorption Mechanism
Impact of Global Warming
The Indian Ocean’s Role in Human EvolutionGeographic Changes and Evolutionary Impact
|
|---|
An analysis by the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) shows that consumption inequality in the rural areas of 11 states has increased.
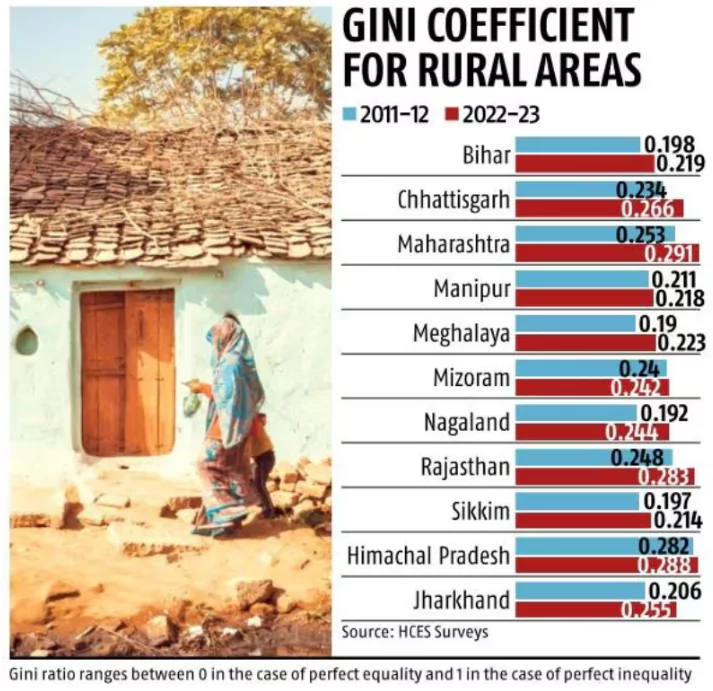 11 out of 25 states taken for analysis, recorded an increase in the GIni Coefficient value.
11 out of 25 states taken for analysis, recorded an increase in the GIni Coefficient value.
About The Gini CoefficientThe Gini Index determines a nation’s level of income inequality by measuring the income distribution or wealth distribution across its population.
|
After endorsing the BJP-led NDA, the Janata Dal (United) called for a reassessment of the Agnipath scheme for military recruitment.
Agnipath scheme was aimed at recruiting personnel below officer ranks — soldiers, airmen, and sailors who are not commissioned officers — to the Indian Armed Forces for a period of four years.
Global Practices
|
|---|
Tooth-to-tail ratioThe Tooth-to-Tail Ratio (T3R) is a military planning concept that measures the balance between combat forces (the “tooth”) and support personnel (the “tail”). Tooth: The “tooth” comprises frontline fighters like infantry, combat pilots, and combat vehicles, while the “tail” encompasses support functions such as logistics, administration, and medical services. Significance: A high T3R signifies a greater number of support personnel relative to combat forces, suggesting robust support and operational sustainability within the military. |
|---|
The Indian Army’s recommendations for the Agnipath scheme focus on enhancing the inclusion and training of Agniveers to maintain operational efficiency and address concerns related to the lack of experience and expertise among new recruits.
Recently, over 6.6 lakh pensioners utilized ‘Facial Authentication Technology’ in 2023-24 to verify their digital life certificates (DLCs) for EPFO pensions.
Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO)
|
|---|
Facial recognition, a type of biometric software, can uniquely identify or verify individuals by analyzing patterns in their facial contours.
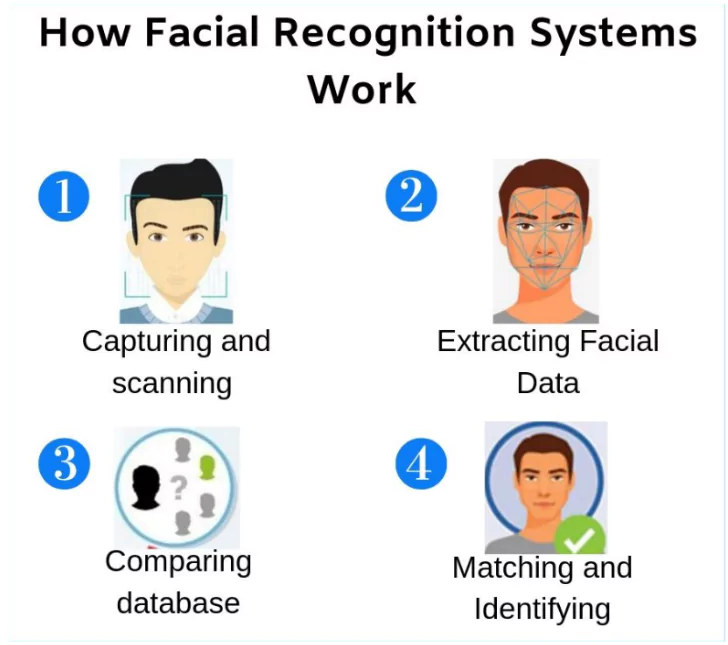
Recently, the Madras High Court ruled that cooperative societies are not amenable to the Right to Information (RTI) Act of 2005.
The Right to Information Act
|
|---|
Recently, the Supreme Court issued a notice to the National Testing Agency (NTA), seeking a reply in the NEET-UG result irregularities case.
About National Eligibility and Entrance Test (NEET) and the Raising Issue
Tamil Nadu’s Opposition to NEET Entrance
About National Testing Agency (NTA)
|
|---|
About Public Examinations Bill 2024
Major Highlights of Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Bill, 2024
Anti Cheating Laws in States
Government Initiatives to Enhance Transparency in Examinations
|
|---|
Recently, renowned Urdu poet Gulzar and Sanskrit scholar Jagadguru Rambhadracharya have been named the recipients of the 58th Jnanpith Award 2024.
This is the second time the Jnanpith Award 2024 has been given to Sanskrit and the fifth time for Urdu. Goan writer Damodar Mauzo has received the prestigious award for 2022.
Here is the list of Jnanpith Award winners 2024;

22 Scheduled Languages:
|
|---|
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
|
Related Articles |
|
| Important Awards in India 2024 | International Awards List |
| List Of Civilian Awards In India 2024 | National Film Awards |
| 70th National Film Awards 2024 | Padma Awards 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>