Muhammad Yunus
|
Muhammad Yunus; also known as ‘Banker to the Poor’, the winner of the 2006 Nobel Peace Prize, will become the chief adviser to the interim government in Bangladesh.
About Muhammad Yunus:
|
Quality Council of India introduces QCI Surajya |
The Quality Council of India (QCI) is introducing the QCI Surajya Recognition & Ranking Framework
About QCI
About QCI Surajya Recognition & Ranking Framework:
|
Nandini Sahakar Yojana |
Recently, the Minister of Cooperation has provided details about the Nandini Sahakar Yojana.
About Nandini Sahakar Scheme:
|
Monkeypox
|
Recently, Democratic Republic of Congo witnessed a rise in mpox cases along with a rapid spread in Kenya and several other African countries, raising concerns among health authorities.
About Monkeypox:
|
Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar |
G Padmanabhan, the Chandrayaan-3 team, Annapurni Subramaniam, and 30 others have been chosen for the inaugural Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP)
About Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP):
Notable Awardees:
|
Chhattisgarh cleared a proposal to establish a new tiger reserve, the third largest in the country, due to the recent plunge in its tiger population.
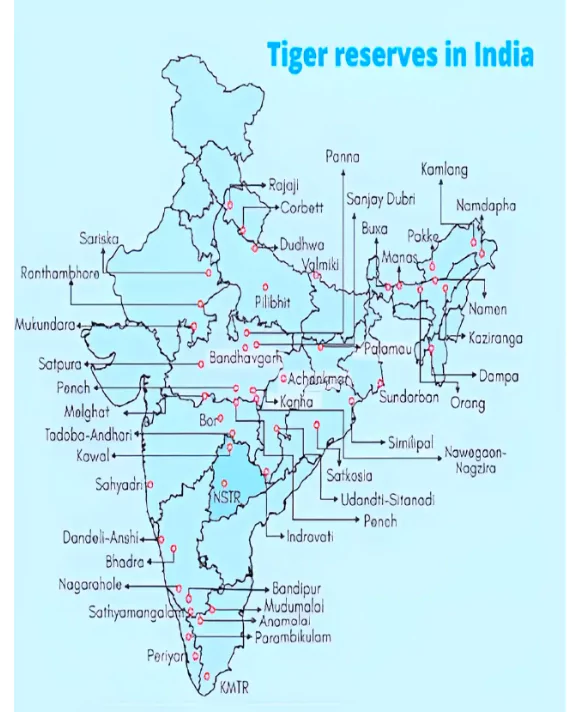
Tiger Reserves in India and National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)Tiger Reserves in India:
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA):
|
|---|
A new study by Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) has revealed that Ground-level ozone pollution is on the rise across India’s major cities.
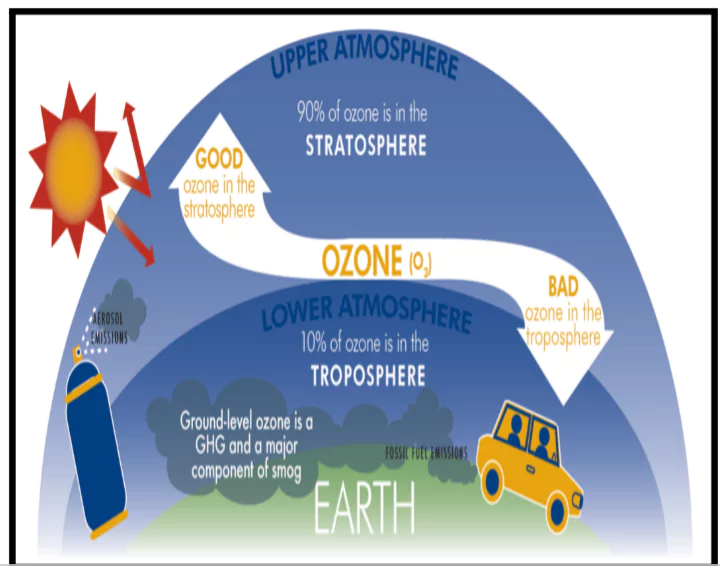
| Centre for Science and Environment (CSE):
About: The Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) is a not-for-profit public interest research and advocacy think tank based in New Delhi, India.
|
|---|
India’s first cultures of indigenous methanotrophs ‘Methylocucumis oryzae’ from rice fields and wetlands have been isolated and described by the scientists from The MACS Agharkar Research Institute (an autonomous institute of Department Science and Technology)
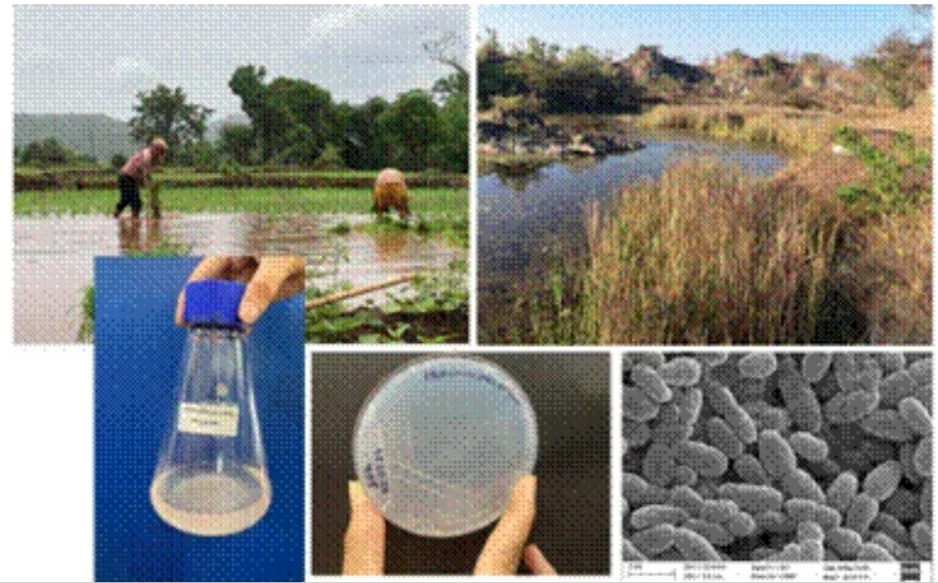

Methanotrophs
|
|---|
The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting has proposed the Broadcasting Services (Regulation) Bill, 2024, which introduces onerous regulations on independent creators of news events on platforms like YouTube, Instagram and X.
Over-The-Top (OTT):
|
|---|
A recent study reported uncovering a novel brain-derived hormone called CCN3 which is responsible for increased bone mass in postpartum lactating mothers.
CCN3 (Cellular Communication Network factor 3) Hormone:
|
|---|
Oestrogen
|
|---|
NARCL aims to take over ₹2 trillion worth of banks’ stressed or non-performing assets (NPAs) by FY26.
By FY24, NARCL had already achieved the ₹1-trillion mark in NPAs acquisition.
Stressed Assets
About NPA
|
|---|
| Pros | Description |
| Consolidation | Aggregates all NPAs under one entity, improving efficiency in asset reconstruction. |
| Freeing up capital | Allows originating banks to use provisions for lending to creditworthy customers. |
| Improved capital buffers | Government backing enhances confidence in lending for originating banks. |
| Cons | Description |
| Inter-government transfer | Shifts the onus of NPAs from one government entity to another without addressing the root problem. |
| Lack of incentives | PSU employees might lack the motivation due to low profit-generation to effectively resolve bad debt issues. |
| Moral hazard | Government bailouts can disincentivize banks from cautious lending practices. |
Swiss Challenge Method
|
|---|
The wildfires currently raging in the United States and Canada are so intense that they have created pyrocumulonimbus clouds.
Pyrocumulonimbus clouds are thunder clouds created by intense heat from the Earth’s surface.
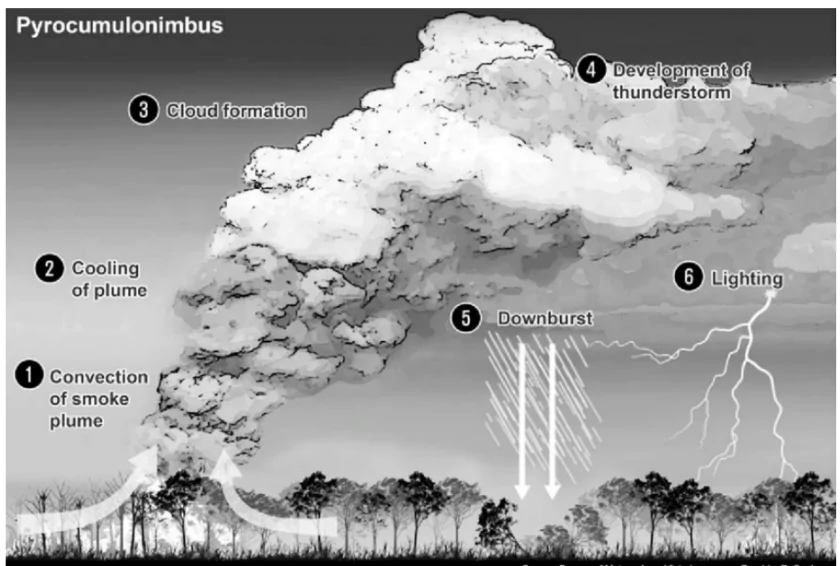 Pyrocumulus cloud: Once the hot air carrying water vapour, smoke, and ash is cool enough, water vapour condenses on ash, forming a grey or brown cloud. At this stage, the cloud is known as a pyrocumulus cloud, also known as ‘fire cloud’.
Pyrocumulus cloud: Once the hot air carrying water vapour, smoke, and ash is cool enough, water vapour condenses on ash, forming a grey or brown cloud. At this stage, the cloud is known as a pyrocumulus cloud, also known as ‘fire cloud’. The development of Pyrocumulonimbus Clouds has become more frequent in recent years.
Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) six-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has kept the repo rate unchanged at 6.5 percent for the ninth time

Repo Rate Trend
|
|---|
The RBI’s intention in keeping rates unchanged is to ensure a stable interest rate environment and price stability in order to achieve sustained growth. While central banks in countries like Canada, Europe, and England have opted for rate cuts, the US Federal Reserve has chosen to keep its policy rate unchanged in its latest meeting.
This year’s budget gave pride of place to the long-term goal of Viksit Bharat 2047 and mentioned that reforms in many areas would be needed to achieve it, particularly in trade policy.
The term ‘Viksit Bharat’ means ‘Developed India’. Viksit Bharat 2047 is the vision to transform India into a developed nation by 2047.
Trade policy refers to a nation’s formal set of practices, laws, regulations, and agreements that govern international trade practices, or imports and exports to foreign countries.
Trade policy is only one of the factors that can deliver strong export performance. Other initiatives, such as developing good infrastructure, reducing logistical costs, development of human skills and improving the ease of doing business, are also important. These factors are relevant not just for exports, but for the economy as a whole.
India won its political freedom in 1947 as a first step in its journey of decolonisation onto poorna swaraj. Now, it must seize its intellectual freedom. Following are the various challenges that India needs to be tackled to achieve the target and dream of Viksit Bharat 2047:
| The CBAM is a carbon tariff on carbon intensive products, such as steel, cement and some electricity, imported to the European Union. Legislated as part of the European Green Deal, it takes effect in 2026. |
|---|
In the last decade, India has witnessed a paradigm shift in its approach towards trade policies, driven by a combination of regulatory reforms, technological advancements, and increased emphasis on quality and safety standards.
Resolution of Internal Differences
Comprehensive Internal Review: The finance minister has recently announced a comprehensive internal review over the next six months of India’s tariff structure.
|
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>