Delimitation Commission:
|
Data Insights: Considering the Census data for 2011
|

Kota had already developed a reputation for student suicides in the last decade or more, having lost more than 100 young people in the last 10 years.

The Rajasthan government held a meeting on the issue with the representatives of coaching institutions and hotel association and decided to introduce measures such as:
Reasons for Student Suicides in UPSC:
|
| Values Needed to Excel in Kota | Values Needed to Live a Happy Life |
|
|
By addressing students’ related issues by holistic approach , it is possible to create a more supportive and nurturing environment for students. However, in the long term, we need to address challenges in the crippling higher education system in india.
Source: Indian Express

Advaita Vedanta ( non-dualism):
Advaita is a subschool of Vedānta, the latter being one of the six classical Hindu Philosophy. (Others are Samkhya, Yoga, Nyaya, Vaisheshika, Mimamsa and Vedanta). |
Source: Deccan Herald
| Bard Extensions | Google announced that it is upgrading its AI-powered chatbot Bard
|
| Primary Reference Time Clock (PRTC) | Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) and CSIR-National Physical laboratory (NPL) signed an agreement for ‘Development of NavIC based IST traceable Primary Reference Time Clock (PRTC) for Telecom Sector’.
|
| Abraham Accords |
|
| Food Animal Tag for Mithun
|
|
| RNA Recovered for the First Time | Scientists recover RNA molecules from a Tasmanian tiger specimen kept at room temperature in a museum collection over a century ago.
|
| Nuakhai | President Droupadi Murmu greeted citizens at the festival of Nuakhai.
|
Subject: GS2: Polity and Governance
Secular state: The Constitution of India stands for a Secular State. Hence, it does not uphold any particular religion as the official religion of the Indian State.
| Indian model of Secularism | Western Model of Secularism |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
News Source: Business Standard
Subject: GS3: Environment
News Source: The Hindu
Subject: GS2: Social Justice
What is Universal health coverage (UHC) ?
|
Out-of- Pocket(OOP) health expenditure Spending:
|
News Source: DTE
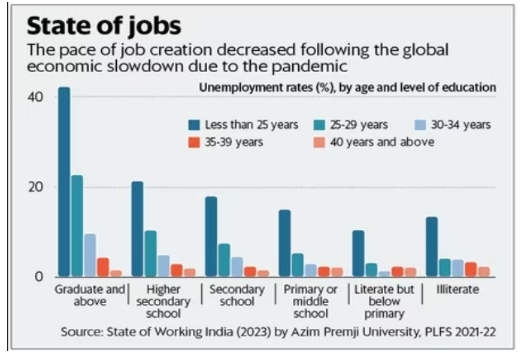
Source: Live Mint
Maharashtra Withdraws GRs on Hindi as Third Langua...
Statistical Report on Value of Output from Agricul...
Skills for the Future: Transforming India’s Work...
National Turmeric Board HQ Inaugurated in Nizamaba...
ECI Moves to De-List 345 Inactive Registered Unrec...
MNRE Issues Revised Biomass Guidelines Under Natio...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>