SASTRA-RAMANUJAN AWARD
|
Context: The 2024 SASTRA Ramanujan Prize will be awarded to Alexander Dunn of the Georgia Institute of Technology, U.S.
About SASTRA Ramanujan Prize:
Contributions Srinivasa Ramanujan:
|
Keffiyeh
|
Context: Renowned Indian-American author Jhumpa Lahiri declined an award from New York City’s Noguchi Museum after it fired three employees for wearing keffiyeh scarves.
About Keffiyeh:
Banning of Keffiyeh:
About Jhumpa Lahiri,
|
India becomes 3rd Most Powerful Nation in Asia
|
Context: In a major shift, India surpassed Japan to become the third-largest power in the Asia Power Index, reflecting its increasing geopolitical stature.
Key Factors Behind India’s Rise:
About Asia Power Index:
Criteria and Parameters of Power Measurement:
|
Vembanad Lake
|
Context: The 70th edition of the Nehru Trophy Boat Race (NTBR) will be held in Punnamada Lake in Alappuzha district of Kerala.
About Vembanad Lake
|
ABHED LightWeight Bullet Proof Jackets
|
Context: Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO), along with researchers of Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi has developed Light Weight Bullet Proof Jackets named ABHED (Advanced Ballistics for High Energy Defeat).
About ABHED LightWeight Bullet Proof Jackets:
About DRDO Industry Academia Centres of Excellence (DIA-CoEs):
|
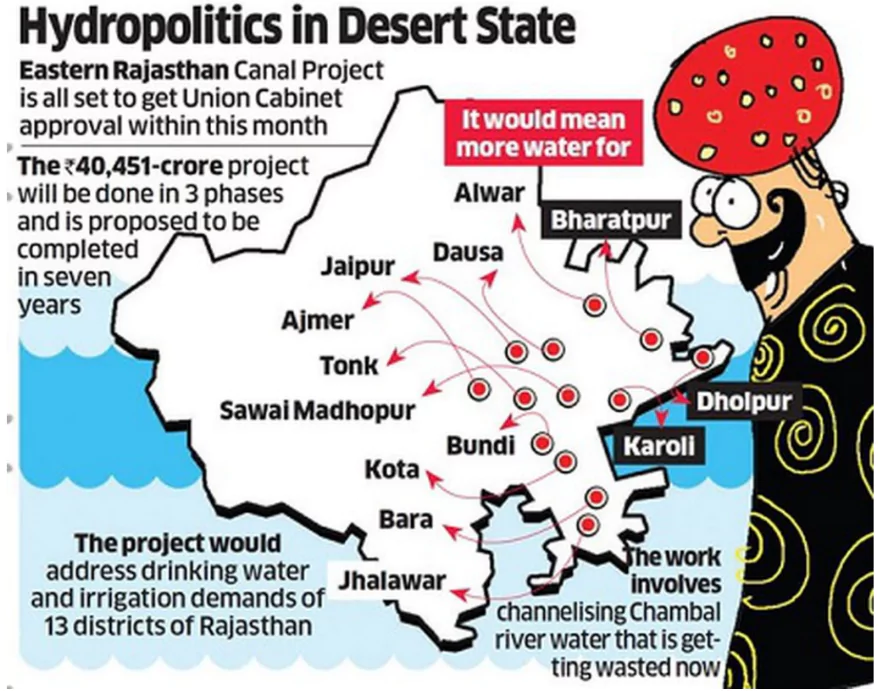
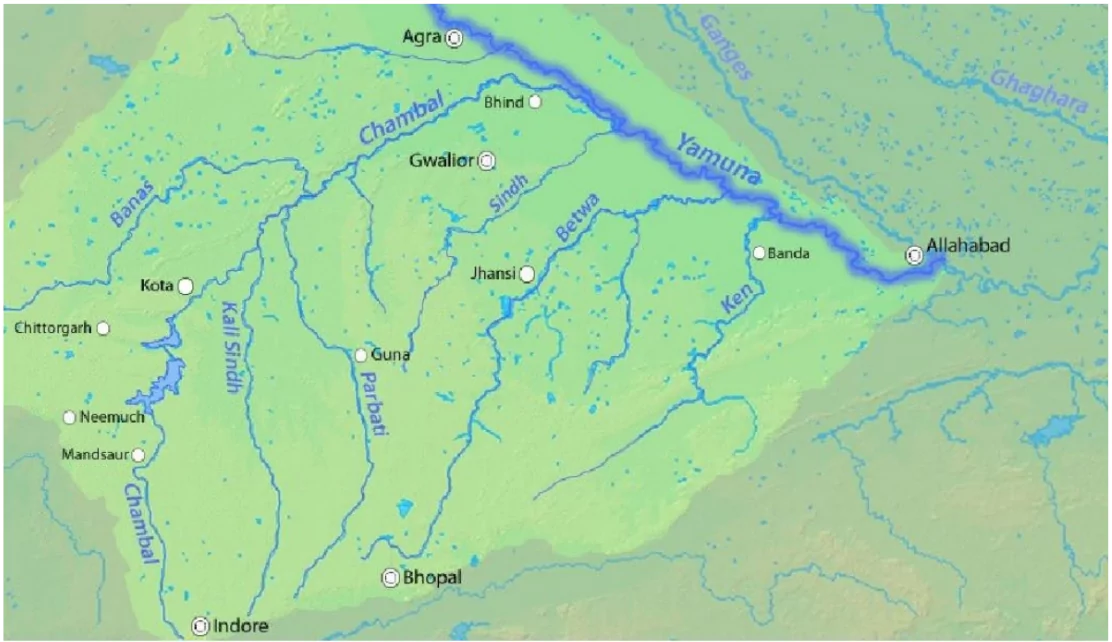
Rajasthan Chief Minister Bhajan Lal Sharma recently said that the Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP) is very big and both Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh are working together to complete it.
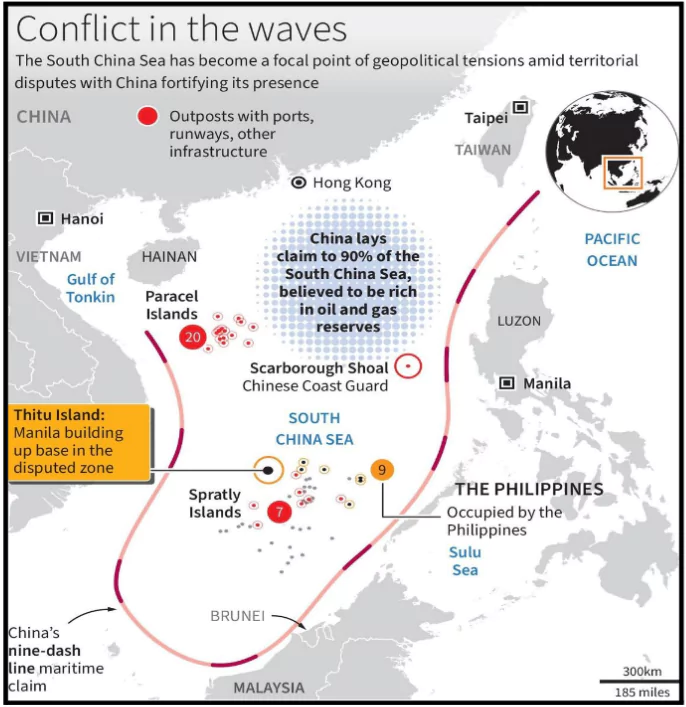
Maritime East Asia has become a hotspot, with China pushing its claims over the Senkaku/Diaoyu islands and the South China Sea, raising tensions and reshaping the region’s power dynamics.
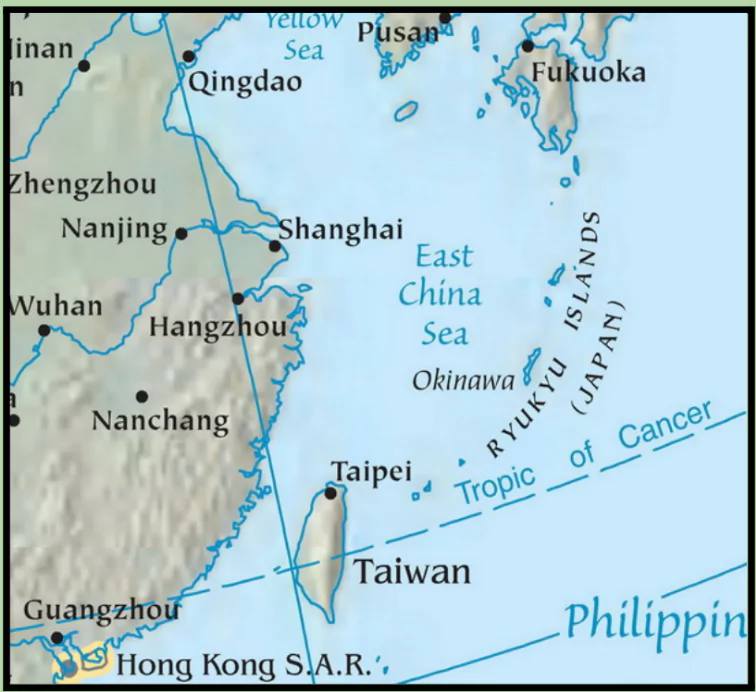
The East China Sea
The South China Sea
Significance of the East and South China Seas
|
India and the US have signed an agreement to establish a semiconductor fabrication plant.
India was elected to the 15-member GlobE Steering Committee during a plenary session in Beijing after multistage voting.
Significance: The GlobE Network strengthens global cooperation in anti-corruption efforts, enabling law enforcement agencies to collaborate effectively against transnational financial crime.
The Group of Four (G4) countries — India, Brazil, Germany and Japan called for the reform of the UN Security Council (UNSC).
India’s pursuit of a permanent seat is supported by many factors, but it faces significant geopolitical and procedural challenges, particularly from China and concerns around veto power.
Karnataka joins many non-BJP ruled States in withdrawing general consent for the CBI in recent years.
Prime Minister virtually launched three Param Rudra Supercomputing Systems under the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM).
National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
|
|---|
About Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs)
|
|---|
High Performance Computing
|
|---|
A recent case of a tragic death of Anna Sebastian Perayil, the 26-year old chartered accountant, working for Ernst and Young Pune due to excessive work pressure highlights the prevailing toxic work culture of the techno-corporate world.
Work Culture
|
|---|
Examples of positive work culture
|
|---|
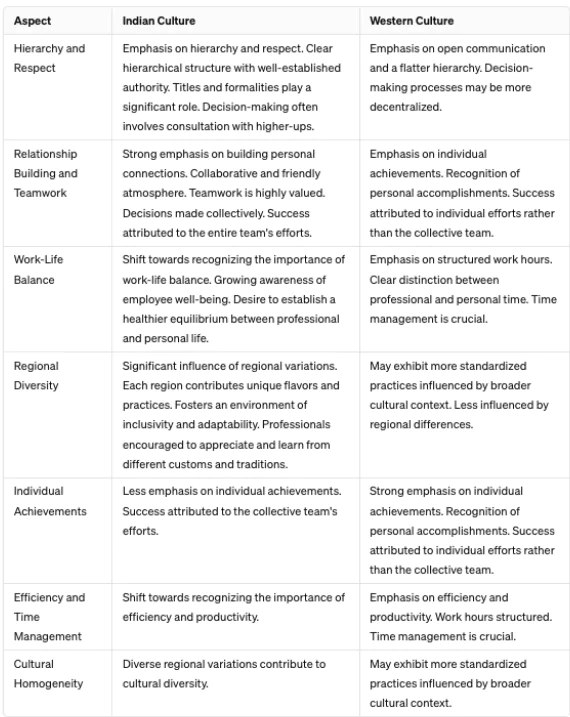 Work-life Balance: A healthy work-life balance can be ensured by offering flexible work hours, remote work options, paid time off and overtime, 5 day work week, mandatory ‘no meeting’ days etc. should be introduced.
Work-life Balance: A healthy work-life balance can be ensured by offering flexible work hours, remote work options, paid time off and overtime, 5 day work week, mandatory ‘no meeting’ days etc. should be introduced.
Constitution on Healthy Work Environment
|
|---|
Maharashtra Withdraws GRs on Hindi as Third Langua...
Statistical Report on Value of Output from Agricul...
Skills for the Future: Transforming India’s Work...
National Turmeric Board HQ Inaugurated in Nizamaba...
ECI Moves to De-List 345 Inactive Registered Unrec...
MNRE Issues Revised Biomass Guidelines Under Natio...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>