| Fifth positive indigenisation list |
What is a positive indigenisation list?
About NIIO:
|
| Dynamic injunction |
About Injunction:
About Dynamic injunction:
|
| Shyamji Krishna Varma
|
About Shyamji Krishna Varma:
|
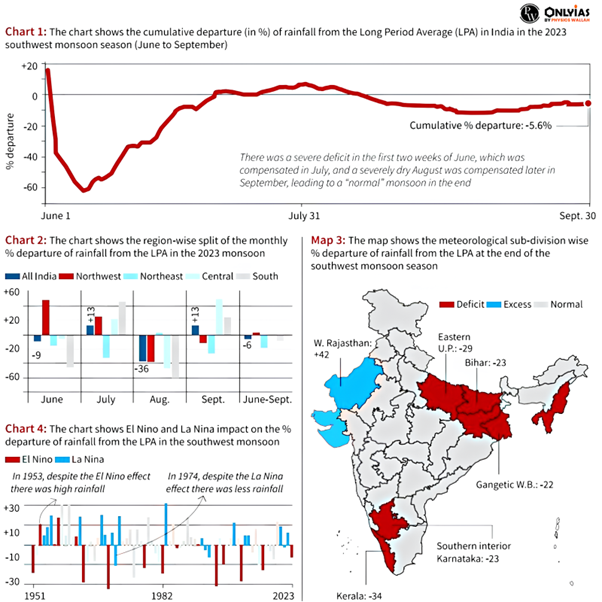
Chart 1: It shows the cumulative departure (in %) of rainfall from the Long Period Average (LPA) in India this monsoon season.
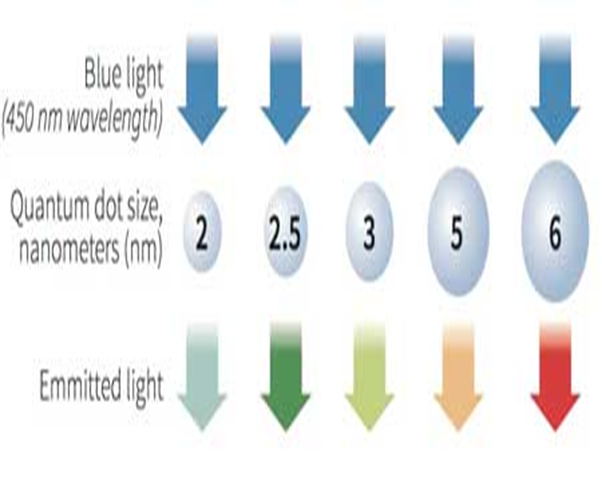
What are quantum dots?
News Source: The Hindu
About Uterus Transplant
News Source: The Hindu
About New GI Tag Products:
|
|---|
News Source: The Print
News Source: Economic times

News Source: The Economic Times
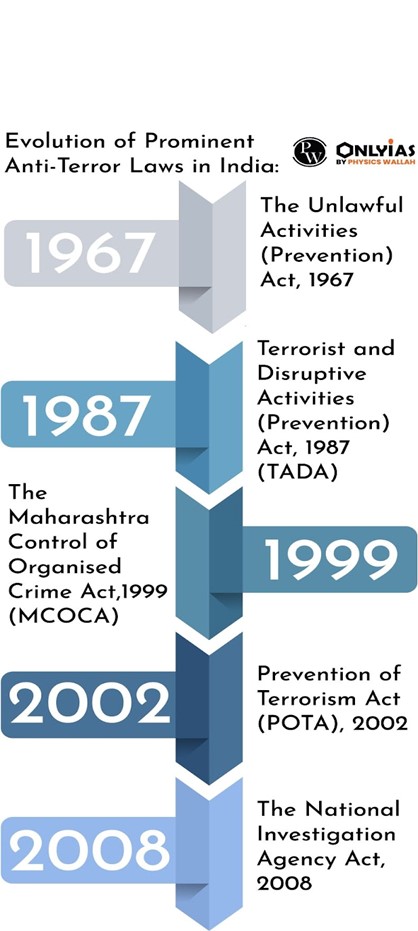
| Relevancy for Prelims: Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act or UAPA, National Investigation Agency (NIA), Fundamental Rights, National Security, and United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
Relevancy for Mains: Illegal funding from China, money laundering, sovereignty and integrity of India, Unlawful Activities, and Counterterrorism Legislation- UAPA. |
|---|
Supreme Court’s (SC) Stand on UAPA:
|
|---|
Also read: FICCI’s Insights On Illicit Trade In India
The Constitution of India guarantees the following Fundamental Rights available to individuals upon being arrested:
|
|---|
Also read: India And UNSC Reform
The concern for the security of the nation is common for all nations. The principle of liberty exists because of the rule of law. It exists and may cease whenever the state deems it necessary only if the state’s survival is in danger and should not be used in common parlance. It is vital to strike a balance between national security imperatives and the protection of individual rights, fostering a legal framework that is effective, transparent, and accountable.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
A legislation which confers on the executive or administrative authority an unguided and uncontrolled discretionary power in the matter of the application of law violates which one of the following Articles of the Constitution of India? (2021)
Ans: A |
|---|
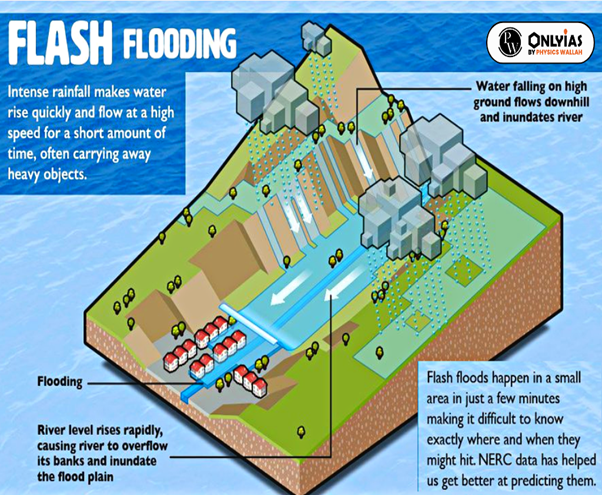
| Relevancy for Prelims: Flash floods, National Disaster Management Authority, India Meteorological Department (IMD) , Cloud Burst, Lhonak Lake, and Teesta River.
Relevancy for Mains: Glacial Lake Outburst Flood, Causes of flash floods, Climate Change, Disaster Management And Technology, etc. |
|---|

ALSO READ: DISASTER MANAGEMENT IN INDIA
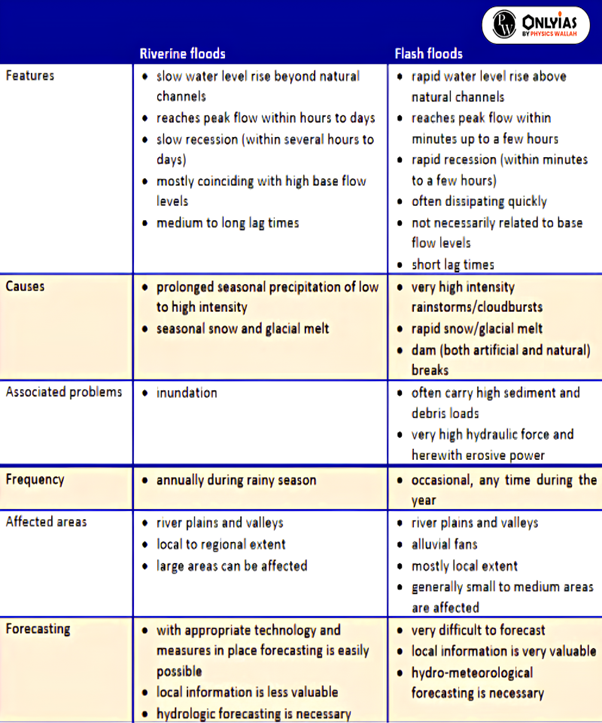
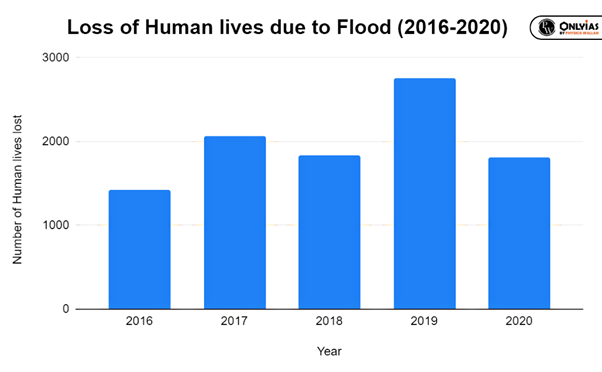
Initiatives taken in this direction
|
|---|
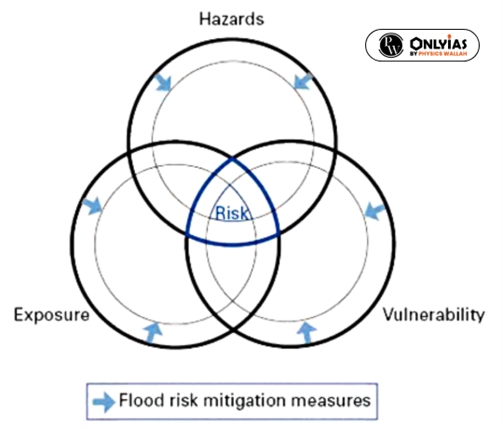
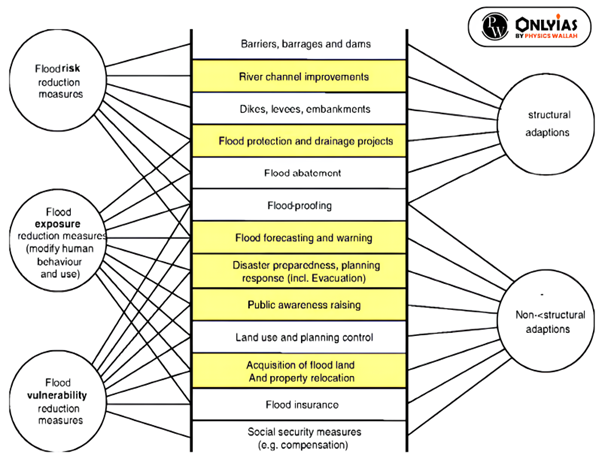
Flash floods are, by their characteristics, difficult to manage by traditional flood management approaches. Reducing the hazard requires the best mix of structural measures and non-structural measures to reduce impacts due to flash floods.
The tragic cloud burst over Lhonak Lake in Sikkim, leading to devastating flash floods, underscores the urgent need for comprehensive disaster management strategies.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
Why are dewdrops not formed on a cloudy night? (2020)
Ans: B |
|---|
Maharashtra Withdraws GRs on Hindi as Third Langua...
Statistical Report on Value of Output from Agricul...
Skills for the Future: Transforming India’s Work...
National Turmeric Board HQ Inaugurated in Nizamaba...
ECI Moves to De-List 345 Inactive Registered Unrec...
MNRE Issues Revised Biomass Guidelines Under Natio...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>