Context: The Indian Navy will deploy its aircraft carriers INS Vikramaditya and INS Vikrant for Exercise Milan-2024 to be held in February.
Also Read: Three Anti submarine Warfare Ships for Indian Navy Launched
News Source: Business Standard
Context: According to a report by Crisil Ratings, Corporate bond market in India is expected to more than double from Rs 43 trillion in the Financial Year 2022-23 (FY23) to Rs 100-120 trillion by FY 2030.
Key Findings of Report: The Corporate bond market in India is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9 percent over the years.
About Crisil: It is an acronym for Credit Rating Information Services of India Limited, is the first Credit Rating Agency established in India.
|
|---|
Corporate Bond:
Corporate Bond Market:
|
|---|
Also Read: US Bond Yields Rise to 16-Year High Above 5%
Source: Live Mint
Context: On December 3, Venezuela held a nonbinding referendum to strengthen the nation’s century-old claim to the oil-rich Essequibo territory governed by Guyana.
Guiana Shield:
|
|---|
Also Read: International Court Of Justice
Source: The Hindu
Context: Recently, the Secretary-General of the Climate Vulnerable Forum (CVF) called for Indian companies to invest in ‘climate-vulnerable’ countries.
Also Read: Loss And Damage Fund Approved At COP28 Summit
Source: The Hindu
Context: The Chairman of Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC) released ‘Smuggling in India Report 2022-23‘.
The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI):
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
Context: The UNEP report “An Eye on Methane: The Road to Radical Transparency” released at COP28 stated that Methane Alert and Response System (MARS) in its pilot stage identified 1,500 plumes and notified governments of 127 plumes on four continents.
What is flare efficiency?
|
|---|
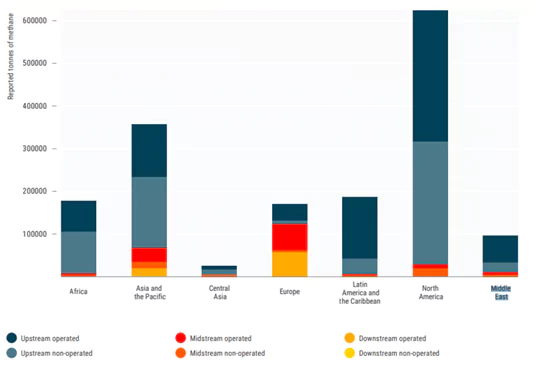
Also Read: Cop28 Turns Attention To Potent Methane Emissions
Source: DTE
Context: Recently, the Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) of Science & Technology inaugurated the 3rd Global Bio-India Summit, a mega international convention on biotechnology from 4th to 6th December in New Delhi.
Source: PIB
Context: Eleven climbers died in Indonesia after the Merapi volcano erupted in West Sumatra, Indonesia.
Stratovolcano:
The Ring of Fire:
Subduction Zone:
|
Also Read: Distribution Of Volcanoes
News Source: Times of India
Context: India has joined the Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) Consortium, at the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP28).
Global Leadership Council:
Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP)
|
|---|
For more information: BSES
Context: Indian Navy Day is celebrated on December 4 each year, to recognize the role and achievements of the Indian Navy.
Operation Trident and its significance:
|
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
Context: Six exoplanets orbiting around a nearby bright star (HD 110067) in the Coma Berenices constellation have been discovered.
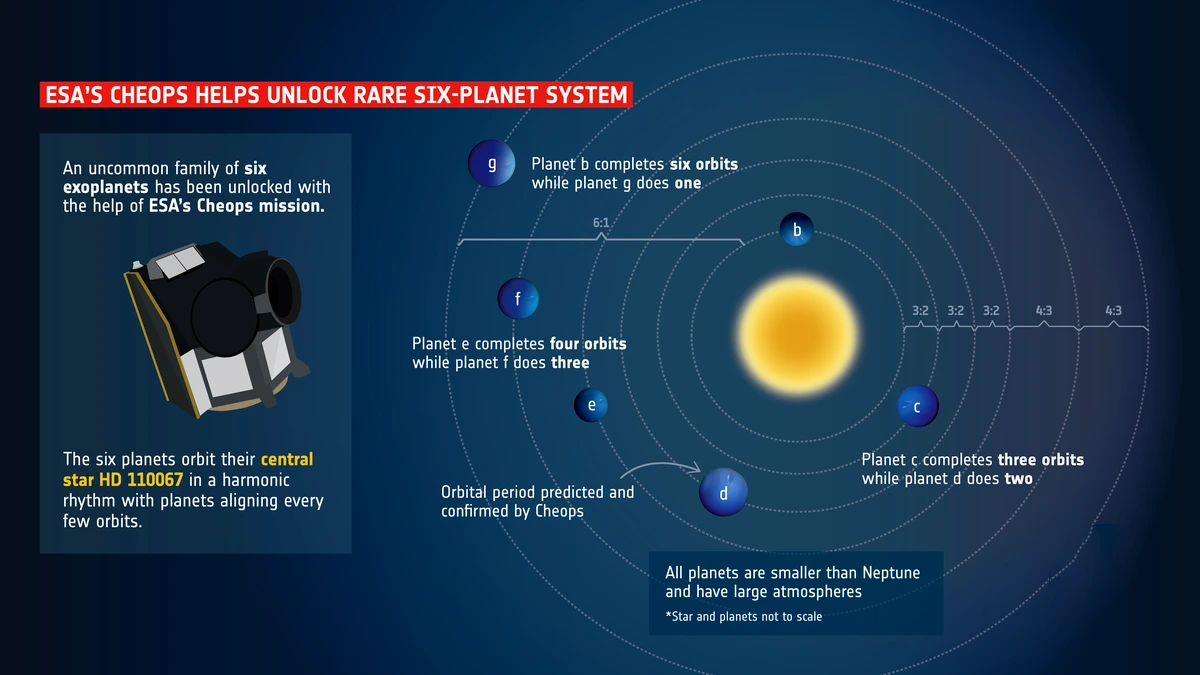
Coma Berenices constellation
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
Context: This article is based on the news “How to read the NCRB 2022 report on crime in India” which was published in the Indian Express. The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) released its annual report on crime in India for the year 2022.
| Relevancy for Prelims: NCRB Report 2022 On Crime in India, National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), National Database of Sexual Offenders (NDSO), Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and System (CCTNS), Indian Penal Code (IPC), Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), and the Indian Evidence Act (IEA).
Relevancy for Mains: What steps can India take to improve its justice system? Is it important to upgrade the police, reform the judiciary, and ensure accurate crime data through NCRB for effective policymaking? |
|---|
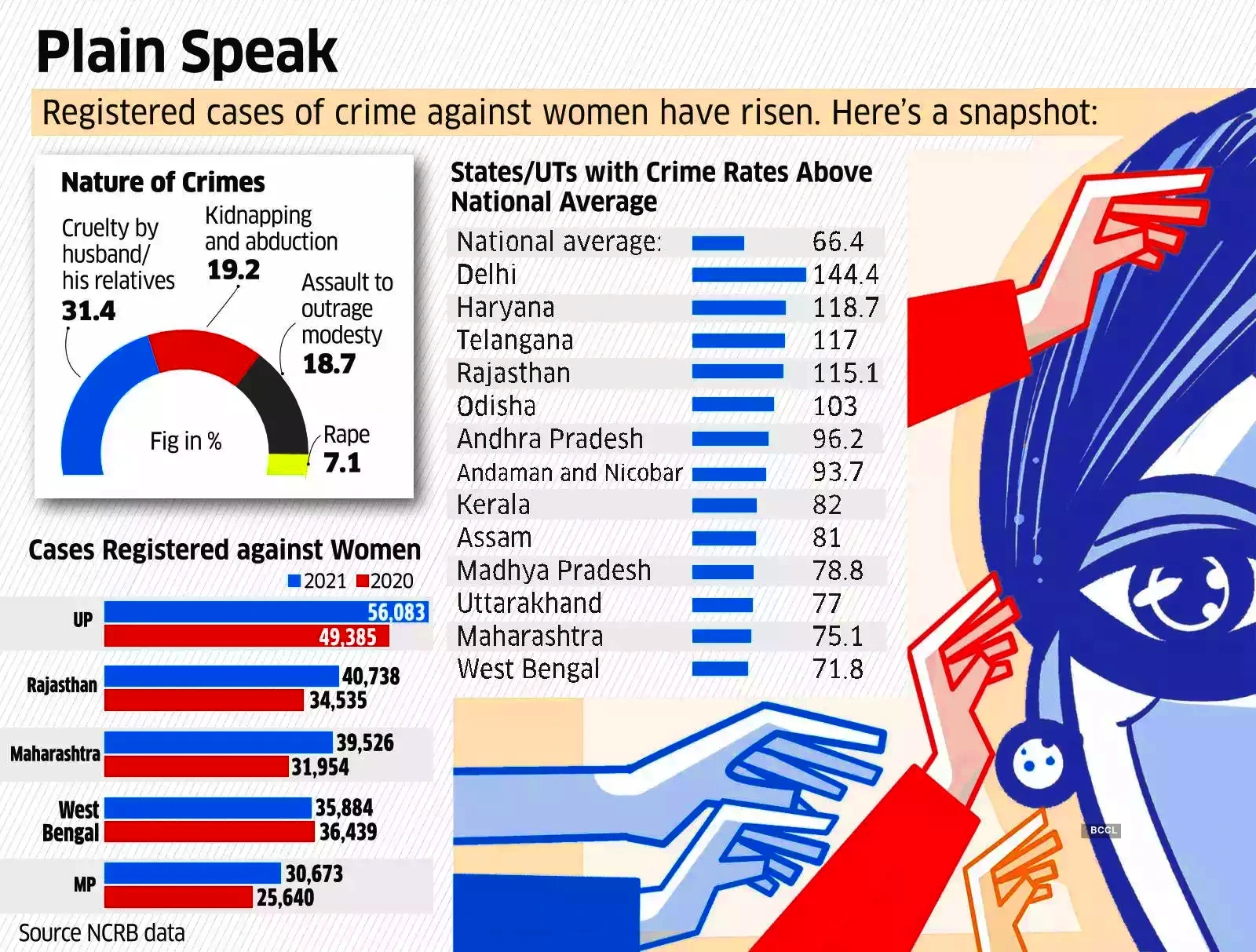
Also Read: Women Safety in India
Also Read: Cyber Security and Rising Incidence of Cyber Crime
Also Read: Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023
The 2022 NCRB report highlights India’s crime situation, indicating a decline in overall cases but an increase in certain areas. To improve the justice system, reforms such as modernizing police, judicial changes, prison reforms, and addressing socio-economic issues are essential.
Context: This article is based on the news “Ministry of Jal Shakti releases Dynamic Ground Water Resource Assessment Report 2023” which was published in the ANI. The Ministry of Jal Shakti has recently released the Dynamic Ground Water Resource Assessment Report 2023.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Dynamic Groundwater Resource Assessment Report 2023, State Groundwater Departments (SGWD) and Central Groundwater Board (CGWB), Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY), Jal Shakti Abhiyan, New National Water Commission (NWC), and Mihir Shah Committee.
Relevancy for Mains: Groundwater Management in India: What challenges are associated with it, Steps has the Indian government taken to improve groundwater management and solutions? |
|---|

Also Read: 8th India Water Impact Summit (IWIS)
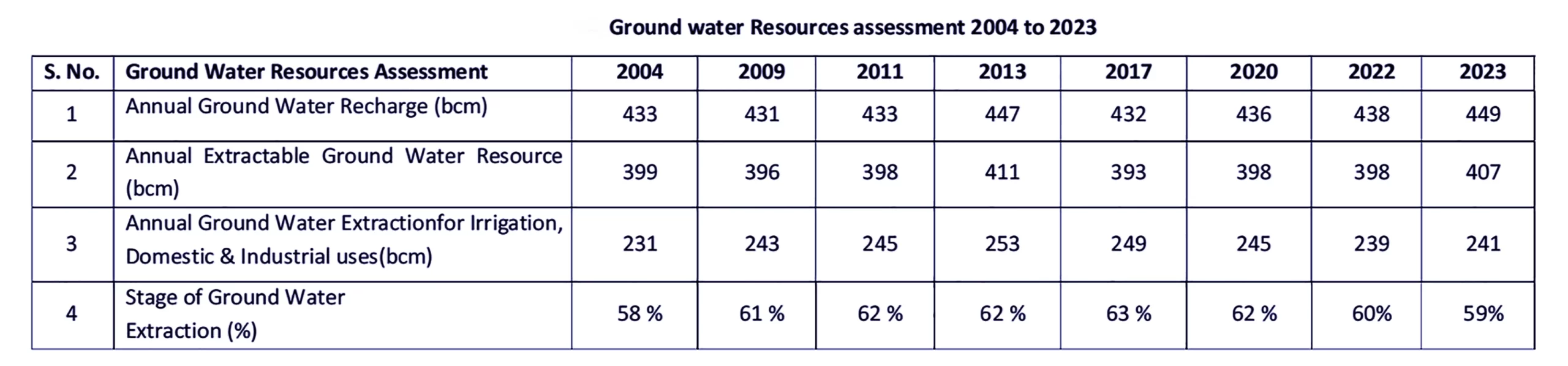
Rainfall and Replenishment of Groundwater:
|
|---|
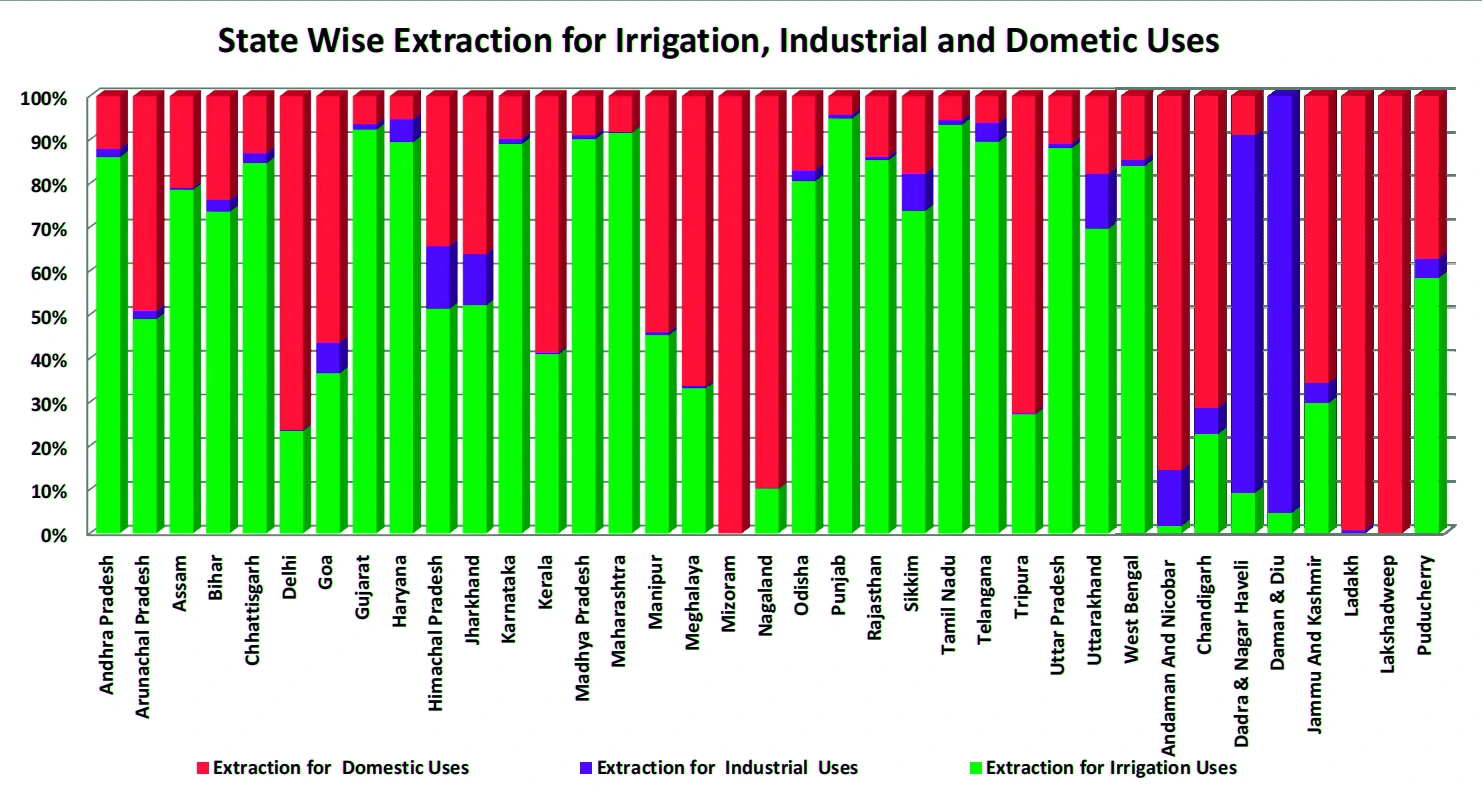
Also Read: India’s excess sugar production is guzzling groundwater
The Dynamic Groundwater Resource Assessment Report 2023 highlights both positive trends and challenges, underscoring the need for a comprehensive and sustainable approach to groundwater management in India, incorporating technological innovation, policy restructuring, and community participation to ensure long-term water security.
| Prelims Question (2020)
Consider the following statements: 1. 36% of India’s districts are classified as “overexploited” or “critical” by the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA). 2. CGWA was formed under the Environment (Protection) Act. 3. India has the largest area under groundwater irrigation in the world. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 2 only (d) 1 and 3 only Ans: (b) |
|---|
| Mains Question: The ideal solution of depleting groundwater resources in India is water harvesting system. How can it be made effective in urban areas? (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
Maharashtra Withdraws GRs on Hindi as Third Langua...
Statistical Report on Value of Output from Agricul...
Skills for the Future: Transforming India’s Work...
National Turmeric Board HQ Inaugurated in Nizamaba...
ECI Moves to De-List 345 Inactive Registered Unrec...
MNRE Issues Revised Biomass Guidelines Under Natio...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>