The 19th G20 summit recently concluded in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Deccan High-Level Principles
|
|---|
GlobE Network
|
|---|
India’s Achievements Highlighted in the Rio G20 Summit
|
|---|
By 2026, with all G20 countries having held the presidency at least once, this milestone marks an opportunity to reinforce the group’s collective commitment to driving global progress and fostering inclusive development.
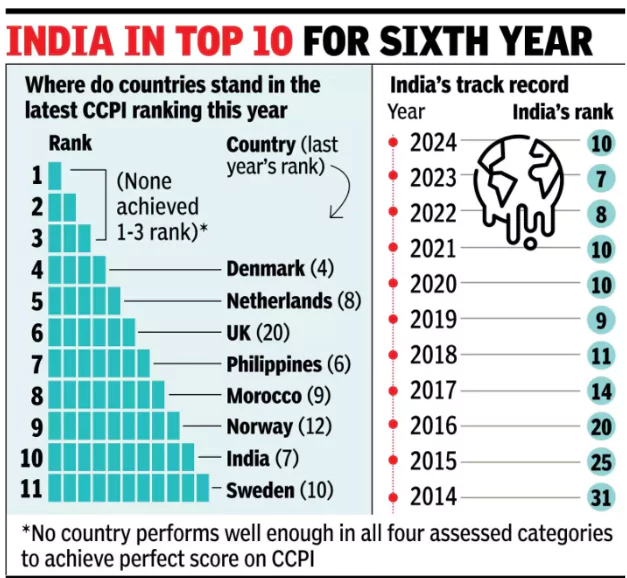
India has been ranked 10th in the Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI 2025) report.
The Ministry of Culture is celebrating the 125th birth anniversary of Dr. Harekrushna Mahtab.
Recently, the Union Minister of Science & Technology Dr. Jitendra Singh formally launched the first indigenous antibiotic “Nafithromycin” for resistant infections.
About Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
|
|---|
The Karnataka Forest Department has imposed restrictions on the annual jathra of Beladakuppe Sri Mahadeshwaraswamy Temple which is in the core area of Bandipur Tiger Reserve.
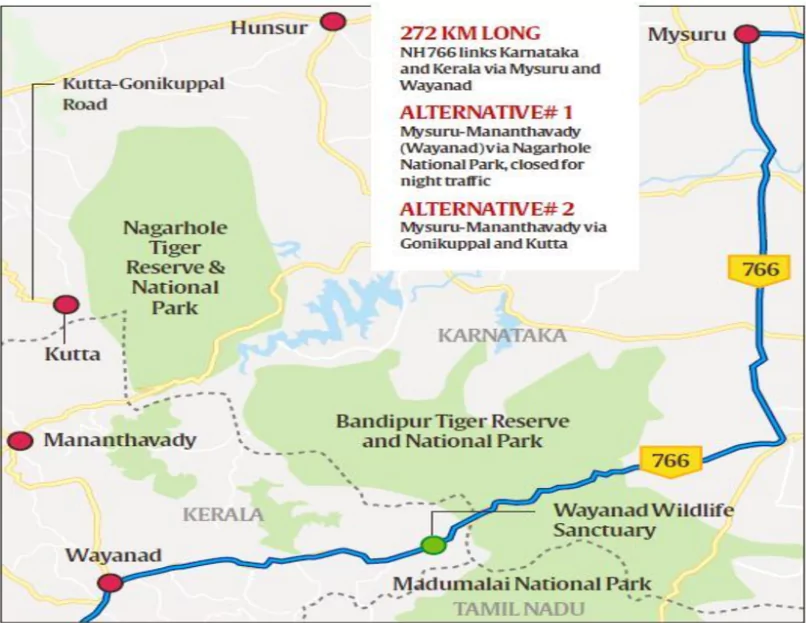
The Union government granted permission for tungsten mining in Arittapatti, Madurai, Tamil Nadu.
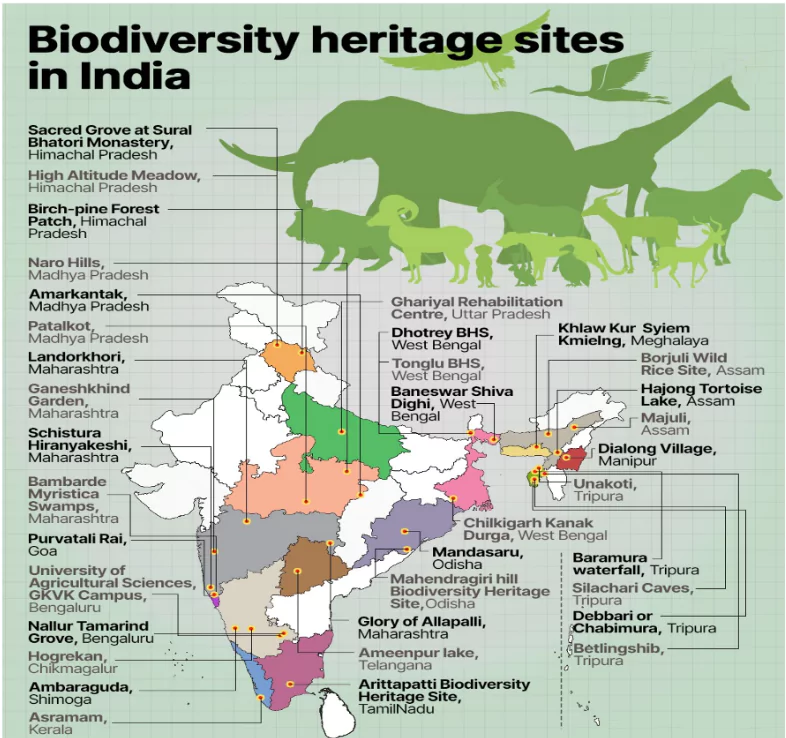
Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) in India
|
|---|
Access to Nutrition Initiative (ATNi) , in its fifth edition of the ‘Global Access to Nutrition Index, highlights disparities in the healthiness of food and beverage (F&B) products sold in different regions.
Health Star Rating System
|
|---|
The Supreme Court has allowed telecom companies to claim Central Value Added Tax (CENVAT) credit for the installation of mobile towers and pre-fabricated buildings (PFBs), which are subject to excise duties.
The Guardian newspaper decided to boycott the social media platform X, for its role in influencing the USA Presidential Elections favouring a certain candidate and the role of its owner, Elon Musk to use its influence to shape political discourse.
Democracy in its essence implies a form of a political system which enables people’s participation and Media being the 4th Pillar of Democracy, facilitates this participation.
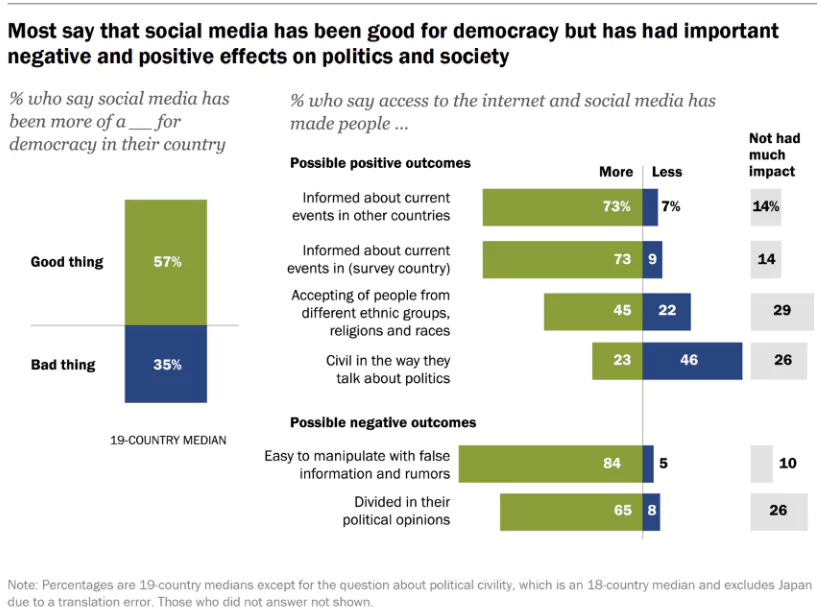 Cyber Governance: The Government functionaries and authorities nowadays maintain a formidable social media presence which has resulted in their greater accessibility to people who now raises their concern directly enabling faster governance.
Cyber Governance: The Government functionaries and authorities nowadays maintain a formidable social media presence which has resulted in their greater accessibility to people who now raises their concern directly enabling faster governance.
Regulating the Political Influence of Social Media
|
|---|
Human-driven warming of ocean temperatures increased the maximum wind speeds of every Atlantic hurricane in 2024, according to a new analysis released recently.
Context: The Ministry of Science and Technology launched India’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) data bank at the 7th Edition of the ASSOCHAM AI Leadership Meet 2024.
The Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India (ASSOCHAM) is a non-governmental trade association and advocacy group that represents businesses, chambers, and associations in India.
Context: India’s public broadcaster, Prasar Bharati, has introduced a new OTT platform called ‘Waves’.
Context: The Ministry of Jal Shakti launched the “Bhu-Neer” portal during the concluding ceremony of India Water Week 2024.
Context: Union Minister inaugurated the “Viksit Bharat Initiative for Student Innovation and Outreach Network” (VISION), portal.
On the Suggestion for an All-India Judicial Servic...
India needs an Environmental Health Regulatory Age...
Is Social Media Doing More Harm than Good to Democ...
Overturning of Sri Lanka’s Old Political Order
Should packaged food content be labelled?
In What Ways Rural-Urban Migration Contribute to U...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
